|
Swampy Cree Language
Swampy Cree (variously known as Maskekon, Maskegon and Omaškêkowak, and often anglicized as Omushkego) is a variety of the Algonquian language, Cree. It is spoken in a series of Swampy Cree communities in northern Manitoba, central northeast of Saskatchewan along the Saskatchewan River and along the Hudson Bay coast and adjacent inland areas to the south and west, and Ontario along the coast of Hudson Bay and James Bay. Within the group of dialects called "West Cree", it is referred to as an "''n''-dialect", as the variable phoneme common to all Cree dialects appears as "n" in this dialect (as opposed to y, r, l, or ð; all of the phonemes are considered a linguistic reflex of Proto-Algonquian ''*r''). It had approximately 4,500 speakers in a population of 5,000 as of 1982 according to the 14th edition of the ''Ethnologue''. Canadian census data does not identify specific dialects of Cree (all estimates now current rely on extrapolations from specific studies), and currentl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, second-largest country by total area, with the List of countries by length of coastline, world's longest coastline. Its Canada–United States border, border with the United States is the world's longest international land border. The country is characterized by a wide range of both Temperature in Canada, meteorologic and Geography of Canada, geological regions. With Population of Canada, a population of over 41million people, it has widely varying population densities, with the majority residing in List of the largest population centres in Canada, urban areas and large areas of the country being sparsely populated. Canada's capital is Ottawa and List of census metropolitan areas and agglomerations in Canada, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnologue
''Ethnologue: Languages of the World'' is an annual reference publication in print and online that provides statistics and other information on the living languages of the world. It is the world's most comprehensive catalogue of languages. It was first issued in 1951 and is now published by SIL International, an American evangelical Parachurch organization, Christian non-profit organization. Overview and content ''Ethnologue'' has been published by SIL Global (formerly known as the Summer Institute of Linguistics), a Christian linguistics, linguistic service organization with an international office in Dallas, Texas. The organization studies numerous minority languages to facilitate language development, and to work with speakers of such language communities in translating portions of the Bible into their languages. Despite the Christian orientation of its publisher, ''Ethnologue'' is not ideologically or theologically biased. ''Ethnologue'' includes alternative names and Exo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alveolar Consonant
Alveolar consonants (; UK also ) are articulated with the tongue against or close to the superior alveolar ridge, which is called that because it contains the alveoli (the sockets) of the upper teeth. Alveolar consonants may be articulated with the tip of the tongue (the apical consonants), as in English, or with the flat of the tongue just above the tip (the "blade" of the tongue; called laminal consonants), as in French and Spanish. The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) does not have separate symbols for the alveolar consonants. Rather, the same symbol is used for all coronal places of articulation that are not palatalized like English palato-alveolar ''sh'', or retroflex. To disambiguate, the ''bridge'' (, ''etc.'') may be used for a dental consonant, or the under-bar (, ''etc.'') may be used for the postalveolars. differs from dental in that the former is a sibilant and the latter is not. differs from postalveolar in being unpalatalized. The bare letter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bilabial Consonant
In phonetics, a bilabial consonant is a labial consonant articulated with both lips. Frequency Bilabial consonants are very common across languages. Only around 0.7% of the world's languages lack bilabial consonants altogether, including Tlingit, Chipewyan, Oneida, and Wichita, though all of these have a labial–velar approximant /w/. Varieties The bilabial consonants identified by the International Phonetic Alphabet The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) is an alphabetic system of phonetic notation based primarily on the Latin script. It was devised by the International Phonetic Association in the late 19th century as a standard written representation ... (IPA) are: Owere Igbo has a six-way contrast among bilabial stops: . Other varieties The extensions to the IPA also define a () for smacking the lips together. A lip-smack in the non-percussive sense of the lips audibly parting would be . The IPA chart shades out ''bilabial lateral consonants'', wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consonant
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract, except for the h sound, which is pronounced without any stricture in the vocal tract. Examples are and [b], pronounced with the lips; and [d], pronounced with the front of the tongue; and [g], pronounced with the back of the tongue; , pronounced throughout the vocal tract; , [v], , and [z] pronounced by forcing air through a narrow channel (fricatives); and and , which have air flowing through the nose (nasal consonant, nasals). Most consonants are Pulmonic consonant, pulmonic, using air pressure from the lungs to generate a sound. Very few natural languages are non-pulmonic, making use of Ejective consonant, ejectives, Implosive consonant, implosives, and Click consonant, clicks. Contrasting with consonants are vowels. Since the number of speech sounds in the world's languages is much greater than the number of letters in any one alphabet, Linguis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
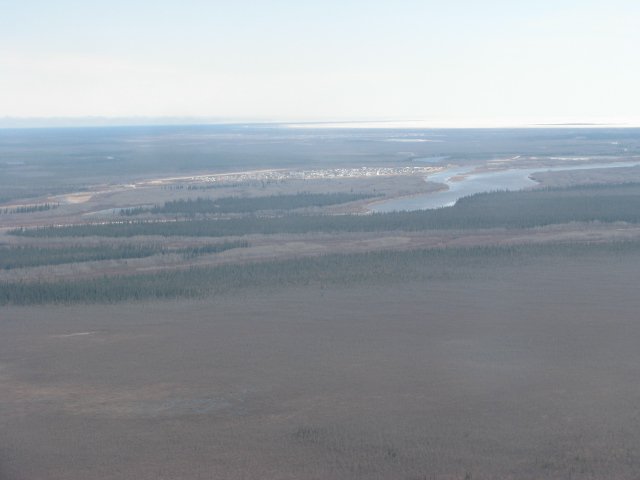
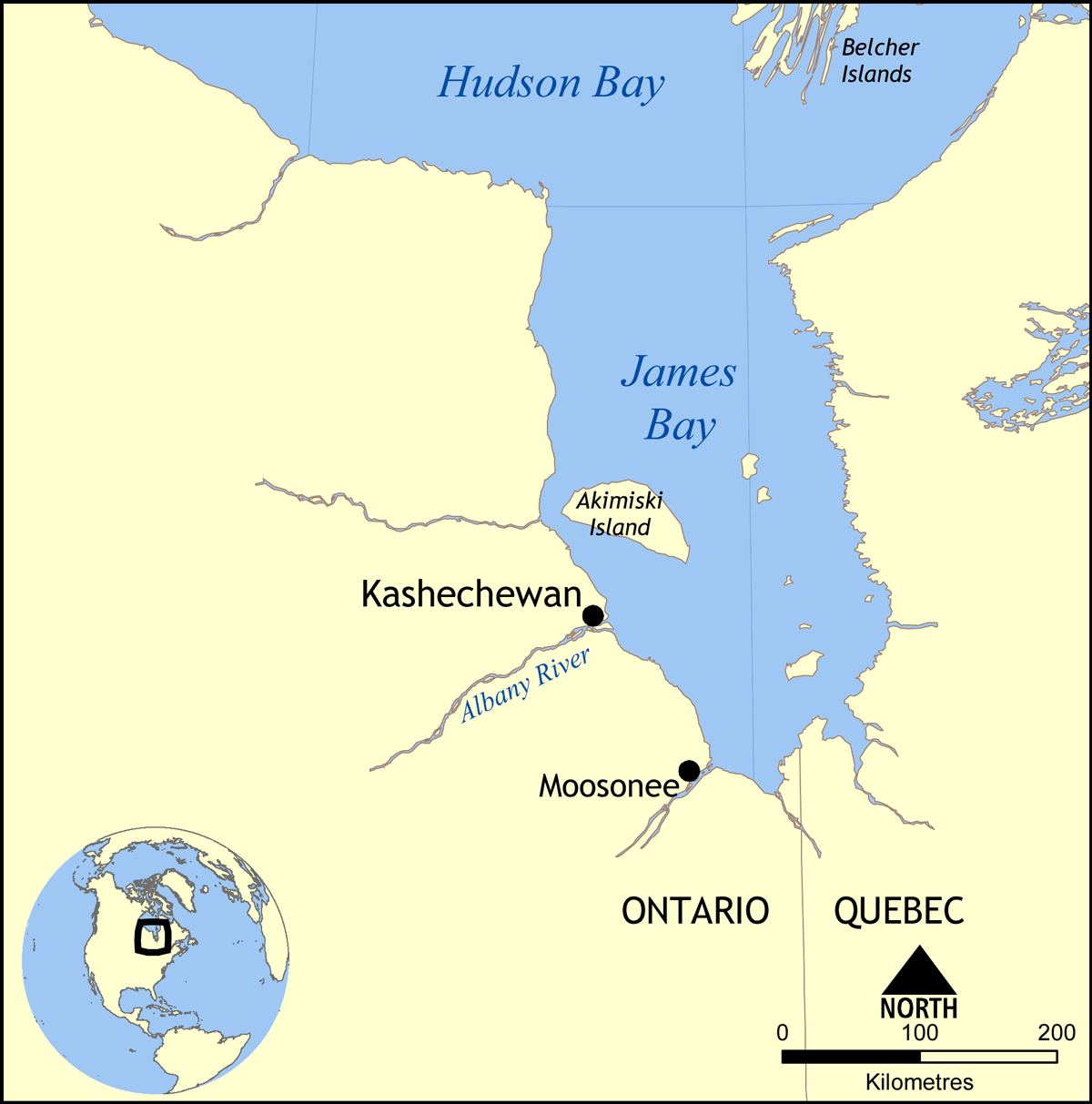
Kashechewan
Kashechewan First Nation, locally known as Kash, is a Cree First Nation located on the northern shore of the Albany River in Northern Ontario, Canada, within territory covered by Treaty 9. The community is located on the west coast of James Bay. Kashechewan came into being when most of the Anglican families of Fort Albany on the south shore of the river moved north in 1958–1961. Kashechewan was granted its own band council under the Indian Act in 1977, though the two still share a reserve, Fort Albany 67. The population was estimated to be about 2,000 as of 2024, according to the CBC, and as of October 2024, the total population of Kashechewan and Fort Albany, which are reported together by CIRNAC, was 5,597. The First Nation was the subject of international media attention due to the discovery of ''E. coli'' in the community's water in October 2005, which brought popular consciousness to the health, housing, and economic crises facing the community. Kashechewan is prone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moose Cree Language
Moose Cree is a dialect of the Cree language spoken mainly in Moose Factory, Ontario. Classification As a dialect of the Cree language, Moose Cree is classified under the Algonquian branch of the Algic language family. Name The term ''Moose Cree'' is derived either from the toponym , meaning 'Moose Island' or , meaning 'Moose River'. The former is the historical name for the summering grounds of the speakers of this dialect, but has been appropriated by the modern municipality of Moosonee, leaving the island with the official English name of Moose Factory, a name that recalls the historical presence of a Hudson's Bay trading post, originally called 'factories'. The above-mentioned hydronym refers to the river where the said island is located. Speakers of the dialect refer to the language as . Official status In Ontario, the Cree language has no official status. Orthography Moose Cree is traditionally written in the Eastern Syllabics, a variant of syllabics used by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Albany, Ontario
Fort Albany First Nation ( , "lagoon Cree") is a Cree First Nation in Cochrane District in Northeastern Ontario, Canada, within the territory covered by Treaty 9. Situated on the southern shore of the Albany River on the west coast of James Bay, Fort Albany First Nation is accessible only by air, water, or by winter road. The First Nation is a signatory of Treaty 9, and is part of the Mushkegowuk Council, within the Nishnawbe Aski Nation. The community is policed by the Nishnawbe-Aski Police Service, an Indigenous police service. It shares band members and the Fort Albany 67 Indian Reserve with the Kashechewan First Nation, which separated from Fort Albany starting in the late 1950s. Fort Albany First Nation is situated on Sinclair and Anderson Islands, as well as on the south shore on the mainland of the river. The Nation controls the Fort Albany Indian Settlement on the south shore of the Albany River, and the Kashechewan First Nation controls the Kashechewan Indian Settl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kashechewan First Nation
Kashechewan First Nation, locally known as Kash, is a Cree First Nation located on the northern shore of the Albany River in Northern Ontario, Canada, within territory covered by Treaty 9. The community is located on the west coast of James Bay. Kashechewan came into being when most of the Anglican families of Fort Albany on the south shore of the river moved north in 1958–1961. Kashechewan was granted its own band council under the Indian Act in 1977, though the two still share a reserve, Fort Albany 67. The population was estimated to be about 2,000 as of 2024, according to the CBC, and as of October 2024, the total population of Kashechewan and Fort Albany, which are reported together by CIRNAC, was 5,597. The First Nation was the subject of international media attention due to the discovery of ''E. coli'' in the community's water in October 2005, which brought popular consciousness to the health, housing, and economic crises facing the community. Kashechewan is prone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attawapiskat First Nation
The Attawapiskat First Nation ( Cree: , "People of the parting of the rocks"; unpointed: ) is an isolated First Nations in Canada, First Nation located in Kenora District in northern Ontario, Canada, at the mouth of the Attawapiskat River on James Bay. The traditional territory of the Attawapiskat First Nation extends beyond their reserve up the coast to Hudson Bay and hundreds of kilometres inland along river tributaries. The community is connected to other towns along the shore of James Bay by the seasonal ice road/winter road constructed each December, linking it to the towns of Kashechewan First Nation, Fort Albany, Ontario, Fort Albany, and Moosonee, Ontario, Moosonee (Minkin 2008:1) Attawapiskat, Fort Albany, and Kashechewan operate and manage the James Bay Winter Road through the jointly owned Kimesskanemenow Corporation, named after the Cree word for "our road" -''kimesskanemenow''. Attawapiskat is the most remote northerly link on the road to Moosonee. They control the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weenusk First Nation
Weenusk First Nation ( (); unpointed: ᐧᐃᓇᐢᑯ ᐃᓂᓂᐧᐊᐠ) is a Cree First Nation band government in the Canadian province of Ontario. In September, 2007, its total registered population was 516. Weenusk First Nation was an independent member of the Nishnawbe Aski Nation (NAN) but now have joined the Mushkegowuk Council, a regional tribal council, who is also a member of NAN. Weenusk First Nation's reserve is the 5310 ha Winisk Indian Reserve 90. Associated with the reserve is their Winisk Indian Settlement also known as Peawanuck, which also holds reserve status. Originally, the Weenusk First Nation was located within their reserve, but they were forced to move southwest to Peawanuck when on May 16, 1986, spring floods swept away much of the original settlement, which had been located upriver from Hudson Bay. In the Cree language, "Peawanuck" means "a place where flint is found," while "Weenusk" means "ground hog." The community, being primarily Swampy Cre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Severn First Nation
Fort Severn First Nation () is a Western Swampy Cree First Nation band government located on the Severn River near Hudson Bay. It is the northernmost community in Ontario, Canada. In 2001, the population was 401, consisting of 90 families in an area of 40 square kilometres. The legal name of the reserve is Fort Severn 89, with the main settlement of Fort Severn (; ). The town is linked by a winter/ ice road called the Wapusk Trail during the winter to Peawanuck, Ontario, in the east, and Shamattawa and Gillam, Manitoba, to the west. Fort Severn is policed by the Nishnawbe-Aski Police Service, an Indigenous-based service. History This area was inhabited for thousands of years by varying cultures of indigenous peoples. At the time of European contact, the historic Swampy Cree, an Algonquian-speaking people, lived in the area. In 1689 the Hudson's Bay Company built Fort Severn at this site, originally naming it Fort James; it was one of the earliest English fur tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |