|
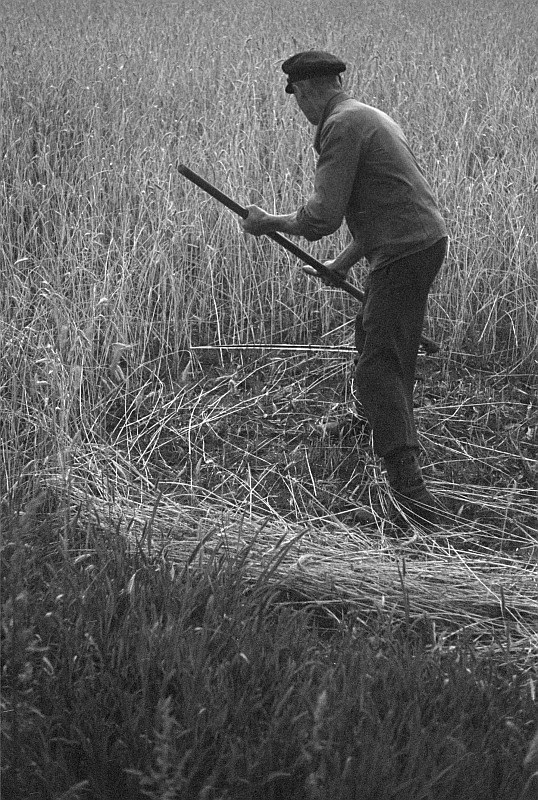
Swath Width
A swathe ( British English, rhymes with "bathe"; or swath American English, rhymes with "cloth") is the strip of cut crop made by a scythe or a mowing-machine. A mower with a scythe cuts a swathe along the mowing-edge leaving the uncut grass to the right and the cut grass laid in a windrow to the left on the previously mown land. The swathe width depends on the blade length, the nature of the crop, and the mower, but for grass is usually about wide. When mowing in a team the mowers start at the edge of a meadow in a staggered line, then proceed clockwise, leaving a series of swathes with windrows and finishing in the middle. The scythe has generally been replaced by machinery, such as a mechanical swather or a combine harvester, which cut much wider swathes while forming windrows. Early in the introduction of machinery, when horses or tractors had to precede a towed cutter, it was still necessary for mowers with scythes to open up a swathe wide enough to take the machine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lidar
Lidar (, also LIDAR, an acronym of "light detection and ranging" or "laser imaging, detection, and ranging") is a method for determining ranging, ranges by targeting an object or a surface with a laser and measuring the time for the reflected light to return to the receiver. Lidar may operate in a fixed direction (e.g., vertical) or it may scan multiple directions, in a special combination of 3-D scanning and laser scanning. Lidar has terrestrial, airborne, and mobile applications. It is commonly used to make high-resolution maps, with applications in surveying, geodesy, geomatics, archaeology, geography, geology, geomorphology, seismology, forestry, atmospheric physics, laser guidance, airborne laser swathe mapping (ALSM), and Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter, laser altimetry. It is used to make digital 3D modeling, 3-D representations of areas on the Earth's surface and ocean bottom of the intertidal and near coastal zone by varying the wavelength of light. It has also been in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agricultural Terminology
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to live in the cities. While humans started gathering grains at least 105,000 years ago, nascent farmers only began planting them around 11,500 years ago. Sheep, goats, pigs, and cattle were domesticated around 10,000 years ago. Plants were independently cultivated in at least 11 regions of the world. In the 20th century, industrial agriculture based on large-scale monocultures came to dominate agricultural output. , small farms produce about one-third of the world's food, but large farms are prevalent. The largest 1% of farms in the world are greater than and operate more than 70% of the world's farmland. Nearly 40% of agricultural land is found on farms larger than . However, five of every six far ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
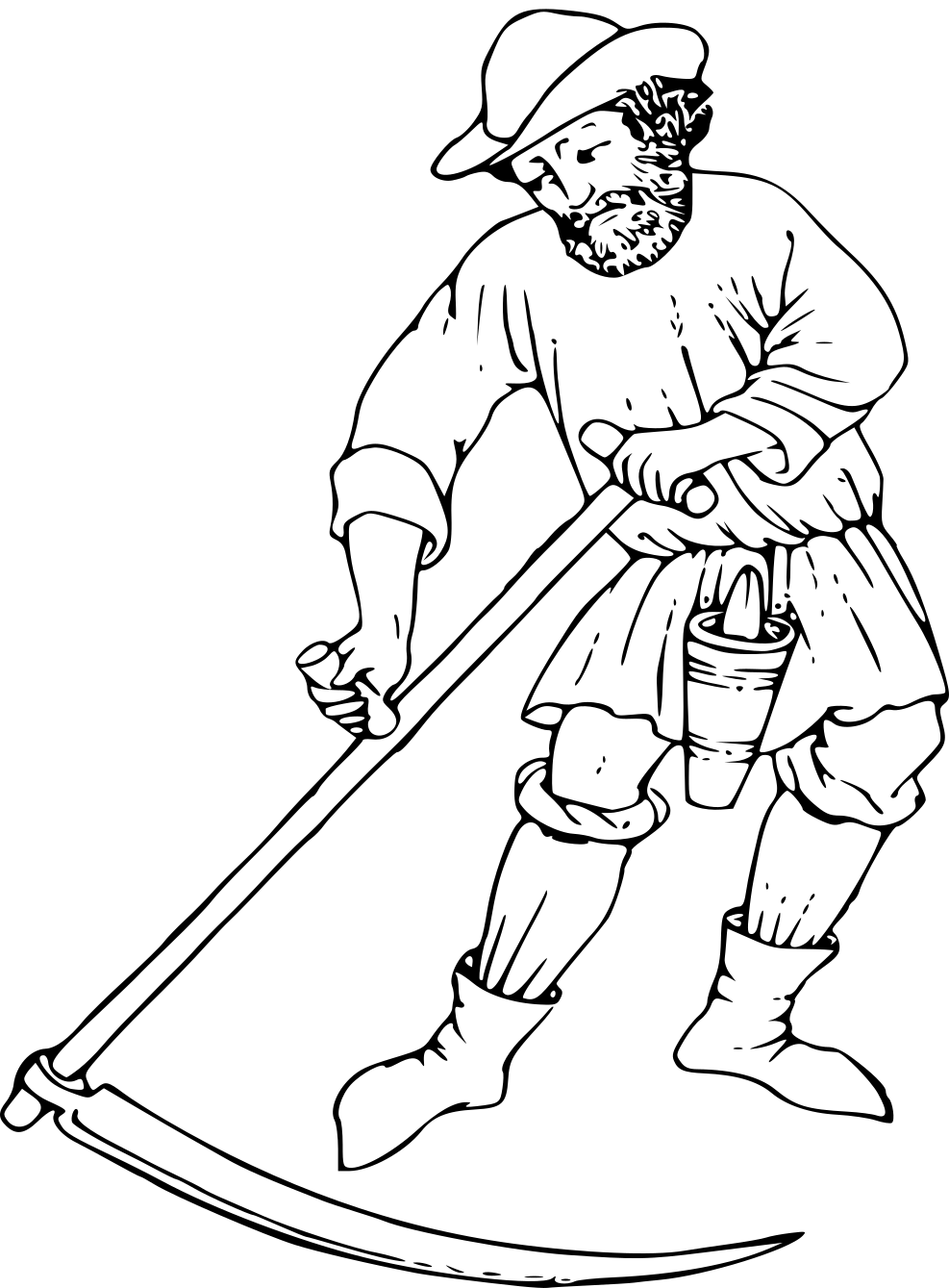
Scythe
A scythe (, rhyming with ''writhe'') is an agriculture, agricultural hand-tool for mowing grass or Harvest, harvesting Crop, crops. It was historically used to cut down or reaping, reap edible grain, grains before they underwent the process of threshing. Horse-drawn and then tractor machinery largely replaced the scythe, but it is still used in some areas of Europe and Asia. Reapers are bladed machines that automate the cutting action of the scythe, and sometimes include subsequent steps in preparing the grain or the straw or hay. The word "scythe" derives from Old English ''siðe''. In Middle English and later, it was usually spelled ''sithe'' or ''sythe''. However, in the 15th century some writers began to use the ''sc-'' spelling as they thought (wrongly) that the word was related to the Latin (meaning "to cut"). Nevertheless, the ''sithe'' spelling lingered, and notably appears in Noah Webster's dictionaries. A scythe consists of a shaft about long called a ''snaith'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combine Harvester
The modern combine harvester, also called a combine, is a machine designed to harvest a variety of cultivated seeds. Combine harvesters are one of the most economically important labour-saving inventions, significantly reducing the fraction of the population engaged in agriculture. Among the crops harvested with a combine are wheat, rice, oats, rye, barley, Maize, corn (maize), sorghum, millet, soybeans, flax (linseed), sunflowers and rapeseed (canola). The separated straw (consisting of stems and any remaining leaves with limited nutrients left in it) is then either chopped onto the field and ploughed back in, or laid out in rows, ready to be Baler, baled and used for bedding and cattle feed. The name of the machine is derived from the fact that the harvester combined multiple separate harvesting operations – Reaper, reaping, threshing or winnowing and gathering – into a single process around the start of the 20th century. A combine harvester still performs its functions ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multibeam Echosounder
A multibeam echosounder (MBES) is a type of sonar that is used to seafloor mapping, map the seabed. It emits acoustic waves in a fan shape beneath its transceiver. The time of flight, time it takes for the sound waves to reflect off the seabed and return to the receiver is used to calculate the water depth. Unlike other sonars and echo sounders, MBES uses beamforming to extract directional information from the returning soundwaves, producing a swathe of depth soundings from a single ping. History and progression Multibeam sonar sounding systems, also known as ''swathe'' (British English) or ''swath'' (American English) , originated for military applications. The concept originated in a radar system that was intended for the Lockheed U-2 high altitude reconnaissance aircraft, but the project was derailed when the aircraft flown by Gary Powers was brought down by a Soviet missile in May 1960. A proposal for using the "Mills Cross" beamforming technique adapted for use with bottom m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sonar
Sonar (sound navigation and ranging or sonic navigation and ranging) is a technique that uses sound propagation (usually underwater, as in submarine navigation) to navigate, measure distances ( ranging), communicate with or detect objects on or under the surface of the water, such as other vessels. "Sonar" can refer to one of two types of technology: ''passive'' sonar means listening for the sound made by vessels; ''active'' sonar means emitting pulses of sounds and listening for echoes. Sonar may be used as a means of acoustic location and of measurement of the echo characteristics of "targets" in the water. Acoustic location in air was used before the introduction of radar. Sonar may also be used for robot navigation, and sodar (an upward-looking in-air sonar) is used for atmospheric investigations. The term ''sonar'' is also used for the equipment used to generate and receive the sound. The acoustic frequencies used in sonar systems vary from very low ( infrasonic) to e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar
Radar is a system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), direction ( azimuth and elevation angles), and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It is a radiodetermination method used to detect and track aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, map weather formations, and terrain. The term ''RADAR'' was coined in 1940 by the United States Navy as an acronym for "radio detection and ranging". The term ''radar'' has since entered English and other languages as an anacronym, a common noun, losing all capitalization. A radar system consists of a transmitter producing electromagnetic waves in the radio or microwave domain, a transmitting antenna, a receiving antenna (often the same antenna is used for transmitting and receiving) and a receiver and processor to determine properties of the objects. Radio waves (pulsed or continuous) from the transmitter reflect off the objects and return to the receiver, giving ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerial Survey
Aerial survey is a method of collecting geomatics or other imagery data using airplanes, helicopters, unmanned aerial vehicle, UAVs, Balloon (aeronautics), balloons, or other aerial methods. Typical data collected includes aerial photography, Lidar, remote sensing (using various visible and invisible bands of the electromagnetic spectrum, such as infrared, gamma ray, gamma, or ultraviolet) and geophysical data (such as aeromagnetic surveys and gravity measurements). It can also refer to a chart or map made by analyzing a region from the air. Aerial survey should be distinguished from satellite imagery technologies because of its better resolution, quality, and resistance to Atmosphere of Earth, atmospheric conditions that can negatively impact and obscure Earth observation satellite, satellite observation. Today, aerial survey is often recognized as a synonym for aerophotogrammetry, a part of photogrammetry where the camera is airborne. Measurements on aerial images are provided b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swather
A swather (North America), or windrower (Australia and rest of world), is a farm implement that cuts hay or small grain crops and forms them into a windrow for drying. They may be self-propelled with an engine, or drawn by a tractor and power take-off powered. A swather uses a reciprocating sickle bar or rotating discs to sever the crop stems. The reel helps cut crop fall neatly onto a canvas or auger conveyor which deposits it into a windrow with stems aligned and supported above the ground by the stubble. A swather does the same task for hay crops as hand scything, cradling and swathing, or mowing and raking. Horizontal rollers behind the cutters may be used to crimp or condition the stems of hay crops to decrease drying time. For grains, as combines replaced threshing machines, the swather introduced an optional step in the harvesting process to provide for the drying time that binding formerly afforded. Swathing is still more common in the northern United Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combine Harvester
The modern combine harvester, also called a combine, is a machine designed to harvest a variety of cultivated seeds. Combine harvesters are one of the most economically important labour-saving inventions, significantly reducing the fraction of the population engaged in agriculture. Among the crops harvested with a combine are wheat, rice, oats, rye, barley, Maize, corn (maize), sorghum, millet, soybeans, flax (linseed), sunflowers and rapeseed (canola). The separated straw (consisting of stems and any remaining leaves with limited nutrients left in it) is then either chopped onto the field and ploughed back in, or laid out in rows, ready to be Baler, baled and used for bedding and cattle feed. The name of the machine is derived from the fact that the harvester combined multiple separate harvesting operations – Reaper, reaping, threshing or winnowing and gathering – into a single process around the start of the 20th century. A combine harvester still performs its functions ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |