|
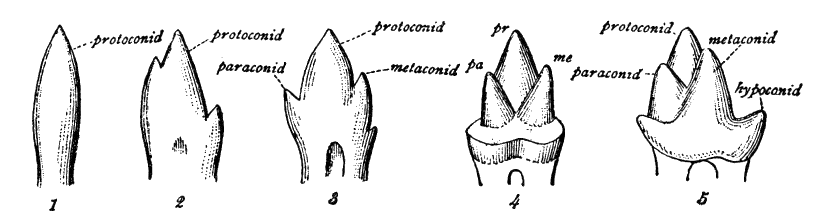
Symmetrodont
Symmetrodonta is a group of Mesozoic mammals and mammal-like synapsids characterized by the triangular aspect of the molars when viewed from above, and the absence of a well-developed talonid. The traditional group of 'symmetrodonts' ranges in age from the latest Triassic to the Late Cretaceous, but most research in the last 20-30 years has concluded that they are not a true taxonomic group, but include several unrelated branches of the mammal tree. Despite this, the name is still used informally by some researchers for convenience, usually restricted to the spalacotheriids and zhangheotheriids. Martin, T., 2018. 6. Mesozoic mammals—early mammalian diversity and ecomorphological adaptations. In Mammalian evolution, diversity and systematics (pp. 199-300). De Gruyter. There are some symmetrodonts with acutely-triangulated molar cusps (“acute-angled symmetrodonts”) that seem to form a true monophyletic group, and lasted from the Early Cretaceous to the Campanian, although ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
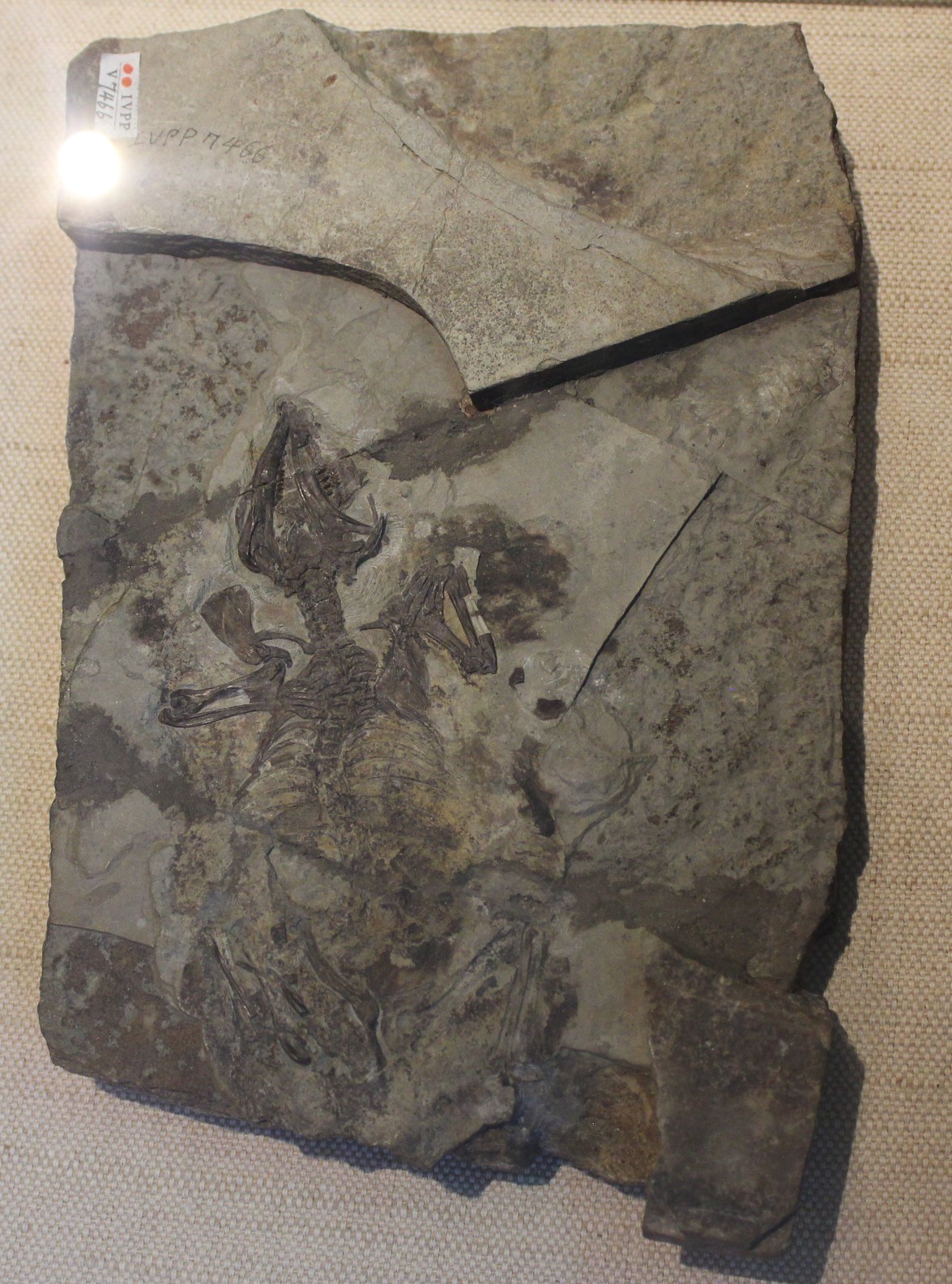
Zhangheotherium
''Zhangheotherium'' is an extinct genus of "symmetrodont" mammal from the Early Cretaceous of China. A single species is known, ''Zhangheotherium quinquecuspidens'' from Jianshangou Beds of the Yixian Formation. ''Zhangheotherium'' was the first "symmetrodont" known from a nearly complete skeleton, expanding knowledge of the group beyond isolated teeth and jaws. The genus name honors Zhang He, who collected the holotype fossil from Liaoning Province prior to its 1997 description. The specific name is Latin for "five-cusped teeth". "Symmetrodonts" and other archaic mammals such as multituberculates and monotremes are still being debated on their taxonomical relationships. ''Zhangheotherium'' provided insight into the evolution of "symmetrodonts", revealing a combination of traits similar to modern therians (such as placentals and marsupials) as well as more "primitive" mammalians. Most likely, "symmetrodonts" are a grade of stem-group therians, with representatives incrementally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhangheotheriids
Zhangheotheriidae is a possibly paraphyletic family of "symmetrodont" mammals that is currently known from Early Cretaceous deposits in China and Russia. Six genera are currently recognized, '' Anebodon'', '' Kiyatherium'', ''Maotherium'', ''Ningchengodon'', '' Origolestes'', and ''Zhangheotherium ''Zhangheotherium'' is an extinct genus of "symmetrodont" mammal from the Early Cretaceous of China. A single species is known, ''Zhangheotherium quinquecuspidens'' from Jianshangou Beds of the Yixian Formation. ''Zhangheotherium'' was the first ...''. References Symmetrodonta Prehistoric mammal families Early Cretaceous mammals of Asia {{cretaceous-mammal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronoperates
''Chronoperates'' (meaning "time wanderer" in Greek) is an extinct genus of mammal whose remains have been found in a late Paleocene deposit in Alberta, Canada. It is represented by the type species ''Chronoperates paradoxus'' and known only from a partial left lower jaw. It was first identified in 1992 as a non-mammalian cynodont, implying a ghost lineage of over 100 million years since the previously youngest known record of non-mammalian cynodonts, which at that time was in the Jurassic period (some non-mammalian cynodonts are now known to have persisted until the Early Cretaceous). Subsequent authors have challenged this interpretation, particularly as the teeth do not resemble any known non-mammalian cynodonts. ''Chronoperates'' is now generally considered to be more likely to be a late-surviving symmetrodont Symmetrodonta is a group of Mesozoic mammals and mammal-like synapsids characterized by the triangular aspect of the molars when viewed from above, and the absence of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhangheotheriidae
Zhangheotheriidae is a possibly paraphyletic family of "symmetrodont" mammals that is currently known from Early Cretaceous deposits in China and Russia. Six genera are currently recognized, ''Anebodon'', ''Kiyatherium'', ''Maotherium'', ''Ningchengodon'', ''Origolestes'', and ''Zhangheotherium''. References Symmetrodonta Prehistoric mammal families Early Cretaceous mammals of Asia {{cretaceous-mammal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spalacotheriidae
Spalacotheriidae is a family of extinct mammals belonging to the paraphyletic group ' Symmetrodonta'. They lasted from the Early Cretaceous to the Campanian in North America, Europe, Asia and North Africa. Spalacotheriids are characterised by having molar teeth with three molar cusps sitting at acute angles to one another.Martin, T., 2018. 6. Mesozoic mammals—early mammalian diversity and ecomorphological adaptations. In Mammalian evolution, diversity and systematics (pp. 199-300). De Gruyter. The shape of their teeth as well as their long lower jaw indicate a carnivorous/insectivorous diet. A sub-group of Spalacotheriidae, the spalacolestines, lack a Meckelian groove in the jaw, indicating that they had a modern ear anatomy. Genera * '' Akidolestes'' * '' Infernolestes'' * '' Spalacotherium'' * ''Symmetrolestes ''Symmetrolestes'' is an extinct genus of small spalacotheriid mammal from the Early Cretaceous period of Japan. The genus contains one species known as ''S. parv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molar (tooth)
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone tooth", from ''mola'', millstone and ''dens'', tooth. Molars show a great deal of diversity in size and shape across the mammal groups. The third molar of humans is sometimes vestigial. Human anatomy In humans, the molar teeth have either four or five cusps. Adult humans have 12 molars, in four groups of three at the back of the mouth. The third, rearmost molar in each group is called a wisdom tooth. It is the last tooth to appear, breaking through the front of the gum at about the age of 20, although this varies among individuals and populations, and in many cases the tooth is missing. The human mouth contains upper (maxillary) and lower (mandibular) molars. They are: maxillary first molar, maxillary second molar, maxillary third mol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talonid
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone tooth", from ''mola'', millstone and ''dens'', tooth. Molars show a great deal of diversity in size and shape across the mammal groups. The third molar of humans is sometimes vestigial. Human anatomy In humans, the molar teeth have either four or five cusps. Adult humans have 12 molars, in four groups of three at the back of the mouth. The third, rearmost molar in each group is called a wisdom tooth. It is the last tooth to appear, breaking through the front of the gum at about the age of 20, although this varies among individuals and populations, and in many cases the tooth is missing. The human mouth contains upper (maxillary) and lower (mandibular) molars. They are: maxillary first molar, maxillary second molar, maxillary third molar, man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spalacotheriids
Spalacotheriidae is a family of extinct mammals belonging to the paraphyletic group 'Symmetrodonta'. They lasted from the Early Cretaceous to the Campanian in North America, Europe, Asia and North Africa. Spalacotheriids are characterised by having molar teeth with three molar cusps sitting at acute angles to one another.Martin, T., 2018. 6. Mesozoic mammals—early mammalian diversity and ecomorphological adaptations. In Mammalian evolution, diversity and systematics (pp. 199-300). De Gruyter. The shape of their teeth as well as their long lower jaw indicate a carnivorous/insectivorous diet. A sub-group of Spalacotheriidae, the spalacolestines, lack a Meckelian groove in the jaw, indicating that they had a Evolution of mammalian auditory ossicles, modern ear anatomy. Genera * ''Akidolestes'' * ''Infernolestes'' * ''Spalacotherium'' * ''Symmetrolestes'' * Spalacolestinae ** ''Aliaga (mammal), Aliaga'' ** ''Heishanlestes'' ** ''Lactodens'' ** ''Shalbaatar'' ** ''Spalacolestes'' * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnivorous
A carnivore , or meat-eater (Latin, ''caro'', genitive ''carnis'', meaning meat or "flesh" and ''vorare'' meaning "to devour"), is an animal or plant whose nutrition and energy requirements are met by consumption of animal tissues (mainly muscle, fat and other soft tissues) as food, whether through predation or scavenging. Nomenclature Mammal order The technical term for mammals in the order Carnivora is ''carnivoran'', and they are so-named because most member species in the group have a carnivorous diet, but the similarity of the name of the order and the name of the diet causes confusion. Many but not all carnivorans are meat eaters; a few, such as the large and small cats (Felidae) are ''obligate'' carnivores (see below). Other classes of carnivore are highly variable. The ursids (bears), for example: while the Arctic polar bear eats meat almost exclusively (more than 90% of its diet is meat), almost all other bear species are omnivorous, and one species, the gia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insectivorous
A robber fly eating a hoverfly An insectivore is a carnivorous animal or plant which eats insects. An alternative term is entomophage, which can also refer to the human practice of eating insects. The first vertebrate insectivores were amphibians. When they evolved 400 million years ago, the first amphibians were piscivores, with numerous sharp conical teeth, much like a modern crocodile. The same tooth arrangement is however also suited for eating animals with exoskeletons, thus the ability to eat insects can stem from piscivory. At one time, insectivorous mammals were scientifically classified in an order called Insectivora. This order is now abandoned, as not all insectivorous mammals are closely related. Most of the Insectivora taxa have been reclassified; those that have not yet been reclassified and found to be truly related to each other remain in the order Eulipotyphla. Although individually small, insects exist in enormous numbers. Insects make up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theria
Theria ( or ; ) is a scientific classification, subclass of mammals amongst the Theriiformes. Theria includes the eutherians (including the Placentalia, placental mammals) and the metatherians (including the marsupials) but excludes the egg-laying monotremes and various extinct mammals evolving prior to the common ancestor of placentals and marsupials. Characteristics Therians give birth to live young without a shelled egg (biology), egg. This is possible thanks to key proteins called Syncytin-1, syncytins which allow exchanges between the mother and its offspring through a placenta, even Marsupial#Reproductive system, rudimental ones such as in marsupials. Genetic studies have suggested a viral origin of syncytins through the Endogenous retrovirus, endogenization process. The marsupials and the placentals evolved from a common therian ancestor that gave live birth by suppressing the mother's immune system. While the marsupials continued to give birth to an underdeveloped fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |