|
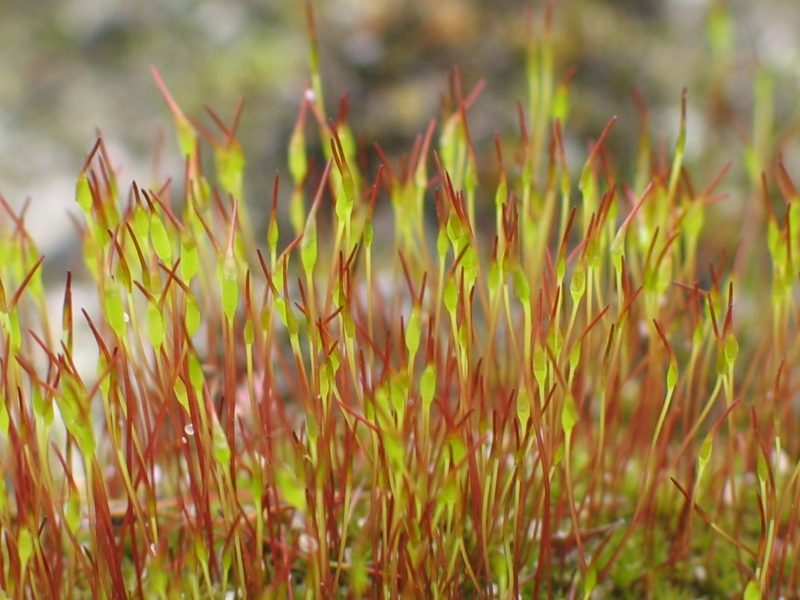
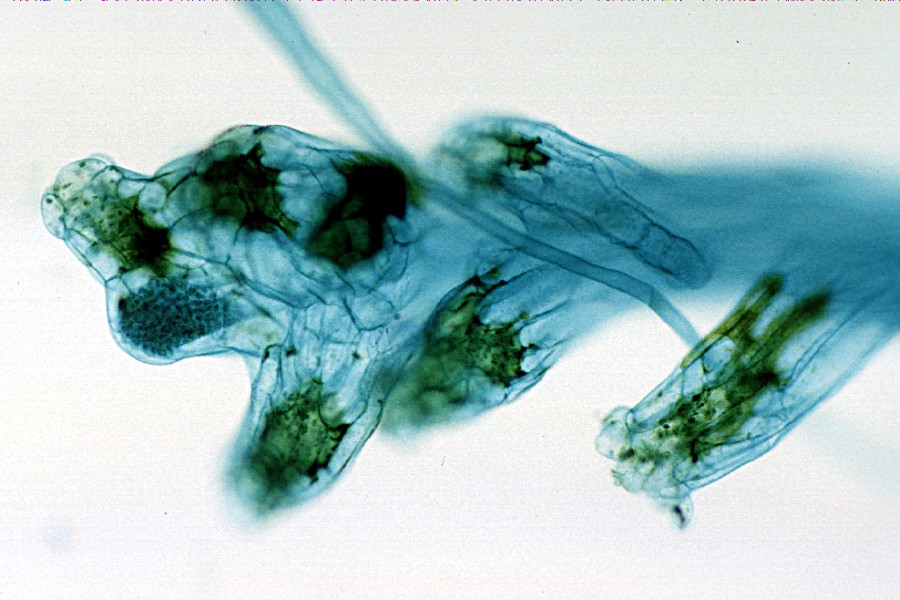
Süsswassertang
''Lomariopsis lineata'' is a species of fern native to South East Asia. The prothallia of this species (or possibly a closely related species) are commonly cultivated as an aquarium plant, where it is known to aquarists as süsswassertang (German spelling: ). It is often incorrectly spelled "subwassertang" due to the German eszett's similarity to the Latin 'B'. It is also called Loma fern or round pellia. Description Adult leaves are pinnate and up to 1 meter in length. It is found in humid forests up to 1,200 meters above sea level. It may grow epiphytic on trees or among rocks in dry river beds. ''Flora of China'' separates a Chinese form as ''L. cochinchinensis'', but this plant is otherwise considered a synonym of ''L. lineata''. The species may grow to be 3 meters in length. In Singapore, ''L. lineata'' is considered critically endangered in the wild. Süsswassertang Süsswassertang is used as a decorative aquarium plant. It was first discovered in the aquarium of bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monosolenium
''Monosolenium tenerum'', is a weedy species of liverwort found in east Asia. It is the only species in the genus ''Monosolenium'' and the family Monosoleniaceae. It is commonly confused with similar-looking plants in the aquarium trade like '' Pellia'' liverworts and Süsswassertang, a fern gametophyte. Ecology ''Monosolenium tenerum'' is a terrestrial plant, growing on moist, shady soil, sometimes in association with '' Marchantia palmata''. The species has an east Asiatic distribution. It has been found in east India (Assam, Himachal Pradesh, & Uttarakhand), Nepal, China (northwestern Sichuan, Guangdong, & Macau), Taiwan, as well as the Ryukyu Islands, Japan, and Hawaii. All areas where the plant grows are subtropical or temperate regions with mesic habitats, where there is ample supply of moisture. Perhaps it is because the species grows in such mesic climates that the thallus (plant body) has become simplified, since the chambered internal anatomy of other Marchantiales ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pellia
''Pellia'' is a small but widespread genus of liverworts in the cool and temperate regions of the northern hemisphere. It is classified in order Pelliales and is a member of the family Pelliaceae within that order. Süsswassertang, a plant grown submerged in aquaria was once considered to be ''Pellia endiviifolia'', but is now known to be the indeterminate gametophyte of a ''Lomariopsis'' species, a type of fern The ferns (Polypodiopsida or Polypodiophyta) are a group of vascular plants (plants with xylem and phloem) that reproduce via spores and have neither seeds nor flowers. They differ from mosses by being vascular, i.e., having specialized tissue .... ''Pellia'' liverworts are also often confused with '' Monosolenium tenerum'', another liverwort. Species Taxonomy based on work by Söderström et al. 2016 * '' Pellia cordaeana'' Trevisan 1877 * '' Pellia crispa'' Kummer 1875 * '' Pellia gottscheana'' Kreh 1909 * '' Pellia longifolia'' Kummer 1875 * '' Pellia un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Phylogenetic
Molecular phylogenetics () is the branch of phylogeny that analyzes genetic, hereditary molecular differences, predominantly in DNA sequences, to gain information on an organism's evolutionary relationships. From these analyses, it is possible to determine the processes by which diversity among species has been achieved. The result of a molecular phylogenetic analysis is expressed in a phylogenetic tree. Molecular phylogenetics is one aspect of molecular systematics, a broader term that also includes the use of molecular data in taxonomy and biogeography. Molecular phylogenetics and molecular evolution correlate. Molecular evolution is the process of selective changes (mutations) at a molecular level (genes, proteins, etc.) throughout various branches in the tree of life (evolution). Molecular phylogenetics makes inferences of the evolutionary relationships that arise due to molecular evolution and results in the construction of a phylogenetic tree. History The theoretical fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gametangia
A gametangium (: gametangia) is a sex organ or cell in which gametes are produced that is found in many multicellular protist A protist ( ) or protoctist is any eukaryotic organism that is not an animal, land plant, or fungus. Protists do not form a natural group, or clade, but are a paraphyletic grouping of all descendants of the last eukaryotic common ancest ...s, algae, Fungus, fungi, and the gametophytes of plants. In contrast to gametogenesis in animals, a gametangium is a haploid structure and formation of gametes does not involve meiosis. Types of gametangia Depending on the type of gamete produced in a gametangium, several types can be distinguished. Female Female gametangia are most commonly called Archegonium, archegonia. They produce egg cells and are the sites for fertilization. Archegonia are common in algae and primitive plants as well as gymnosperms. In flowering plants, they are replaced by the embryo sac inside the ovule. Male The male gametangia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all life, forms of life. Every cell consists of cytoplasm enclosed within a Cell membrane, membrane; many cells contain organelles, each with a specific function. The term comes from the Latin word meaning 'small room'. Most cells are only visible under a light microscope, microscope. Cells Abiogenesis, emerged on Earth about 4 billion years ago. All cells are capable of Self-replication, replication, protein synthesis, and cell motility, motility. Cells are broadly categorized into two types: eukaryotic cells, which possess a Cell nucleus, nucleus, and prokaryotic, prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus but have a nucleoid region. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms such as bacteria, whereas eukaryotes can be either single-celled, such as amoebae, or multicellular organism, multicellular, such as some algae, plants, animals, and fungi. Eukaryotic cells contain organelles including Mitochondrion, mitochondria, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indeterminate Growth
In biology and botany, indeterminate growth is growth that is not terminated, in contrast to determinate growth that stops once a genetically predetermined structure has completely formed. Thus, a plant that grows and produces flowers and fruit until killed by frost or some other external factor is called indeterminate. For example, the term is applied to tomato varieties that grow in a rather gangly fashion, producing fruit throughout the growing season. In contrast, a determinate tomato plant grows in a more bushy shape and is most productive for a single, larger harvest, then either tapers off with minimal new growth or fruit or dies. Inflorescences In reference to an inflorescence (a shoot specialised for bearing flowers, and bearing no leaves other than bracts), an indeterminate type (such as a raceme) is one in which the first flowers to develop and open are from the buds at the base, followed progressively by buds nearer to the growing tip. The growth of the shoot is not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habit (biology)
Habit, equivalent to habitus in some applications in biology, refers variously to aspects of behaviour or structure, as follows: *In zoology (particularly in ethology), ''habit'' usually refers to aspects of more or less predictable ''behaviour'', instinctive or otherwise, though it also has broader application. ''Habitus'' refers to the characteristic form or morphology of a species. *In botany, the plant habit is the characteristic form in which a given species of plant grows.Jackson, Benjamin, Daydon; A Glossary of Botanic Terms with their Derivation and Accent; Published by Gerald Duckworth & Co. London, 4th ed 1928 Behavior In zoology, ''habit'' (not to be confused with ''habitus'' as described below) usually refers to a specific behavior pattern, either adopted, learned, pathological, innate, or directly related to physiology. For example: * ...the atwas in the ''habit'' of springing upon the oor knockerin order to gain admission... * If these sensitive parrots are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thallus
Thallus (: thalli), from Latinized Greek (), meaning "a green shoot" or "twig", is the vegetative tissue of some organisms in diverse groups such as algae, fungi, some liverworts, lichens, and the Myxogastria. A thallus usually names the entire body of a multicellular non-moving organism in which there is no organization of the tissues into organs. Many of these organisms were previously known as the thallophytes, a polyphyletic group of distantly related organisms. An organism or structure resembling a thallus is called thalloid, thalloidal, thalliform, thalline, or thallose. Even though thalli do not have organized and distinct parts ( leaves, roots, and stems) as do the vascular plants, they may have analogous structures that resemble their vascular "equivalents". The analogous structures have similar function or macroscopic structure, but different microscopic structure; for example, no thallus has vascular tissue. In exceptional cases such as the Lemnoideae, where th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fragmentation (reproduction)
Fragmentation in multicellular or colonial organisms is a form of asexual reproduction or cloning, where an organism is split into fragments upon maturation and the split part becomes the new individual. The organism may develop specific organs or zones to shed or be easily broken off. If the splitting occurs without the prior preparation of the organism, both fragments must be able to regeneration (biology), regenerate the complete organism for it to function as reproduction. Fragmentation as a method of reproduction is seen in organisms such as spirogyra, filamentous cyanobacteria, Mold (fungus), molds, lichens, sponges, acoelomorpha, acoel flatworms, some annelid worms and sea stars. Fragmentation in various organisms Molds, yeasts and mushrooms, all of which are part of the Fungi kingdom (biology), kingdom, produce tiny filaments called hyphae. These hyphae obtain food and nutrients from the body of other organisms to grow and fertilize. Then a piece of hyphae breaks off an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reproduction
Reproduction (or procreation or breeding) is the biological process by which new individual organisms – "offspring" – are produced from their "parent" or parents. There are two forms of reproduction: Asexual reproduction, asexual and Sexual reproduction, sexual. In asexual reproduction, an organism can reproduce without the involvement of another organism. Asexual reproduction is not limited to unicellular organism, single-celled organisms. The cloning of an organism is a form of asexual reproduction. By asexual reproduction, an organism creates a genetically similar or identical copy of itself. The evolution of sexual reproduction is a major puzzle for biologists. The two-fold cost of sexual reproduction is that only 50% of organisms reproduce and organisms only pass on 50% of their genes.John Maynard Smith ''The Evolution of Sex'' 1978. Sexual reproduction typically requires the sexual interaction of two specialized reproductive cells, called gametes, which contain half t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxonomic Rank
In biology, taxonomic rank (which some authors prefer to call nomenclatural rank because ranking is part of nomenclature rather than taxonomy proper, according to some definitions of these terms) is the relative or absolute level of a group of organisms (a ''taxon'') in a hierarchy that reflects evolutionary relationships. Thus, the most inclusive clades (such as Eukarya and Animalia) have the highest ranks, whereas the least inclusive ones (such as ''Homo sapiens'' or ''Bufo bufo'') have the lowest ranks. Ranks can be either relative and be denoted by an indented taxonomy in which the level of indentation reflects the rank, or absolute, in which various terms, such as species, genus, Family (biology), family, Order (biology), order, Class (biology), class, Phylum (biology), phylum, Kingdom (biology), kingdom, and Domain (biology), domain designate rank. This page emphasizes absolute ranks and the rank-based codes (the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature, Zoological Code, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sporophyte
A sporophyte () is one of the two alternation of generations, alternating multicellular organism, multicellular phases in the biological life cycle, life cycles of plants and algae. It is a diploid multicellular organism which produces asexual Spore, spores. This stage Alternation of generations, alternates with a multicellular haploid gametophyte phase. Life cycle The sporophyte develops from the zygote produced when a haploid egg cell is fertilized by a haploid sperm and each sporophyte cell therefore has a double set of chromosomes, one set from each parent. All Embryophyta, land plants, and most multicellular algae, have life cycles in which a multicellular diploid sporophyte phase alternates with a multicellular haploid gametophyte phase. In the Spermatophyte, seed plants, the largest groups of which are the gymnosperms (bare seeds) and angiosperms (fruiting plants), the sporophyte phase is more prominent than the gametophyte, and is the familiar green plant with its roots, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |