|
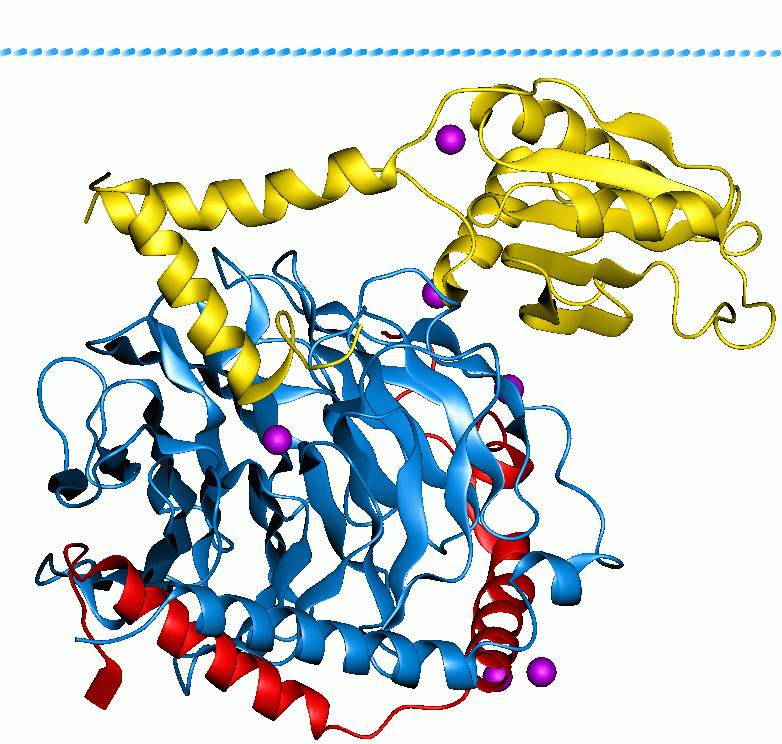
T1R3
Taste receptor type 1 member 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TAS1R3'' gene. The ''TAS1R3'' gene encodes the human homolog of mouse Sac taste receptor, a major determinant of differences between sweet-sensitive and -insensitive mouse strains in their responsiveness to sucrose, saccharin, and other sweeteners. Structure The protein encoded by the ''TAS1R3'' gene is a G protein-coupled receptor with seven trans-membrane domains and is a component of the heterodimeric amino acid taste receptor TAS1R1+3 and sweet taste receptor TAS1R2+3. This receptor is formed as a protein dimer with either TAS1R1 or TAS1R2. Experiments have also shown that a homo-dimer of TAS1R3 is also sensitive to natural sugar substances. This has been hypothesized as the mechanism by which sugar substitutes do not have the same taste qualities as natural sugars. APA Ligands The G protein-coupled receptors for sweet and umami taste are formed by dimers of the TAS1R proteins. The TAS1R1+3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TAS1R2
T1R2 - Taste receptor type 1 member 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TAS1R2'' gene. The sweet taste receptor is predominantly formed as a dimer of T1R2 and T1R3 by which different organisms sense this taste. In songbirds, however, the T1R2 monomer does not exist, and they sense the sweet taste through the umami taste receptor (T1R1 and T1R3) as a result of an evolutionary change that it has undergone. Structure and molecular function Both T1R2 and T1R3 receptors belongs to the class C G protein-coupled receptor family that features a common structure comprised a large extracellular domain, called the venus flytrap domain (VFD), which is connected to a 7-helix TMD by a cysteine-rich domain (CRD). The canonical activation mechanism of class C GPCRs follows a multiple-step process that requires communication between the VFDs (housing the orthosteric-binding site) and the TMDs via the CRDs. Although the main binding site for most sweet compounds was found to resid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taste Receptor
A taste receptor or tastant is a type of cellular receptor that facilitates the sensation of taste. When food or other substances enter the mouth, molecules interact with saliva and are bound to taste receptors in the oral cavity and other locations. Molecules which give a sensation of taste are considered "sapid". Vertebrate taste receptors are divided into two families: * Type 1, sweet, first characterized in 2001: – * Type 2, bitter, first characterized in 2000: In humans there are 25 known different bitter receptors, in cats there are 12, in chickens there are three, and in mice there are 35 known different bitter receptors. Visual, olfactive, "sapictive" (the perception of tastes), trigeminal (hot, cool), mechanical, all contribute to the perception of ''taste''. Of these, transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 1 ( TRPV1) vanilloid receptors are responsible for the perception of heat from some molecules such as capsaicin, and a CMR1 receptor i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sweet
Sweetness is a basic taste most commonly perceived when eating foods rich in sugars. Sweet tastes are generally regarded as pleasurable. In addition to sugars like sucrose, many other chemical compounds are sweet, including aldehydes, ketones, and sugar alcohols. Some are sweet at very low concentrations, allowing their use as non-caloric sugar substitutes. Such non-sugar sweeteners include saccharin, aspartame, sucralose and stevia. Other compounds, such as miraculin, may alter perception of sweetness itself. The perceived intensity of sugars and high-potency sweeteners, such as aspartame and neohesperidin dihydrochalcone, are heritable, with gene effect accounting for approximately 30% of the variation. The chemosensory basis for detecting sweetness, which varies between both individuals and species, has only begun to be understood since the late 20th century. One theoretical model of sweetness is the multipoint attachment theory, which involves multiple binding sites be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNAT3
Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(t) subunit alpha-3, also known as gustducin alpha-3 chain, is a protein subunit that in humans is encoded by the ''GNAT3'' gene. Gustducin alpha-3 chain is a subunit of the heterotrimeric G protein gustducin Gustducin is a G protein associated with taste and the gustatory system, found in some taste receptor cells. Research on the discovery and isolation of gustducin is recent. It is known to play a large role in the transduction of bitter, sweet ... that is responsible for basic taste. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-7-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Knockout
Gene knockouts (also known as gene deletion or gene inactivation) are a widely used genetic engineering technique that involves the gene targeting, targeted removal or inactivation of a specific gene within an organism's genome. This can be done through a variety of methods, including homologous recombination, CRISPR gene editing, CRISPR-Cas9, and transcription activator-like effector nuclease, TALENs. One of the main advantages of gene knockouts is that they allow researchers to study the function of a specific gene in vivo, and to understand the role of the gene in normal development and physiology as well as in the pathology of diseases. By studying the phenotype of the organism with the knocked out gene, researchers can gain insights into the biological processes that the gene is involved in. There are two main types of gene knockouts: complete and conditional. A complete gene knockout permanently inactivates the gene, while a conditional gene knockout allows for the gene to b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dulcin
Dulcin is an artificial sweetener about 250 times sweeter than sugar, discovered in 1883 by the Polish chemist Józef (Joseph) Berlinerblau (27 August 1859 – 1935). It was first mass-produced about seven years later. Although it was discovered only five years after saccharin, it never enjoyed the latter compound's market success. Nevertheless, it was an important sweetener of the early 20th century and had an advantage over saccharin in that it did not possess a bitter aftertaste. Early medical tests marked the substance as safe for human consumption, and it was considered ideal for diabetics. However, an FDA study in 1951 raised many questions about its safety, resulting in its removal from the market in 1954 after animal testing revealed chronic toxicity. The FDA has also said that "the Federal Security Administrator regards these chemicals as poisonous substances which have no place in any food." In Japan, poisoning accidents by dulcin occurred frequently, and use of du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanidinoacetic Acid
Glycocyamine (or guanidinoacetate) is a metabolite of glycine in which the amino group has been converted into a guanidine by guanylation (transfer of a guanidine group from arginine). In vertebrate organism it is then transformed into creatine by methylation. Glycocyamine is used as a supplement and as a feed additive in poultry farming. However, the metabolism of creatine from glycocyamine in the liver causes a depletion of methyl groups. This causes homocysteine levels to rise, which has been shown to produce cardiovascular and skeletal problems. Glycocyamine plays a role in the metabolism of the amino acids serine, threonine, and proline. Production Biochemical synthesis Glycocyamine is formed in the mammalian organism primarily in the kidneys by transferring the guanidine group of L-arginine by the enzyme L-Arg:Gly-amidinotransferase (AGAT) to the amino acid glycine. From L-arginine, ornithine is thus produced, which is metabolized in the urea cycle by carbamoylation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G Protein
G proteins, also known as guanine nucleotide-binding proteins, are a Protein family, family of proteins that act as molecular switches inside cells, and are involved in transmitting signals from a variety of stimuli outside a cell (biology), cell to its interior. Their activity is regulated by factors that control their ability to bind to and hydrolyze guanosine triphosphate (GTP) to guanosine diphosphate (GDP). When they are bound to GTP, they are 'on', and, when they are bound to GDP, they are 'off'. G proteins belong to the larger group of enzymes called GTPases. There are two classes of G proteins. The first function as monomeric small GTPases (small G-proteins), while the second function as heterotrimeric G protein protein complex, complexes. The latter class of complexes is made up of ''G alpha subunit, alpha'' (Gα), ''beta'' (Gβ) and ''gamma'' (Gγ) protein subunit, subunits. In addition, the beta and gamma subunits can form a stable Protein dimer, dimeric complex re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gustducin
Gustducin is a G protein associated with taste and the gustatory system, found in some taste receptor cells. Research on the discovery and isolation of gustducin is recent. It is known to play a large role in the transduction of bitter, sweet and umami stimuli. Its pathways (especially for detecting bitter stimuli) are many and diverse. An intriguing feature of gustducin is its similarity to transducin. These two G proteins have been shown to be structurally and functionally similar, leading researchers to believe that the sense of taste evolved in a similar fashion to the sense of sight. Gustducin is a heterotrimeric protein composed of the products of the GNAT3 (α-subunit), GNB1 (β-subunit) and GNG13 (γ-subunit). Discovery Gustducin was discovered in 1992 when degenerate oligonucleotide primers were synthesized and mixed with a taste tissue cDNA library. The DNA products were amplified by the polymerase chain reaction method, and eight positive clones were shown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenylyl Cyclase
Adenylate cyclase (EC 4.6.1.1, also commonly known as adenyl cyclase and adenylyl cyclase, abbreviated AC) is an enzyme with systematic name ATP diphosphate-lyase (cyclizing; 3′,5′-cyclic-AMP-forming). It catalyzes the following reaction: :ATP = 3′,5′-cyclic AMP + diphosphate It has key regulatory roles in essentially all Cell (biology), cells. It is the most Polyphyly, polyphyletic known enzyme: six distinct classes have been described, all catalysis, catalyzing the same reaction but representing unrelated gene Gene family, families with no known Sequence homology, sequence or structural homology. The best known class of adenylyl cyclases is class III or AC-III (Roman numerals are used for classes). AC-III occurs widely in eukaryotes and has important roles in many human Tissue (biology), tissues. All classes of adenylyl cyclase Catalysis, catalyse the conversion of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to cyclic adenosine monophosphate, 3',5'-cyclic AMP (cAMP) and pyrophosphate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saccharin
Saccharin, also called saccharine, benzosulfimide, or E954, or used in saccharin sodium or saccharin calcium forms, is a non-nutritive artificial sweetener. Saccharin is a sultam that is about 500 times sweeter than sucrose, but has a bitter or metallic aftertaste, especially at high concentrations. It is used to sweeten products, such as drinks, candies, baked goods, tobacco products, excipients, and for masking the bitter taste of some medicines. It appears as white crystals and is odorless. Etymology Saccharin derives its name from the word "saccharine", meaning "sugary". The word saccharine is used figuratively, often in a derogative sense, to describe something "unpleasantly over-polite" or "overly sweet". Both words are derived from the Greek word (''sakkharon'') meaning "gravel". Similarly, saccharose is an obsolete name for sucrose (table sugar). Properties Saccharin is heat-stable. It does not react chemically with other food ingredients; as such, it stores we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |