|
Aerodramus
''Aerodramus'' is a genus of small, dark, cave-nesting birds in the swiftlet, Collocaliini tribe (biology), tribe of the Swift (bird), swift family. Its members are confined to tropical and subtropical regions in southern Asia, Oceania and northeastern Australia. Many of its members were formerly classified in ''Collocalia'', but were first placed in a separate genus by American ornithology, ornithologist Harry Church Oberholser in 1906. This is a taxonomically difficult group of very similar species. Animal echolocation, Echolocation, DNA sequencing and Parasite, parasitic louse, lice have all been used to establish relationships, but some problems, such as the placement of the Papuan swiftlet are not fully resolved. These swiftlets can pose major identification problems where several species occur. What distinguishes ''Aerodramus'' swiftlets from other swifts, and indeed almost all other birds, is their ability to use a simple but effective form of echolocation. This enables t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiftlet
Swiftlets are birds from the four genera ''Aerodramus'', ''Collocalia'', ''Hydrochous'' and ''Schoutedenapus'', which form the tribe (biology), tribe Collocaliini within the swift (bird), swift family (biology), family Apodidae. The group contains around thirty species mostly confined to southern Asia, south Pacific islands, and northeastern Australia, all within the tropical and subtropical regions. They are in many respects typical members of the Apodidae, having narrow wings for fast flight, with a wide gape and small reduced beak surrounded by bristles for catching insects in flight. What distinguishes many but not all species from other swifts and indeed almost all other birdsThe oilbird is a notable exception. The presence of echolocation was formerly used to argue for a close relationship of the Apodiformes and the oilbird, but the actual situation is more complicated. ''See also'': Caprimulgiformes. is their ability to use a simple but effective form of animal echolocation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Himalayan Swiftlet
The Himalayan swiftlet (''Aerodramus brevirostris'') is a small swift. It is a common colonial breeder in the Himalayas and Southeast Asia. Some populations are migratory. This swiftlet was formerly placed in the genus ''Collocalia''. Two of its five subspecies are frequently given full species status, ''A. b. rogersi'' as the Indochinese swiftlet, ''Aerodramus rogersi'', and the isolated Javan form ''A. b. vulcanorum'' as the Volcano swiftlet, ''Aerodramus vulcanorum''. Description This 13–14 cm long swiftlet has swept-back wings that resemble a crescent or a boomerang. The body is slender, and the tail is forked. It is, in many respects, a typical swift, having narrow wings for fast flight, and a wide gape and small beak surrounded by bristles for catching insects in flight. Its legs are very short, preventing the bird from perching, but allowing it to cling to vertical surfaces. It is mainly grey-brown above and paler brown below. It has a pale grey rump and a pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
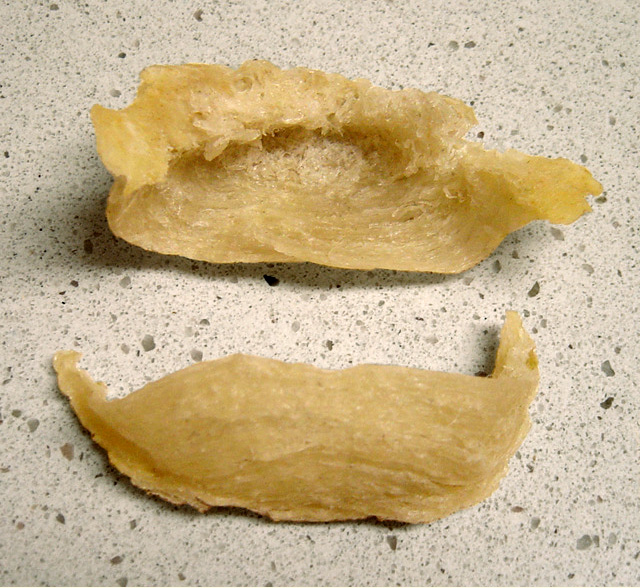
Bird's Nest Soup
Edible bird's nests, also known as swallow nests ( zh, c=燕窝, p=yànwō), are bird nests created from solidified saliva by edible-nest swiftlets, Indian swiftlets and other swiftlets of the genera ''Aerodramus'', '' Hydrochous'', '' Schoutedenapus'' and '' Collocalia'', which are harvested for human consumption. Swiftlet nests have been used as a delicacy for over 400 years, most often as soup. They are particularly prized in Chinese cuisine due to the rarity, high protein content and rich flavor, and are among the most expensive animal products consumed by humans, with prices up to about depending on grading. The type or grading of a swiftlet nest depends on the bird species, as well as the shape and colour of the bird's nest. It is usually white in colour, but there also exists a red version that is sometimes called 'blood nest' ( zh, c=血燕, p=Xuě Yàn). According to traditional Chinese medicine, it promotes good health, especially for the skin. Etymology The Chine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papuan Swiftlet
The three-toed swiftlet or Papuan swiftlet (''Aerodramus papuensis'', formerly ''Collocalia papuensis'') is a species of swift. It is found in New Guinea New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; , fossilized , also known as Papua or historically ) is the List of islands by area, world's second-largest island, with an area of . Located in Melanesia in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is .... References three-toed swiftlet Birds of New Guinea three-toed swiftlet three-toed swiftlet Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{apodiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allan Octavian Hume
Allan Octavian Hume, Order of the Bath, CB Indian Civil Service, ICS (4 June 1829 – 31 July 1912) was a British political reformer, ornithologist, civil servant and botanist who worked in British Raj, British India and was the founding spirit and key founder of the Indian National Congress. He was a proponent of Indian self-rule and strongly supported the idea of Indian independence. He supported the idea of self-governance by Indians. A notable ornithologist, Hume has been called "the Father of Indian Ornithology" and, by those who found him dogmatic, "the Pope of Indian Ornithology". As the collector of Etawah, he saw the Indian Rebellion of 1857 as a result of misgovernance and made great efforts to improve the lives of the common people. The district of Etawah was among the first to be returned to normality and over the next few years Hume's reforms led to the district being considered a model of development. Hume rose in the ranks of the Indian Civil Service (British India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saliva
Saliva (commonly referred as spit or drool) is an extracellular fluid produced and secreted by salivary glands in the mouth. In humans, saliva is around 99% water, plus electrolytes, mucus, white blood cells, epithelial cells (from which DNA can be extracted), enzymes (such as lingual lipase and amylase), and antimicrobial agents (such as secretory IgA, and lysozymes). The enzymes found in saliva are essential in beginning the process of digestion of dietary starches and fats. These enzymes also play a role in breaking down food particles entrapped within dental crevices, thus protecting teeth from bacterial decay. Saliva also performs a lubricating function, wetting food and permitting the initiation of swallowing, and protecting the oral mucosa from drying out. Saliva has specialized purposes for a variety of animal species beyond predigestion. Certain swifts construct nests with their sticky saliva. The foundation of bird's nest soup is an aerodramus nest. Venom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swift (bird)
The Apodidae, or swifts, form a family of highly aerial birds. They are superficially similar to swallows, but are not closely related to any passerine species. Swifts are placed in the order Apodiformes along with hummingbirds. The treeswifts are closely related to the true swifts, but form a separate family, the Hemiprocnidae. Resemblances between swifts and swallows are due to convergent evolution, reflecting similar life styles based on catching insects in flight. The family name, Apodidae, is derived from the Greek ἄπους (''ápous''), meaning "footless", a reference to the small, weak legs of these most aerial of birds.Jobling (2010) pp. 50–51.Kaufman (2001) p. 329. The tradition of depicting swifts without feet continued into the Middle Ages, as seen in the heraldic martlet. Taxonomy Taxonomists have long classified swifts and treeswifts as relatives of the hummingbirds, a judgment corroborated by the discovery of the Jungornithidae (apparently swift-like hum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Echolocation
Echolocation, also called bio sonar, is a biological active sonar used by several animal groups, both in the air and underwater. Echolocating animals emit calls and listen to the Echo (phenomenon) , echoes of those calls that return from various objects near them. They use these echoes to locate and identify the objects. Echolocation is used for animal navigation , navigation, foraging, and predation, hunting prey. Echolocation calls can be Frequency modulation, frequency modulated (FM, varying in pitch during the call) or constant frequency (CF). FM offers precise range discrimination to localize the prey, at the cost of reduced operational range. CF allows both the prey's velocity and its movements to be detected by means of the Doppler effect. FM may be best for close, cluttered environments, while CF may be better in open environments or for hunting while perched. Echolocating animals include mammals, especially odontocetes (toothed whales) and some bat species, and, using s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collocalia
''Collocalia'' is a genus of Swift (bird), swifts, containing some of the smaller species termed "swiftlets". Formerly a catch-all genus for these, a number of its former members are now normally (though not by all authors) placed in ''Aerodramus''. The genus ''Collocalia'' was introduced by the English zoologist George Robert Gray in 1854. The name ''Collocalia'' combines the classical Greek words ''kolla'' meaning "glue" and ''kalia'' for "nest". The genus previously contained fewer species. Seven subspecies of the glossy swiftlet were promoted to species status based on a detailed analysis of the swiftlets in the genus ''Collocalia'' published in 2017. Species Extant The genus now contains the following 11 species: * Plume-toed swiftlet, ''Collocalia affinis'' (formerly treated as a subspecies of the glossy swiftlet) * Grey-rumped swiftlet, ''Collocalia marginata'' (formerly treated as a subspecies of the glossy swiftlet) * Ridgetop swiftlet, ''Collocalia isonota'' (for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Sequencing
DNA sequencing is the process of determining the nucleic acid sequence – the order of nucleotides in DNA. It includes any method or technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases: adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine. The advent of rapid DNA sequencing methods has greatly accelerated biological and medical research and discovery. Knowledge of DNA sequences has become indispensable for basic biological research, Genographic Project, DNA Genographic Projects and in numerous applied fields such as medical diagnosis, biotechnology, forensic biology, virology and biological systematics. Comparing healthy and mutated DNA sequences can diagnose different diseases including various cancers, characterize antibody repertoire, and can be used to guide patient treatment. Having a quick way to sequence DNA allows for faster and more individualized medical care to be administered, and for more organisms to be identified and cataloged. The rapid advancements in DNA seque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasite
Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the Host (biology), host, causing it some harm, and is Adaptation, adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson characterised parasites' way of feeding as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as Armillaria mellea, honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the Orobanchaceae, broomrapes. There are six major parasitic Behavioral ecology#Evolutionarily stable strategy, strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), wikt:trophic, trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louse
Louse (: lice) is the common name for any member of the infraorder Phthiraptera, which contains nearly 5,000 species of wingless parasitic insects. Phthiraptera was previously recognized as an order (biology), order, until a 2021 genetic study determined that they are a highly modified lineage of the order Psocodea, whose members are commonly known as booklice, barklice or barkflies. Lice are obligate parasites, living externally on warm-blooded Host (biology), hosts, which include every species of bird and mammal, except for monotremes, pangolins, and bats. Chewing lice live among the hairs or feathers of their host and feed on skin and debris, whereas sucking lice pierce the host's skin and feed on blood and other secretions. They usually spend their whole life on a single host, cementing their eggs, called Head louse#Eggs/Nits, nits, to hairs or feathers. The eggs hatch into Nymph (biology), nymphs, which moult three times before becoming fully grown, a process that takes a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |