|
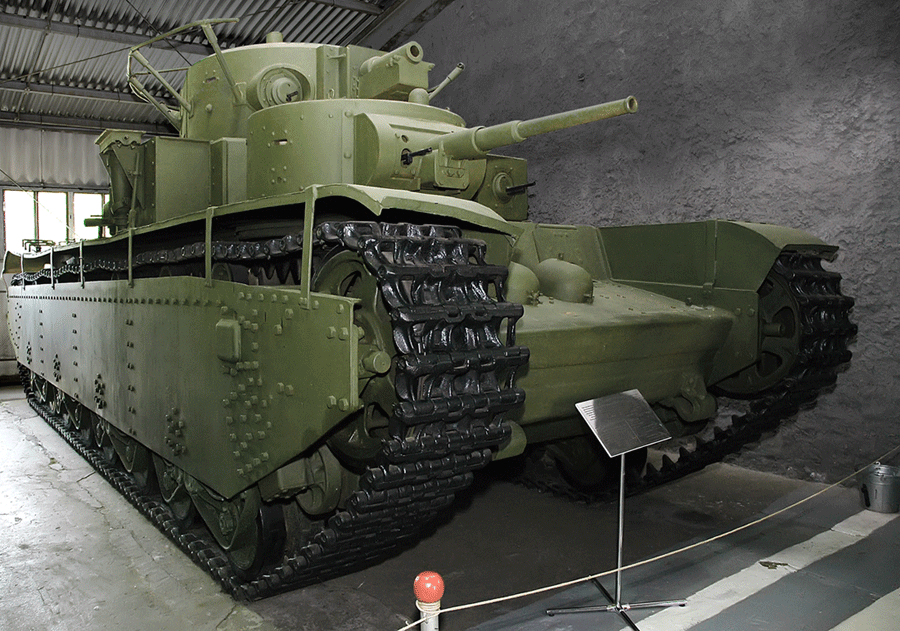
T-35 Pillán
The T-35 was a Soviet multi- turreted heavy tank of the interwar period and early Second World War that saw limited service with the Red Army. Often called a land battleship, it was the only five-turreted heavy tank in the world to reach production, but proved to be slow and mechanically unreliable. Most of the T-35 tanks still operational at the time of Operation Barbarossa were lost due to mechanical failure rather than enemy action. It was designed to complement the contemporary T-28 medium tank; however, very few were built. Outwardly, it was large; but internally, the spaces were cramped with the fighting compartments separated from each other. Some of the turrets obscured the entrance hatches. Production history The T-35 was developed by the OKMO design bureau of the Bolshevik Factory, which began work on a heavy tank in 1930. Two teams developed separate designs. The team headed by German engineer Grotte worked on the 100-ton four-turreted TG-5 tank, armed with a 107&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet Union, it dissolved in 1991. During its existence, it was the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country by area, extending across Time in Russia, eleven time zones and sharing Geography of the Soviet Union#Borders and neighbors, borders with twelve countries, and the List of countries and dependencies by population, third-most populous country. An overall successor to the Russian Empire, it was nominally organized as a federal union of Republics of the Soviet Union, national republics, the largest and most populous of which was the Russian SFSR. In practice, Government of the Soviet Union, its government and Economy of the Soviet Union, economy were Soviet-type economic planning, highly centralized. As a one-party state go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T-28 (medium Tank)
The T-28 was a Soviet multi-turreted medium tank. The prototype was completed in 1931, and production began in late 1932. It was an infantry support tank intended to break through fortified defences. The T-28 was designed to complement the heavier T-35 (also multi-turreted), with which it shared turret designs. The type did not have great success in combat, but it played an important role as a development project for Soviet tank designers. A series of new ideas and solutions that were tried out on the T-28 were later incorporated in future models. Design history The T-28 was in many ways similar to the British Vickers A1E1 Independent tank, which greatly influenced tank design in the period between the wars, even though only a single prototype was manufactured in 1926. The Kirov Factory in Leningrad began manufacturing a tank that was based on the design of the British Independent in 1932. The T-28 tank was officially approved on 11 August 1933. The T-28 had one large turr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vickers 6-Ton
The Vickers 6-ton tank or Vickers Mark E, also known as the "Six-tonner", was a British light tank designed in 1928 in a private project at Vickers. Though not adopted by the British Army, it was picked up by several other armed forces, and licensed by the Soviet Union as the T-26. It was also the direct predecessor of the Polish 7TP tank. History The first Mark E was built in 1928 by a design team that included the famed tank designers John Valentine Carden and Vivian Loyd. The hull was made of riveted steel plates, thick at the front and over most of the turrets, and about thick on the rear of the hull. The power was provided by an Armstrong Siddeley engine of (depending on the version), which gave it a top speed of on roads. Its suspension used two axles, each of which carried a two-wheel bogie to which a second set of bogies was connected with a leaf spring. It was patented by Carden in 1929 and apparently derived from a similar but simpler suspension on Light Ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carden Loyd Tankette
The Carden Loyd tankettes were a series of British tankettes of the period between the World Wars, the most successful of which was the Mark VI, the only version built in significant numbers. It became a classic tankette design worldwide, was licence-built by several countries and became the basis of several designs produced in various countries. Development The Carden Loyd tankette came about from an idea started, as a private project, by the British military engineer and tank strategist Major Giffard LeQuesne Martel. He built a one-man tank in his garage from various parts and showed it to the War Office in the mid-1920s. With the publication of the idea, other companies produced their own interpretations of the idea. One of these was ''Carden-Loyd Tractors Ltd'', a firm founded by Sir John Carden and Vivian Loyd and later purchased by Vickers-Armstrongs. Besides one-man vehicles they also proposed two-man vehicles which turned out to be a more effective and popular idea. V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coaxial Weapon
A weapon mount is an assembly or mechanism used to hold a weapon (typically a gun) onto a platform in order for it to function at maximum capacity. Weapon mounts can be broken down into two categories: static mounts and non-static mounts. Static mount A static mount is a non-portable weapon support component either mounted directly to the ground, on a fortification, or as part of a vehicle. Turret A gun turret protects the crew or mechanism of a weapon and at the same time lets the weapon be aimed and fired in many directions. A turret is a rotating weapon platform, strictly one that crosses the armour of whatever it is mounted on with a structure called a barbette (on ships) or basket (on tanks) and has a protective structure on top (gunhouse). If it has no gunhouse it is a barbette, if it has no barbette (i.e., it is mounted to the outside of the vehicle's armour) it is an installation. Turrets are typically used to mount machine guns, autocannons or large-calibre guns. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
45 Mm Anti-tank Gun M1932 (19-K)
The 45 mm anti-tank gun model 1932 (factory designation 19-K and GRAU index 52-P-243A) was a light quick-firing anti-tank gun used in the interwar period and in the first stage of the German-Soviet War. It was created by :ru:Завод № 8, factory No. 8 which was located in now Korolyov, Moscow Oblast, Korolyov city, under leadership of engineer :ru:Беринг (фон Беринг), Владимир Михайлович, V. Bering. History The gun bearing Designations of Russian artillery, factory designation 19-K (Cyrillic ''19-К'') was a combination of a modified carriage of the 37 mm anti-tank gun M1930 (1-K), 37 mm anti-tank gun model 1930 (built according to a documentation bought from Rheinmetall) with a 45 mm barrel designed in March 1932. and adopted by the Red Army on March 23, 1932. The 45 mm caliber was selected because the large reserves of the French 47 mm shells could be converted to 45 mm by milling out the driving bands. The resu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rkka
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army, often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Republic and, from 1922, the Soviet Union. The army was established in January 1918 by a decree of the Council of People's Commissars to oppose the military forces of the new nation's adversaries during the Russian Civil War, especially the various groups collectively known as the White Army. In February 1946, the Red Army (which embodied the main component of the Soviet Armed Forces alongside the Soviet Navy) was renamed the "Soviet Army". Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union it was split between the post-Soviet states, with its bulk becoming the Russian Ground Forces, commonly considered to be the successor of the Soviet Army. The Red Army provided the largest land warfare, ground force in the Allies of World War II, Allied victory in the European theatre of World War II, and its Soviet invasion of Manchuria, invasion of Manchuria assisted the un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arc Of Fire
The field of fire or zone of fire (ZF) of a weapon, or group of weapons, is the area around it that can easily and effectively be reached by projectiles from a given position. Field of fire The term originally came from the ''field of fire'' in front of fort A fortification (also called a fort, fortress, fastness, or stronghold) is a military construction designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from La ...s (and similar defensive positions), cleared so there was no shelter for an approaching enemy. Sector of fire A similar term sector of fire is used to describe the area into which each gunner or group are ''allowed'' to fire. The boundaries are assigned by the commanding officer and thus can be arbitrary, even three-dimensional (a rifleman attacking a building might be assigned a set of windows to target). Arc of fire The arc of fire of a mounted gun is a horizontal ("Traverse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sloped Armour
Sloped armour is armour that is oriented neither Vertical and horizontal, vertically nor horizontally. Such angled armour is typically mounted on tanks and other armoured fighting vehicles (AFVs), as well as Naval ship, naval vessels such as battleships and cruisers. Sloping an armour plate makes it more difficult to penetrate by anti-tank weapons, such as Armour-piercing shell, armour-piercing shells, kinetic energy penetrators and Rocket (weapon), rockets, if they follow a more or less horizontal trajectory to their target, as is often the case. The improved protection is caused by three main effects. Firstly, a projectile hitting a plate at an angle other than 90° has to move through a greater thickness of armour, compared to hitting the same plate at a right-angle. In the latter case only the plate thickness (the surface normal, normal to the surface of the armour) must be pierced. Increasing the armour slope improves, for a given plate thickness, the level of protection at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BT-5
The BT-5 ("Bystrohodnyi tank" or "Fast Tank type 5") was the second tank in the Soviet BT series of tanks. The BT-5 improved on the previous BT-2, such as a new turret fitted with a 45 mm anti-tank gun that was also used on the T-26 and the BT-5's younger brother, the BT-7. The BT-5 would enter service in 1933, with the Red Army first seeing action with the Second Spanish Republic in the Spanish Civil War in 1937 until the end of World War II, with between 1884 and 2108 units being produced with production of the tank beginning in March 1933 with production ending in 1935. Design The BT-5 had no armor improvements over the BT-2, with its thickest armor being 13 mm at its thickest and the thinnest being 6 mm thick. The suspension was a Christie suspension, which could have the tracks taken off to have road-wheels to use on the road. To turn the tank without the tracks, the driver had a steering wheel that turned the first wheel on each side. It took about a half hour to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kharkov Locomotive Factory
The Malyshev Factory (; abbreviated ), formerly the Kharkov Locomotive Factory (, ), is a state-owned manufacturer of heavy equipment in Kharkiv, Ukraine. It was named after the Soviet politician Vyacheslav Malyshev. The factory is part of the state concern, Ukroboronprom. It produces diesel engines, farm machinery, coal mining, sugar refining, and wind farm equipment, but is best known for its production of Soviet tanks, including the BT tank series of fast tanks, the famous T-34 of the Second World War, the Cold War T-64 and T-80, and their modern Ukrainian successor, the T-84. The factory is closely associated with the Morozov Design Bureau (KMDB), designer of military armoured fighting vehicles and the Kharkiv Engine Design Bureau (KEDB) for engines. In 1958, it developed the Kharkovchanka, an off-road vehicle which reached the South Pole the following year. At its height during the Soviet era, the factory employed 60,000 of Kharkiv's 1.5 million inhabitants. , 5,000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |