|
Surface-guided Radiation Therapy
Surface-guided radiation therapy (SGRT) (sometimes referred to as Surface-image Guided Radiation Therapy) is the process of using 3D imaging to position and track movement of radiation therapy patients during treatment. Goals and clinical benefits SGRT can help to improve the safety, effectiveness and efficiency of radiation therapy treatments, by offering guidance across every step of the radiation therapy workflow, including simulation, planning, treatment and dose visualisation. Developed as an advancement to image-guided radiation therapy, SGRT relies on 3D imaging as opposed to an x-ray. SGRT uses cameras to feed data into a software program linked to the linear accelerator delivering the radiation. Each camera uses a projector and image sensors to create a 3D surface model of a patient, by projecting a red light containing a pseudo-random speckle pattern on their skin. The pattern allows the SGRT system to reference thousands of points on the skin, acting as virtual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy (RT, RTx, or XRT) is a therapy, treatment using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of treatment of cancer, cancer therapy to either kill or control the growth of malignancy, malignant cell (biology), cells. It is normally delivered by a linear particle accelerator. Radiation therapy may be cure, curative in a number of types of cancer if they are localized to one area of the body, and have not metastasis, spread to other parts. It may also be used as part of adjuvant therapy, to prevent tumor recurrence after surgery to remove a primary malignant tumor (for example, early stages of breast cancer). Radiation therapy is synergistic with chemotherapy, and has been used before, during, and after chemotherapy in susceptible cancers. The subspecialty of oncology concerned with radiotherapy is called radiation oncology. A physician who practices in this subspecialty is a radiation oncologist. Radiation therapy is commonly applied to the canc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image-guided Radiation Therapy
Image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT) is the process of frequent imaging, during a course of radiation treatment, used to direct the treatment, position the patient, and compare to the pre-therapy imaging from the treatment plan. Immediately prior to, or during, a treatment fraction, the patient is localized in the treatment room in the same position as planned from the reference imaging dataset. An example of IGRT would include comparison of a cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) dataset, acquired on the treatment machine, with the computed tomography (CT) dataset from planning. IGRT would also include matching planar kilovoltage (kV) radiographs or megavoltage (MV) images with digital reconstructed radiographs (DRRs) from the planning CT. This process is distinct from the use of imaging to delineate targets and organs in the planning process of radiation therapy. However, there is a connection between the imaging processes as IGRT relies directly on the imaging modalities from pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Tattoo
A medical tattoo is a tattoo used to treat a condition, communicate medical information, or mark a body location for treatment. People may get a paramedical tattoo to conceal a condition or the effects of treatment, such as creating the appearance of an areola after breast reconstruction, or a cover-up tattoo to disguise the area in an artistic way. Historical uses Ötzi, a man who lived between 3350 and 3105 BC and whose remains were found near the Austria–Italy border, had tattoos over his joints that may have been part of pain relief treatments similar to acupuncture. A crude practice of corneal tattooing was performed by the Greek physician Galen in 150 CE. He tried to cover leucomatous opacities of the cornea by cauterizing the surface with a heated stilet and applying powdered nutgalls and iron or pulverized pomegranate bark mixed with copper salt. With the rise of Christianity, tattooing declined and eventually became banned by a papal edict in 787 CE. In 1835, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tissue (biology)
In biology, tissue is an assembly of similar cells and their extracellular matrix from the same embryonic origin that together carry out a specific function. Tissues occupy a Biological organisation#Levels, biological organizational level between cell (biology), cells and a complete organ (biology), organ. Accordingly, organs are formed by the functional grouping together of multiple tissues. The English word "tissue" Morphological derivation, derives from the French word "", the past participle of the verb tisser, "to weave". The study of tissues is known as histology or, in connection with disease, as histopathology. Xavier Bichat is considered as the "Father of Histology". Plant histology is Studied Space Shuttle designs, studied in both plant anatomy and Plant physiology, physiology. The classical tools for studying tissues are the Microtome#Applications, paraffin block in which tissue is embedded and then sectioned, the staining, histological stain, and the Microscope, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
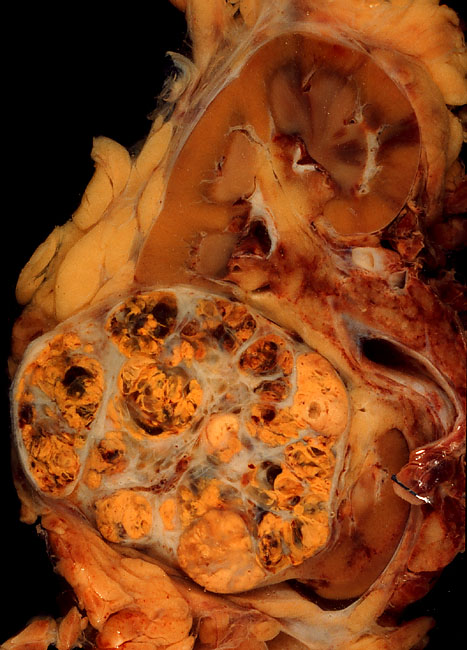
Sarcoma
A sarcoma is a rare type of cancer that arises from cells of mesenchymal origin. Originating from mesenchymal cells means that sarcomas are cancers of connective tissues such as bone, cartilage, muscle, fat, or vascular tissues. Sarcomas are one of five different types of cancer, classified by the cell type from which they originate. While there are five types under this category, sarcomas are most frequently contrasted with carcinomas which are much more common. Sarcomas are quite rare, making up about 1% of all adult cancer diagnoses and 15% of childhood cancer diagnoses. There are many subtypes of sarcoma, which are classified based on the specific tissue and type of cell from which the tumor originates. Common examples of sarcoma include liposarcoma, leiomyosarcoma, and osteosarcoma. Sarcomas are ''primary'' connective tissue tumors, meaning that they arise in connective tissues. This is in contrast to ''secondary'' (or " metastatic") connective tissue tumors, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Inspiration Breath-hold
Deep inspiration breath-hold (DIBH) is a method of delivering radiotherapy while limiting radiation exposure to the heart and lungs. It is used primarily for treating left-sided breast cancer. The technique involves a patient holding their breath during treatment. In DIBH techniques, treatment is only delivered at certain points in the breathing cycle, where the patient holds their breath. Since the relative positions of organs in the chest naturally changes during breathing, this allows treatment to be delivered to the target (tumour) while other organs are in the optimal position to receive least dose. Treatment Methods In the DIBH technique, the patient is initially maintained at quiet tidal breathing (i.e. normal, relaxed breathing), followed by a deep inspiration, a deep expiration, a second deep inspiration, and breath-hold. At this point the patient is at approximately 100% vital capacity, and simulation, verification, and treatment take place during this phase of breat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy
Radiosurgery is surgery using radiation, that is, the destruction of precisely selected areas of tissue using ionizing radiation rather than excision with a blade. Like other forms of radiation therapy (also called radiotherapy), it is usually used to treat cancer. Radiosurgery was originally defined by the Swedish neurosurgeon Lars Leksell as "a single high dose fraction of radiation, stereotactically directed to an intracranial region of interest". In stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS), the word "stereotactic" refers to a three-dimensional coordinate system that enables accurate correlation of a virtual target seen in the patient's diagnostic images with the actual target position in the patient. Stereotactic radiosurgery may also be called stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) or stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR) when used outside the central nervous system (CNS). History Stereotactic radiosurgery was first developed in 1949 by the Swedish neurosurgeon Lars Leksell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereotactic Surgery
Stereotactic surgery is a minimally invasive form of surgery, surgical intervention that makes use of a three-dimensional coordinates, coordinate system to locate small targets inside the body and to perform on them some action such as ablation, biopsy, lesion, injection, Deep brain stimulation, stimulation, implantation, radiosurgery (SRS), etc. In theory, any organ system inside the body can be subjected to stereotactic surgery. However, difficulties in setting up a reliable frame of reference (such as bone landmarks, which bear a constant spatial relation to soft tissues) mean that its applications have been, traditionally and until recently, limited to neurosurgery, brain surgery. Besides the brain, biopsy and surgery of the breast are done routinely to locate, sample (biopsy), and remove tissue. Plain X-ray images (radiography, radiographic mammography), computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging can be used to Image-guided surgery, guide the procedure. Another acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiography
Radiography is an imaging technology, imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical ("diagnostic" radiography and "therapeutic radiography") and industrial radiography. Similar techniques are used in airport security, (where "body scanners" generally use backscatter X-ray). To create an image in conventional radiography, a beam of X-rays is produced by an X-ray generator and it is projected towards the object. A certain amount of the X-rays or other radiation are absorbed by the object, dependent on the object's density and structural composition. The X-rays that pass through the object are captured behind the object by a X-ray detector, detector (either photographic film or a digital detector). The generation of flat two-dimensional images by this technique is called Projection radiography, projectional radiography. In computed tomography (C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treatment Of Cancer
Cancer treatments are a wide range of treatments available for the many different types of cancer, with each cancer type needing its own specific treatment. Treatments can include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormonal therapy (oncology), hormonal therapy, targeted therapy including small-molecule drugs or monoclonal antibodies, and PARP inhibitors such as olaparib. Other therapies include hyperthermia, immunotherapy, photodynamic therapy, and stem-cell therapy. Most commonly cancer treatment involves a series of separate therapies such as chemotherapy before surgery. Angiogenesis inhibitors are sometimes used to enhance the effects of immunotherapies. The choice of therapy depends upon the location and Grading (tumors), grade of the tumor and the Cancer staging, stage of the disease, as well as the performance status, general state of the patient. Cancer biomarker, Biomarker testing can help to determine the type of cancer, and indicate the best therapy. A number of e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiation Therapy Procedures
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or a material medium. This includes: * ''electromagnetic radiation'' consisting of photons, such as radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, x-rays, and gamma radiation (γ) * ''particle radiation'' consisting of particles of non-zero rest energy, such as alpha radiation (α), beta radiation (β), proton radiation and neutron radiation * '' acoustic radiation'', such as ultrasound, sound, and seismic waves, all dependent on a physical transmission medium * ''gravitational radiation'', in the form of gravitational waves, ripples in spacetime Radiation is often categorized as either '' ionizing'' or '' non-ionizing'' depending on the energy of the radiated particles. Ionizing radiation carries more than 10 electron volts (eV), which is enough to ionize atoms and molecules and break chemical bonds. This is an important distinction due to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |