|
Syrensk
Vasknarva (, Syrenets; ) is a village in Alutaguse Parish, Ida-Viru County in northeastern Estonia. Geography The settlement is located on the northern shore of Lake Peipus, on the left bank of the Narva River headwaters forming the border with Russia. Vasknarva has a population of 40 (as of 2011), most of them are Orthodox Old Believers. Nearly the entire population is Russian-speaking. There is a small boat harbour, a border guard cordon, a nunnery and the St. Elijah Orthodox church. By its architecture Vasknarva is a common Peipsi Russian linear village where one-storey wooden buildings are situated side by side just beside the street. The Peipus lakeshore and the extended forests in the surrounding area are a popular destination for daytrippers. On the other bank of Narva River there is the Russian locality of Skamya, part of Slantsevsky District. History The name is derived from Estonian: ''Vask'', "Copper", and the Narva River. According to etymology, it referred to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Populated Places In Estonia
Populated places in Estonia (officially: settlement units), are cities or settlement units of rural municipality, municipalities, but only cities have administrative functions. Settlement units are divided into settlements and urban regions (subdivisions of cities). Officially there are four types of settlement unit in Estonia: * village () - a sparsely populated settlement or a densely populated settlement with fewer than 300 permanent inhabitants * township () - a densely populated settlement with at least 300 permanent inhabitants * town () - a densely populated settlement with at least 1000 permanent inhabitants * city () As of 2024, there were 47 cities, 13 towns, 186 hamlets and 4457 villages in Estonia. See also *Municipalities of Estonia *List of cities and towns in Estonia *Counties of Estonia Notes References External links Place Names Board of Estonia [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estonian Language
Estonian ( ) is a Finnic language and the official language of Estonia. It is written in the Latin script and is the first language of the majority of the country's population; it is also an official language of the European Union. Estonian is spoken natively by about 1.1 million people: 922,000 people in Estonia and 160,000 elsewhere. Classification By Convention (norm), conventions of historical linguistics, Estonian is classified as a part of the Finnic languages, Finnic (a.k.a. Baltic Finnic) branch of the Uralic languages, Uralic (a.k.a. Uralian, or Finno-Ugric languages, Finno-Ugric) language family. Other Finnic languages include Finnish language, Finnish and several endangered languages spoken around the Baltic Sea and in northwestern Russia. Estonian is typically subclassified as a Southern Finnic language, and it is the second-most-spoken language among all the Finnic languages. Alongside Finnish, Hungarian language, Hungarian and Maltese language, Maltese, Estonian is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pontus De La Gardie
Baron Pontus De la Gardie ( – 5 November 1585) was a French nobleman and general in the service of Denmark and Sweden. Life and career He was born Ponce d'Escouperie in Caunes-Minervois (Aude), Languedoc, a son of Jacques Escoperier and X Armengaud. As a youngster, he wanted to become a priest and was educated in a monastery. He changed his mind, however, and left Languedoc to become a mercenary in the service of Denmark. De la Gardie was promoted to officer and was in charge of a regiment of mercenaries. In 1565, during the Northern Seven Years' War, he was captured by Swedish troops at Varberg and changed allegiance to Sweden. De la Gardie quickly became a favourite of John III of Sweden and in 1569, after only four years in the Swedish service, he received nobility status. In 1571, he was created a baron and was given Ekholmen Castle. Alleged involvement in Mornay plot He was suspected to have taken part in the Mornay plot to assassinate John III. The plot was led b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Livonian War
The Livonian War (1558–1583) concerned control of Terra Mariana, Old Livonia (in the territory of present-day Estonia and Latvia). The Tsardom of Russia faced a varying coalition of the Denmark–Norway, Dano-Norwegian Realm, the Kingdom of Sweden (1523–1611), Kingdom of Sweden, and the Polish–Lithuanian union, Union (later Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Commonwealth) of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Kingdom of Poland (1385–1569), Kingdom of Poland. From 1558 to 1578, Russia dominated the region with early military successes at Tartu, Dorpat (Tartu) and Narva. The Russian dissolution of the Livonian Confederation brought Poland–Lithuania into the conflict, and Sweden and Denmark-Norway intervened between 1559 and 1561. Swedish Estonia was established despite constant invasion from Russia, and Frederick II of Denmark, Frederick II of Denmark-Norway bought the old Bishopric of Ösel–Wiek, which he placed under the control of his brother Magnus of Holstein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Narva (1558)
The siege of Narva (; ) was a Russian siege of the Livonian Confederation, Livonian city of Narva (in modern-day eastern Estonia) from April through May 1558, during the Livonian War.Летописец Русский (Московская летопись) // Чтения в Императорском Обществе Истории и Древностей Российских, Книга 3. 1895 (Chronicler Russian (Moscow Chronicle) // Readings in the Imperial Society of Russian History and Antiquities,) After capturing the city in July 1558, the Russians used Narva as a trading center and port to move goods from Pskov and Novgorod. The Russians controlled the city until 1581, when it was captured by Swedish forces under Pontus De La Gardie. References Conflicts in 1558 Battles of the Livonian War Sieges involving the Tsardom of Russia, Narva (1558) 1558 in Europe 16th century in Estonia Military history of Estonia Battles involving the Livonian Order {{Estonia- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vogt
An , sometimes simply advocate, (German, ), or (French, ), was a type of medieval office holder, particularly important in the Holy Roman Empire, who was delegated some of the powers and functions of a major feudal lord, or for an institution such as an abbey. They typically had responsibility for the "comital" functions which defined the office of early medieval "counts", such as taxation, recruitment of militias, and maintaining law and order. This type of office could apply to specific agricultural lands, villages, castles, and even cities. In some regions, advocates came to be governors of large provinces, sometimes distinguished by terms such as . In different parts of medieval Europe, the term advocate developed different meanings, and other terms were also sometimes used to represent similar offices. For example, Anglo-Norman comital functions for larger districts were executed by vicomtes in Normandy, and sheriffs in England. In contrast, the or advocate as an offic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
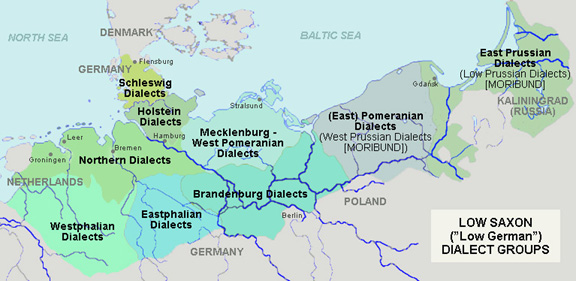
Low German
Low German is a West Germanic languages, West Germanic language variety, language spoken mainly in Northern Germany and the northeastern Netherlands. The dialect of Plautdietsch is also spoken in the Russian Mennonite diaspora worldwide. "Low" refers to the altitude of the areas where it is typically spoken. Low German is most closely related to Frisian languages, Frisian and English language, English, with which it forms the North Sea Germanic group of the West Germanic languages. Like Dutch language, Dutch, it has historically been spoken north of the Benrath line, Benrath and Uerdingen line, Uerdingen isoglosses, while forms of High German languages, High German (of which Standard German is a standardized example) have historically been spoken south of those lines. Like Frisian, English, Dutch and the North Germanic languages, Low German has not undergone the High German consonant shift, as opposed to Standard German, Standard High German, which is based on High German langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pskov Republic
The Pskov Republic () was a city-state in northwestern Russia. It is traditionally considered to have won its formal independence from the Novgorod Republic in 1348. Its capital city was Pskov and its territory was roughly equivalent to modern-day Pskov Oblast. History Origins After the disintegration of Kievan Rus' in the 12th century, the city of Pskov and its dependent territory became part of the Novgorod Republic, but it continued to enjoy self-government under the supervision of a ''posadnik'', or chief executive, that was appointed by Novgorod. Pskov had the status of a borough (), but was given the unique right to have boroughs of its own, with Izborsk being the most ancient among them. The first period of self-declared independence lasted from 1228 to 1242, ending when the city was temporarily annexed by the Livonian Order. After being liberated by Aleksandr Nevsky, the city pledged its fealty to the grand prince and Novgorod. Due to Pskov's leading role in the strug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terra Mariana
Terra Mariana (Medieval Latin for 'Land of Mary (mother of Jesus), Mary') was the formal name for Medieval Livonia or Old Livonia. It was formed in the aftermath of the Livonian Crusade, and its territories were composed of present-day Estonia and Latvia. It was established on 2 February 1207, as a principality of the Holy Roman Empire, and lost this status in 1215 when Pope Innocent III proclaimed it as directly subject to the Holy See. The papal legate William of Modena divided Terra Mariana into feudal principalities: the Duchy of Estonia (1219–1346), Duchy of Estonia (dominum directum to the king of Denmark); the Archbishopric of Riga; the Bishopric of Courland; the Bishopric of Dorpat; the Bishopric of Ösel–Wiek; and territories under the military administration of the Livonian Brothers of the Sword. After the 1236 Battle of Saule, the surviving members of the Brothers merged in 1237 with the Teutonic Order of Prussia and became known as the Livonian Order. In 1346 the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Livonian Order
The Livonian Order was an autonomous branch of the Teutonic Order, formed in 1237. From 1435 to 1561 it was a member of the Livonian Confederation. History The order was formed from the remnants of the Livonian Brothers of the Sword after their defeat by Samogitians in 1236 at the Battle of Saule, Battle of Schaulen (Saule). They were incorporated into the Teutonic Knights and became known as the Livonian Order in 1237. In the summer of that year, the Master of Prussia Hermann Balk rode into Riga to install his men as castle commanders and administrators of Livonia. In 1238, the Teutonic Knights of Livonia signed the Treaty of Stensby with the Denmark, Kingdom of Denmark. Under this agreement, Denmark would support the expansion ambitions of the order in exchange for northern maritime Estonia. In 1242, the Livonian Order tried to take the city of Veliky Novgorod, Novgorod. However, they were defeated by Alexander Nevsky in the Battle on the Ice. Fortresses as Paide in land c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordensburg
''Ordensburg'' (plural ''Ordensburgen'') is a German language, German term meaning a "castle of a (military) order". It is used specifically for the fortified structures built by Crusades, crusading German Military order (religious society), military orders during the Middle Ages. Medieval ''Ordensburgen'' ''Ordensburgen'' were originally constructed by the Livonian Brothers of the Sword and later by the Teutonic Order to fortify territory in Prussia (region), Prussia and Livonia captured from the native populations – Old Prussians, Lithuanians and native peoples of what is now Latvia and Estonia. Later, ''Ordensburgen'' were used to attack Lithuania. Since they were built and used by religious military orders, the ''Ordensburgen'' often resembled monastery , monasteries. While they were considerably larger than those in the Holy Roman Empire, they were much scarcer in the Monastic state of the Teutonic Knights. While a normal castle in the Holy Roman Empire would control a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |