|
Susan E. Evans
Susan Elizabeth Evans is a British palaeontologist and herpetologist. She is the author or co-author of over 100 peer-reviewed papers and book chapters. She received a BSc in Zoology at Bedford College (London), Bedford College in 1974, and in 1977 a PhD in vertebrate palaeontology from the University College London. In 1980 she was Assistant Professor in biology at the University College of Bahrain and went continued as a lecturer in Anatomy at Middlesex Hospital Medical School. She was also Senior Lecturer with the Department of Anatomy and Developmental Biology at the University College, London In 2003, she became a Professor of Vertebrate Morphology and Palaeontology at University College London. Research Her research focuses on the evolution of key morphological features in lizards, Lissamphibia, amphibians and their extinct relatives. In particular the research focuses on the implications of the above with regards to macroevolution, phylogenetic relationships, function, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeontologist
Paleontology, also spelled as palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of the life of the past, mainly but not exclusively through the study of fossils. Paleontologists use fossils as a means to classify organisms, measure geologic time, and assess the interactions between prehistoric organisms and their natural environment. While paleontological observations are known from at least the 6th century BC, the foundation of paleontology as a science dates back to the work of Georges Cuvier in 1796 in paleontology, 1796. Cuvier demonstrated evidence for the concept of extinction and how life of the past was not necessarily the same as that of the present. The field developed rapidly over the course of the following decades, and the French word ''paléontologie'' was introduced for the study in 1822 in paleontology, 1822, which was derived from the Ancient Greek word for "ancient" and words describing relatedness and a field of study. Further advances in the field accom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linnean Society Of London
The Linnean Society of London is a learned society dedicated to the study and dissemination of information concerning natural history, evolution, and Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy. It possesses several important biological specimen, manuscript and literature collections, and publishes academic journals and books on plant and animal biology. The society also awards a number of prestigious medals and prizes. A product of the Age of Enlightenment, 18th-century enlightenment, the society is the oldest extant biological society in the world and is historically important as the venue for the first public presentation of the theory of evolution by natural selection on 1 July 1858. The patron of the society is Anne, Princess Royal. Honorary members include: King Charles III of the United Kingdom, Emeritus Emperor Akihito of Japan, King Carl XVI Gustaf of Sweden (both of the latter have active interests in natural history), and the eminent naturalist and broadcaster Sir David Attenboroug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alumni Of Bedford College, London
Alumni (: alumnus () or alumna ()) are former students or graduates of a school, college, or university. The feminine plural alumnae is sometimes used for groups of women, and alums (: alum) or alumns (: alumn) as gender-neutral alternatives. The word comes from Latin, meaning nurslings, pupils or foster children, derived from "to nourish". The term is not synonymous with "graduates": people can be alumni without graduating, e.g. Burt Reynolds was an alumnus of Florida State University but did not graduate. The term is sometimes used to refer to former employees, former members of an organization, former contributors, or former inmates. Etymology The Latin noun means "foster son" or "pupil". It is derived from the Latin verb "to nourish". Separate, but from the same root, is the adjective "nourishing", found in the phrase ''alma mater'', a title for a person's home university. Usage in Roman law In Latin, is a legal term (Roman law) to describe a child placed in fosterag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gray's Anatomy
''Gray's Anatomy'' is a reference book of human anatomy written by Henry Gray, illustrated by Henry Vandyke Carter and first published in London in 1858. It has had multiple revised editions, and the current edition, the 42nd (October 2020), remains a standard reference, often considered "the doctors' bible". Earlier editions were called ''Anatomy: Descriptive and Surgical'', ''Anatomy of the Human Body'' and ''Gray's Anatomy: Descriptive and Applied'', but the book's name is commonly shortened to, and later editions are titled, ''Gray's Anatomy''. The book is widely regarded as an extremely influential work on the subject. Publication history Origins The English anatomist Henry Gray was born in 1827. He studied the development of the endocrine glands and spleen and in 1853 was appointed Lecturer on Anatomy at St George's Hospital Medical School in London. In 1855, he approached his colleague Henry Vandyke Carter with his idea to produce an inexpensive and access ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
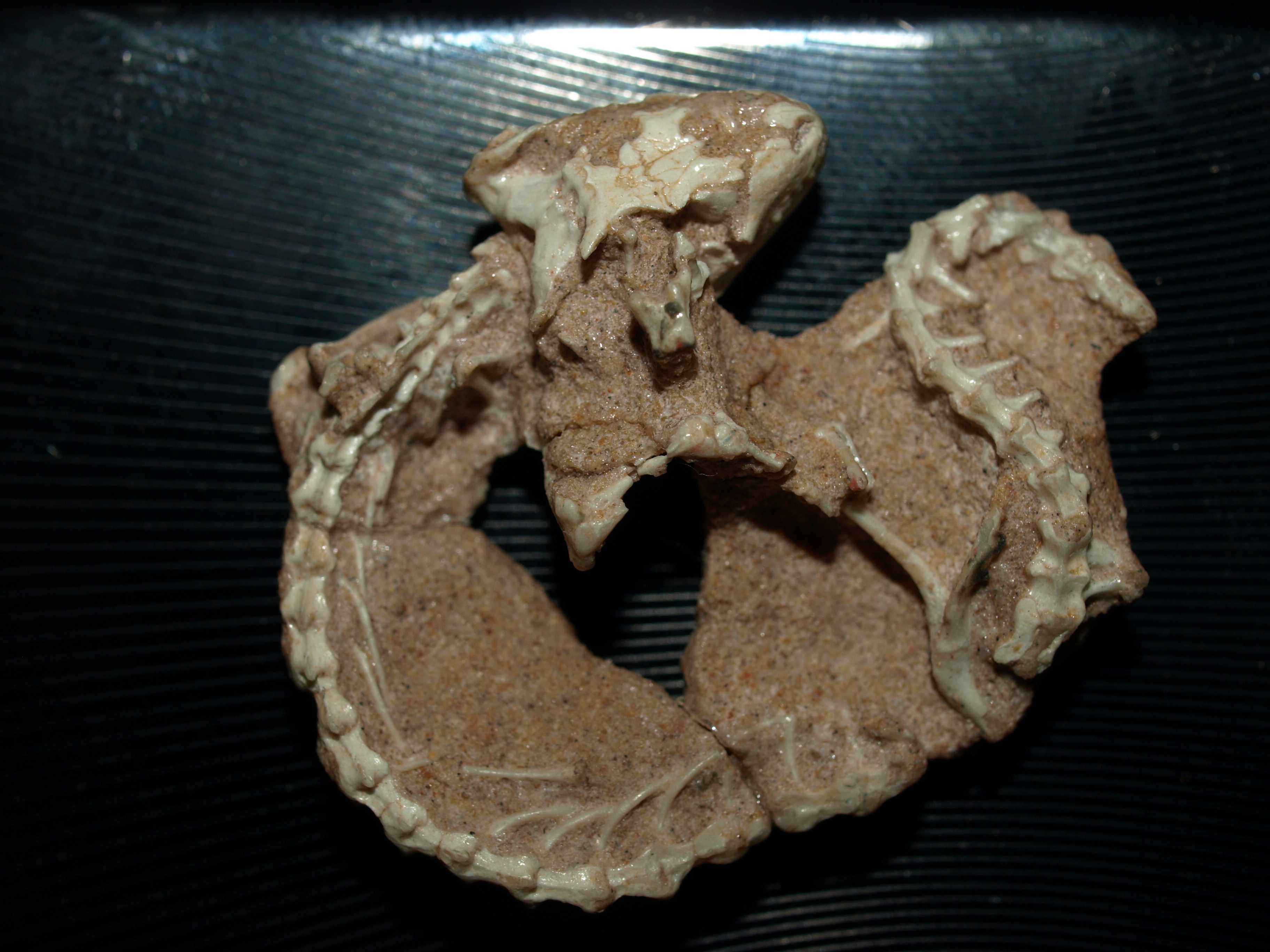
Ceoptera Evansae
''Ceoptera'' (meaning "mist wing") is an extinct genus of darwinopteran pterosaur from the Middle Jurassic Kilmaluag Formation of Scotland. The genus contains a single species, ''C. evansae'', known from a partial skeleton. It is the only pterosaur from Kilmaluag Formation. ''Ceoptera'' represents the second pterosaur named from Scotland, after '' Dearc'' in 2022. Discovery and naming In 2006, a set of rocks with protruding fossilized bones was noticed by a team of palaeontologists on Cladach a’Ghlinne, a beach north of Elgol on the Isle of Skye in Scotland. Fossils of this site are considered to be part of the Kilmaluag Formation, dated to the Middle Jurassic. The site was administered by the Scottish Natural Heritage as a Site of Special Scientific Interest, disallowing the disturbance of rocks on the clifface, and the land was owned by a private trust. However, permission was granted by both parties for collection of the specimen as it had fallen naturally onto the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darwinoptera
Monofenestrata is a clade of pterosaurs. It includes the pterosaurs in which the nasal and antorbital fenestra (openings/holes) in the skull are merged into a single fenestra. The clade includes the pterodactyloids and their close relatives. Classification The clade Monofenestrata was in 2010 defined as the group consisting of ''Pterodactylus'' and all species sharing with ''Pterodactylus'' the synapomorphy of an external nostril confluent with the antorbital fenestra, the major skull opening on the side of the snout. The name is derived from Greek ''monos'', "single", and Latin ''fenestra'', "window". The concept was inspired by the discovery of '' Darwinopterus'', a species combining a pterodactyloid-type skull with a more basal build of the remainder of the body. The Darwinoptera, a primitive subgroup of monofenestratans showing this transitional anatomy, was also named for ''Darwinopterus'' and defined as all descendants of its common ancestor with '' Pterorhynchus''. Belo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clade
In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach to taxonomy adopted by most biological fields. The common ancestor may be an individual, a population, or a species (extinct or Extant taxon, extant). Clades are nested, one in another, as each branch in turn splits into smaller branches. These splits reflect evolutionary history as populations diverged and evolved independently. Clades are termed ''monophyletic'' (Greek: "one clan") groups. Over the last few decades, the cladistic approach has revolutionized biological classification and revealed surprising evolutionary relationships among organisms. Increasingly, taxonomists try to avoid naming Taxon, taxa that are not clades; that is, taxa that are not Monophyly, monophyletic. Some of the relationships between organisms that the molecul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squamata
Squamata (, Latin ''squamatus'', 'scaly, having scales') is the largest Order (biology), order of reptiles; most members of which are commonly known as Lizard, lizards, with the group also including Snake, snakes. With over 11,991 species, it is also the second-largest order of Neontology, extant (living) vertebrates, after the Perciformes, perciform fish. Squamates are distinguished by their skins, which bear horny scale (zoology), scales or shields, and must periodically engage in molting. They also possess movable quadrate bones, making possible movement of the Maxilla, upper jaw relative to the neurocranium. This is particularly visible in snakes, which are able to open their mouths very widely to accommodate comparatively large prey. Squamates are the most variably sized living reptiles, ranging from the Sphaerodactylus ariasae, dwarf gecko (''Sphaerodactylus ariasae'') to the reticulated python (''Malayopython reticulatus''). The now-Extinction, extinct mosasaurs reached ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agamidae
Agamidae is a family containing 582 species in 64 genera of iguanian lizards indigenous to Africa, Asia, Australia, and a few locations in Southern Europe. Many species are commonly called dragons or dragon lizards. Overview Phylogenetically, they may be sister to the Iguanidae, and have similar appearances. Agamids usually have well-developed, strong legs. Their tails cannot be shed and regenerated like those of geckos (and several other families such as skinks), though a certain amount of regeneration is observed in some. Many agamid species are capable of limited change of their colours to regulate their body temperature. In some species, males are more brightly coloured than females, and colours play a part in signaling and reproductive behaviours. Although agamids generally inhabit warm environments, ranging from hot deserts to tropical rainforests, at least one species, the mountain dragon, is found in cooler regions. They are particularly diverse in Australia. This gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biotechnology And Biological Sciences Research Council
Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC), part of UK Research and Innovation, is a non-departmental public body (NDPB), and is the largest UK public funder of non-medical bioscience. It predominantly funds science, scientific research institutes and university research departments in the United Kingdom, UK. Purpose Receiving its funding through the science budget of the Department for Science, Innovation and Technology, BBSRC's mission is to "promote and support, by any means, high-quality basic, strategic and applied research and related postgraduate training relating to the understanding and exploitation of biological systems". Structure BBSRC's head office is at Polaris House in Swindon - the same building as the other councils of United Kingdom Research and Innovation, UK Research and Innovation, Arts and Humanities Research Council, AHRC Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council, EPSRC, Economic and Social Research Council, ESRC, Innovate U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |