|
Swiftlet
Swiftlets are birds from the four genera ''Aerodramus'', ''Collocalia'', ''Hydrochous'' and ''Schoutedenapus'', which form the tribe (biology), tribe Collocaliini within the swift (bird), swift family (biology), family Apodidae. The group contains around thirty species mostly confined to southern Asia, south Pacific islands, and northeastern Australia, all within the tropical and subtropical regions. They are in many respects typical members of the Apodidae, having narrow wings for fast flight, with a wide gape and small reduced beak surrounded by bristles for catching insects in flight. What distinguishes many but not all species from other swifts and indeed almost all other birdsThe oilbird is a notable exception. The presence of echolocation was formerly used to argue for a close relationship of the Apodiformes and the oilbird, but the actual situation is more complicated. ''See also'': Caprimulgiformes. is their ability to use a simple but effective form of animal echolocation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerodramus
''Aerodramus'' is a genus of small, dark, cave-nesting birds in the swiftlet, Collocaliini tribe (biology), tribe of the Swift (bird), swift family. Its members are confined to tropical and subtropical regions in southern Asia, Oceania and northeastern Australia. Many of its members were formerly classified in ''Collocalia'', but were first placed in a separate genus by American ornithology, ornithologist Harry Church Oberholser in 1906. This is a taxonomically difficult group of very similar species. Animal echolocation, Echolocation, DNA sequencing and Parasite, parasitic louse, lice have all been used to establish relationships, but some problems, such as the placement of the Papuan swiftlet are not fully resolved. These swiftlets can pose major identification problems where several species occur. What distinguishes ''Aerodramus'' swiftlets from other swifts, and indeed almost all other birds, is their ability to use a simple but effective form of echolocation. This enables t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collocalia
''Collocalia'' is a genus of Swift (bird), swifts, containing some of the smaller species termed "swiftlets". Formerly a catch-all genus for these, a number of its former members are now normally (though not by all authors) placed in ''Aerodramus''. The genus ''Collocalia'' was introduced by the English zoologist George Robert Gray in 1854. The name ''Collocalia'' combines the classical Greek words ''kolla'' meaning "glue" and ''kalia'' for "nest". The genus previously contained fewer species. Seven subspecies of the glossy swiftlet were promoted to species status based on a detailed analysis of the swiftlets in the genus ''Collocalia'' published in 2017. Species Extant The genus now contains the following 11 species: * Plume-toed swiftlet, ''Collocalia affinis'' (formerly treated as a subspecies of the glossy swiftlet) * Grey-rumped swiftlet, ''Collocalia marginata'' (formerly treated as a subspecies of the glossy swiftlet) * Ridgetop swiftlet, ''Collocalia isonota'' (for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swift (bird)
The Apodidae, or swifts, form a family of highly aerial birds. They are superficially similar to swallows, but are not closely related to any passerine species. Swifts are placed in the order Apodiformes along with hummingbirds. The treeswifts are closely related to the true swifts, but form a separate family, the Hemiprocnidae. Resemblances between swifts and swallows are due to convergent evolution, reflecting similar life styles based on catching insects in flight. The family name, Apodidae, is derived from the Greek ἄπους (''ápous''), meaning "footless", a reference to the small, weak legs of these most aerial of birds.Jobling (2010) pp. 50–51.Kaufman (2001) p. 329. The tradition of depicting swifts without feet continued into the Middle Ages, as seen in the heraldic martlet. Taxonomy Taxonomists have long classified swifts and treeswifts as relatives of the hummingbirds, a judgment corroborated by the discovery of the Jungornithidae (apparently swift-like hum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
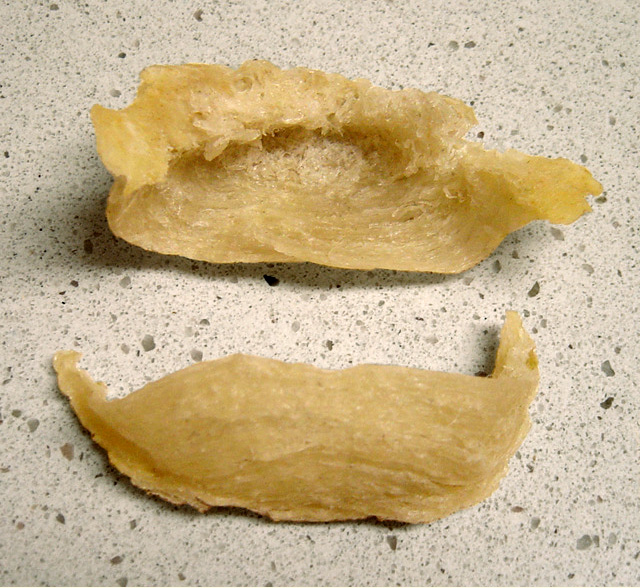
Bird's Nest Soup
Edible bird's nests, also known as swallow nests ( zh, c=燕窝, p=yànwō), are bird nests created from solidified saliva by edible-nest swiftlets, Indian swiftlets and other swiftlets of the genera ''Aerodramus'', '' Hydrochous'', '' Schoutedenapus'' and '' Collocalia'', which are harvested for human consumption. Swiftlet nests have been used as a delicacy for over 400 years, most often as soup. They are particularly prized in Chinese cuisine due to the rarity, high protein content and rich flavor, and are among the most expensive animal products consumed by humans, with prices up to about depending on grading. The type or grading of a swiftlet nest depends on the bird species, as well as the shape and colour of the bird's nest. It is usually white in colour, but there also exists a red version that is sometimes called 'blood nest' ( zh, c=血燕, p=Xuě Yàn). According to traditional Chinese medicine, it promotes good health, especially for the skin. Etymology The Chine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apodidae
The Apodidae, or swifts, form a family of highly aerial birds. They are superficially similar to swallows, but are not closely related to any passerine species. Swifts are placed in the order Apodiformes along with hummingbirds. The treeswifts are closely related to the true swifts, but form a separate family, the Hemiprocnidae. Resemblances between swifts and swallows are due to convergent evolution, reflecting similar life styles based on catching insects in flight. The family name, Apodidae, is derived from the Greek language, Greek ἄπους (''ápous''), meaning "footless", a reference to the small, weak legs of these most aerial of birds.Jobling (2010) pp. 50–51.Kaufman (2001) p. 329. The tradition of depicting swifts without feet continued into the Middle Ages, as seen in the heraldic martlet. Taxonomy Taxonomists have long classified swifts and treeswifts as relatives of the hummingbirds, a judgment corroborated by the discovery of the Jungornithidae (apparently swi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrochous
The giant swiftlet (''Hydrochous gigas''), also known as the waterfall swift, is a species of bird in the swift family, Apodidae. It is the only member of the monotypic genus ''Hydrochous''. It is found in Malaysia, Sumatra and Java, where its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist montane forests and rivers. It is threatened by habitat loss Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss or habitat reduction) occurs when a natural habitat is no longer able to support its native species. The organisms once living there have either moved elsewhere, or are dead, leading to a decrease .... The giant swiftlet has the largest average wingspan of all the swiftlets, at 150 millimeters. It is a fairly large swift that can grow to 16 cm in length. The female weighs 35 to 39 grams, and the male around 37 grams. Unlike other swiftlets, it builds its nest on a flat horizontal surface instead of molding it against a vertical surface with saliva. It is not totally noctur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Echolocation
Echolocation, also called bio sonar, is a biological active sonar used by several animal groups, both in the air and underwater. Echolocating animals emit calls and listen to the Echo (phenomenon) , echoes of those calls that return from various objects near them. They use these echoes to locate and identify the objects. Echolocation is used for animal navigation , navigation, foraging, and predation, hunting prey. Echolocation calls can be Frequency modulation, frequency modulated (FM, varying in pitch during the call) or constant frequency (CF). FM offers precise range discrimination to localize the prey, at the cost of reduced operational range. CF allows both the prey's velocity and its movements to be detected by means of the Doppler effect. FM may be best for close, cluttered environments, while CF may be better in open environments or for hunting while perched. Echolocating animals include mammals, especially odontocetes (toothed whales) and some bat species, and, using s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papuan Swiftlet
The three-toed swiftlet or Papuan swiftlet (''Aerodramus papuensis'', formerly ''Collocalia papuensis'') is a species of swift. It is found in New Guinea New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; , fossilized , also known as Papua or historically ) is the List of islands by area, world's second-largest island, with an area of . Located in Melanesia in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is .... References three-toed swiftlet Birds of New Guinea three-toed swiftlet three-toed swiftlet Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{apodiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black-nest Swiftlet
The black-nest swiftlet (''Aerodramus maximus'') is a species of swift in the family Apodidae. It is found in Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist lowland forest and subtropical or tropical moist montane forest. Its saliva is one of the main sources of edible nests for bird's nest soup Edible bird's nests, also known as swallow nests ( zh, c=燕窝, p=yànwō), are bird nests created from solidified saliva by edible-nest swiftlets, Indian swiftlets and other swiftlets of the genera ''Aerodramus'', '' Hydrochous'', '' Schout .... References black-nest swiftlet Birds of Southeast Asia black-nest swiftlet Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{apodiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oilbird
The oilbird (''Steatornis caripensis''), locally known as the , is a bird species found in the northern areas of South America including the Caribbean island of Trinidad. It is the only living species in the genus ''Steatornis'', the family Steatornithidae, and the order Steatornithiformes. Nesting in colonies in caves, oilbirds are nocturnal feeders on the fruits of the List of plants known as oil palm, oil palm and tropical Lauraceae, laurels. They are the only nocturnal flying fruit-eating birds in the world (the kākāpō, also nocturnal, is flightless). They forage at night, with specially adapted eyesight. However, they navigate by Animal echolocation, echolocation in the same way as bats, one of the few birds to do so. They produce a high-pitched clicking sound of around 2 kHz that is audible to humans. Taxonomy and etymology Oilbirds are related to the nightjars and have sometimes been placed with these in the order (biology), order Caprimulgiformes. However, the ni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight Bird skeleton, skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the common ostrich. There are over 11,000 living species and they are split into 44 Order (biology), orders. More than half are passerine or "perching" birds. Birds have Bird wing, wings whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the Flightless bird, loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemism, endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribe (biology)
In biology, a tribe is a taxonomic rank above genus, but below family and subfamily. It is sometimes subdivided into subtribes. By convention, all taxa ranked above species are capitalized, including both tribe and subtribe. In zoology, the standard ending for the name of a zoological tribe is "-ini". Examples include the tribes Caprini (goat-antelopes), Hominini (hominins), Bombini (bumblebees), and Thunnini (tunas). The tribe Hominini is divided into subtribes by some scientists; subtribe Hominina then comprises "humans". The standard ending for the name of a zoological subtribe is "-ina". In botany, the standard ending for the name of a botanical tribe is "-eae". Examples include the tribes Acalypheae and Hyacintheae. The tribe Hyacintheae is divided into subtribes, including the subtribe Massoniinae. The standard ending for the name of a botanical subtribe is "-inae". In bacteriology, the form of tribe names is as in botany, e.g., Pseudomonadeae, based on the ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |