|
Surendra Nath Sehgal
Surendra Nath Sehgal (1932–2003) was an Indian-Canadian-American microbiologist and pharmaceutical scientist most widely known for his discovery and development of ''Rapamycin'' (Sirolimus), a immunosuppressant drug widely used in organ transplantation. Rapamycin has also attracted attention as a potential anti-cancer and anti-aging drug. Early life and education Surendra (Suren) Nath Sehgal, as born in Khushab in pre-partition India (now Pakistan). His father, Sita Ram Sehgal, owned a pharmaceutical factory, but relocated to New Delhi in 1947 after the Partition of India. Sehgal completed a B.Pharm in 1952 and an M.Pharm in 1953 from Banaras Hindu University. At 21, he moved to England to pursue his Ph.D. in Microbiology and Immunology at the University of Bristol, graduating in 1957. Career After completing his Ph.D., Sehgal accepted a postdoctoral fellowship at the National Research Council of Canada. In 1959, he joined Ayerst Research Laboratories in Montreal, becoming ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khushab
Khushab (Punjabi language, punjabi: خُوشاب) is a city as well as a district of Sargodha Division, located in the Punjab (Pakistan), Punjab province of Pakistan. The word ''Khushab'' means "sweet water." Khushab city also serves as the headquarters of Khushab Tehsil, an administrative subdivision of the district Khushab. It is the List of most populous cities in Pakistan, 77th most populous city of Pakistan. The city of Khushab is the location of the Khushab Nuclear Complex, a critical part of Pakistan's Special Weapons Programme. Demographics Population According to 2023 Pakistani census, 2023 census, Khushab had a population of 139,905. The population, according to the 1901 census, was 11,403. Etymology "Khushab" is a combination of two Persian language, Persian words: ''khush'' (), meaning "sweet or tasty", and ''aab'' (), meaning "water". A common belief is that the Persian people, Persians from the west first used the word ''khush-aab'' in admiration of the sweet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptomyces Hygroscopicus
''Streptomyces hygroscopicus'' is a bacterial species in the genus '' Streptomyces''. It was first described by Hans Laurits Jensen in 1931. Biochemistry Cultures of different strains of ''S. hygroscopicus'' can be used to produce several chemical compounds or enzymes. Small molecules Immunosuppressants Sirolimus (also known as rapamycin) is an antifungal and immunosuppressant that has been isolated from ''S. hygroscopicus'' from soil samples from Easter Island. Ascomycin is another immunosuppressant produced by some strains of ''S. hygroscopicus;'' it has a similar structure to sirolimus and can be used to treat autoimmune diseases and skin diseases and can help prevent rejection after an organ transplant. Antibiotics The antibiotics geldanamycin, hygromycin B, nigericin, validamycin, and cyclothiazomycin are found in ''S. hygroscopicus''. Experimental cancer drugs Indolocarbazoles can be found in ''S. hygroscopicus'' . Anthelmintics and insecticides Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Khushab District
The term "the people" refers to the public or Common people, common mass of people of a polity. As such it is a concept of human rights law, international law as well as constitutional law, particularly used for claims of popular sovereignty. In contrast, a people is any plurality of Person, persons considered as a whole. Used in politics and law, the term "a people" refers to the collective or community of an ethnic group or nation. Concepts Legal Chapter One, Article One of the Charter of the United Nations states that "peoples" have the right to self-determination. Though the mere status as peoples and the right to self-determination, as for example in the case of Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples, Indigenous peoples (''peoples'', as in all groups of indigenous people, not merely all indigenous persons as in ''indigenous people''), does not automatically provide for independence, independent sovereignty and therefore secession. Indeed, judge Ivor Jennings i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alumni Of The University Of Bristol
This is a list of University of Bristol people, including a brief description of their notability. This list includes not just former students but persons who are or have been associated with the university, including former academics, Chancellors, and recipients of honorary degrees. Staff and academics Chancellors and Vice-Chancellors Alumni Government and politics United Kingdom International The Law *Alexander Cameron (barrister), Alexander Cameron, English Barrister *Eve Cornwell, YouTuber and former lawyer *Sir Richard Field (judge), Richard Field, English High Court judge (England and Wales), High Court Judge, Academic of University of British Columbia, University of Hong Kong, McGill University * Louisa Ghevaert, British family law lawyer *Brenda Hale, Baroness Hale of Richmond, English judge and first woman to be appointed as the President of the Supreme Court of the United Kingdom, Chancellor of university (2004–2016) * Sir Stephen Laws, British lawyer and civ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banaras Hindu University Alumni
Varanasi (, also Benares, Banaras ) or Kashi, is a city on the Ganges river in northern India that has a central place in the traditions of pilgrimage, death, and mourning in the Hindu world.* * * * The city has a syncretic tradition of Islamic artisanship that underpins its religious tourism.* * * * * Located in the middle-Ganges valley in the southeastern part of the state of Uttar Pradesh, Varanasi lies on the left bank of the river. It is to the southeast of India's capital New Delhi and to the southeast of the state capital, Lucknow. It lies downstream of Prayagraj, where the confluence with the Yamuna river is another major Hindu pilgrimage site. Varanasi is one of the world's oldest continually inhabited cities. Kashi, its ancient name, was associated with a kingdom of the same name of 2,500 years ago. The Lion capital of Ashoka at nearby Sarnath has been interpreted to be a commemoration of the Buddha's first sermon there in the fifth century BCE. In the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Microbiologists
American(s) may refer to: * American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America" ** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America ** American ancestry, people who self-identify their ancestry as "American" ** American English, the set of varieties of the English language native to the United States ** Native Americans in the United States, indigenous peoples of the United States * American, something of, from, or related to the Americas, also known as "America" ** Indigenous peoples of the Americas * American (word), for analysis and history of the meanings in various contexts Organizations * American Airlines, U.S.-based airline headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas * American Athletic Conference, an American college athletic conference * American Recordings (record label), a record label that was previously known as Def American * American University, in Washington, D.C. Sports teams S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Microbiologists
Canadians () are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of their being ''Canadian''. Canada is a multilingual and multicultural society home to people of groups of many different ethnic, religious, and national origins, with the majority of the population made up of Old World immigrants and their descendants. Following the initial period of French and then the much larger British colonization, different waves (or peaks) of immigration and settlement of non-indigenous peoples took place over the course of nearly two centuries and continue today. Elements of Indigenous, French, British, and more recent immigrant customs, languages, and religions have combined to form the culture of Canada, and thus a Canadian identity and Canadian values. Canada has also been strongly influenced by its linguistic, geographic, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Microbiologists
Indian or Indians may refer to: Associated with India * of or related to India ** Indian people ** Indian diaspora ** Languages of India ** Indian English, a dialect of the English language ** Indian cuisine Associated with indigenous peoples of the Americas * Indigenous peoples of the Americas ** First Nations in Canada ** Native Americans in the United States ** Indigenous peoples of the Caribbean ** Indigenous languages of the Americas Places * Indian, West Virginia, U.S. * The Indians, an archipelago of islets in the British Virgin Islands Arts and entertainment Film * ''Indian'' (film series), a Tamil-language film series ** ''Indian'' (1996 film) * ''Indian'' (2001 film), a Hindi-language film Music * Indians (musician), Danish singer Søren Løkke Juul * "The Indian", an unreleased song by Basshunter * "Indian" (song), by Sturm und Drang, 2007 * "Indians" (song), by Anthrax, 1987 * Indians, a song by Gojira from the 2003 album '' The Link'' Other uses i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sirolimus
Sirolimus, also known as rapamycin and sold under the brand name Rapamune among others, is a macrolide compound that is used to coat coronary stents, prevent organ transplant rejection, treat a rare lung disease called lymphangioleiomyomatosis, and treat perivascular epithelioid cell tumour (PEComa). It has immunosuppressant functions in humans and is especially useful in preventing the rejection of kidney transplants. It is a mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) kinase inhibitor that reduces the sensitivity of T cells and B cells to interleukin-2 (IL-2), inhibiting their activity. This compound also has a use in cardiovascular drug-eluting stent technologies to inhibit restenosis. It is produced by the bacterium '' Streptomyces hygroscopicus'' and was isolated for the first time in 1972, from samples of ''Streptomyces hygroscopicus'' found on Easter Island. The compound was originally named rapamycin after the native name of the island, Rapa Nui. Sirolimus was initially deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
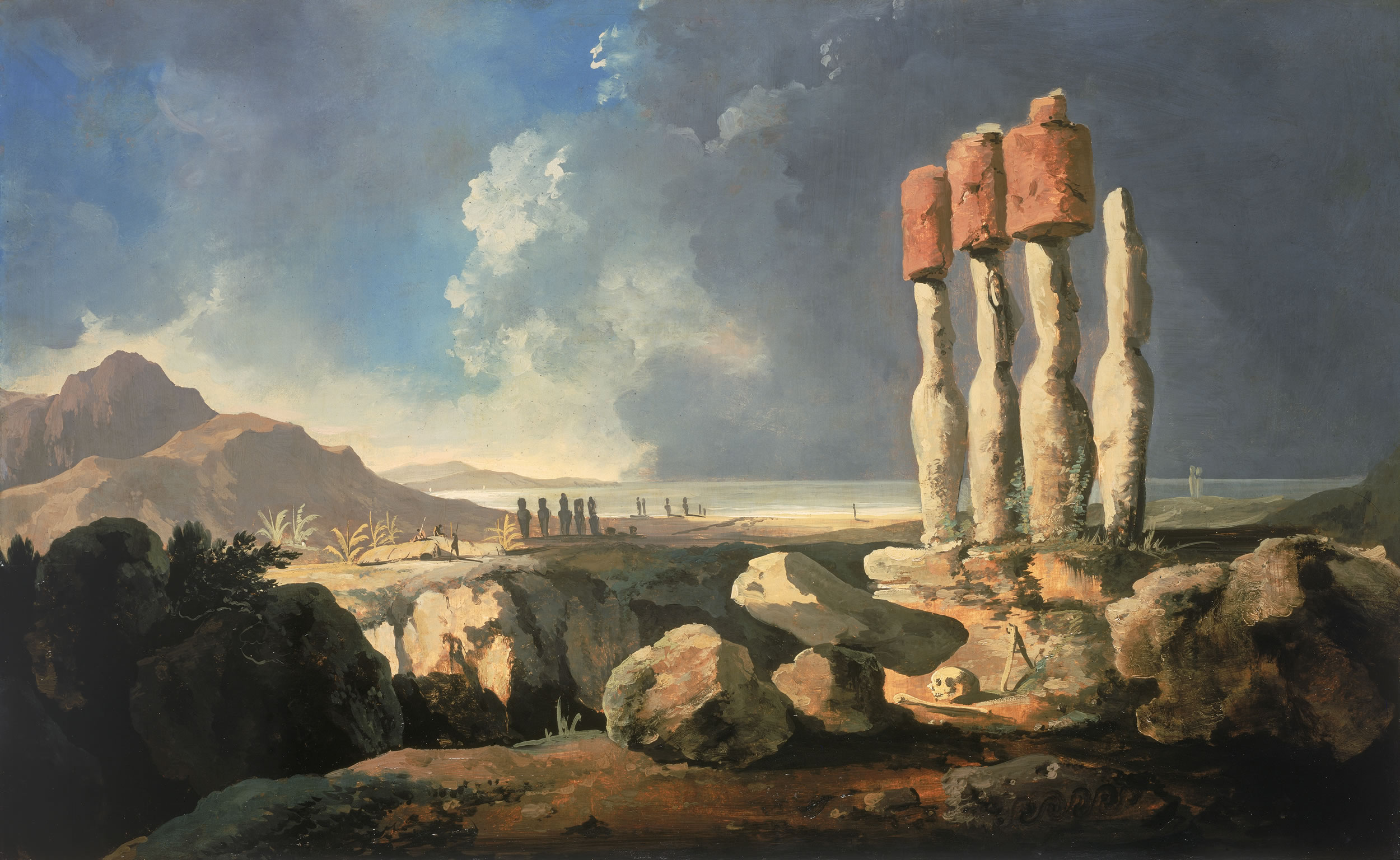
Easter Island
Easter Island (, ; , ) is an island and special territory of Chile in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian Triangle in Oceania. The island is renowned for its nearly 1,000 extant monumental statues, called ''moai'', which were created by the early Rapa Nui people. In 1995, UNESCO named Easter Island a World Heritage Site, with much of the island protected within Rapa Nui National Park. Experts differ on when the island's Polynesian inhabitants first reached the island. While many in the research community cited evidence that they arrived around the year 800, a 2007 study provided compelling evidence suggesting their arrival was closer to 1200. The inhabitants created a thriving and industrious culture, as evidenced by the island's numerous enormous stone ''moai'' and other artifacts. Land clearing for cultivation and the introduction of the Polynesian rat led to gradual deforestation. By the time of European arrival in 1722, the i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
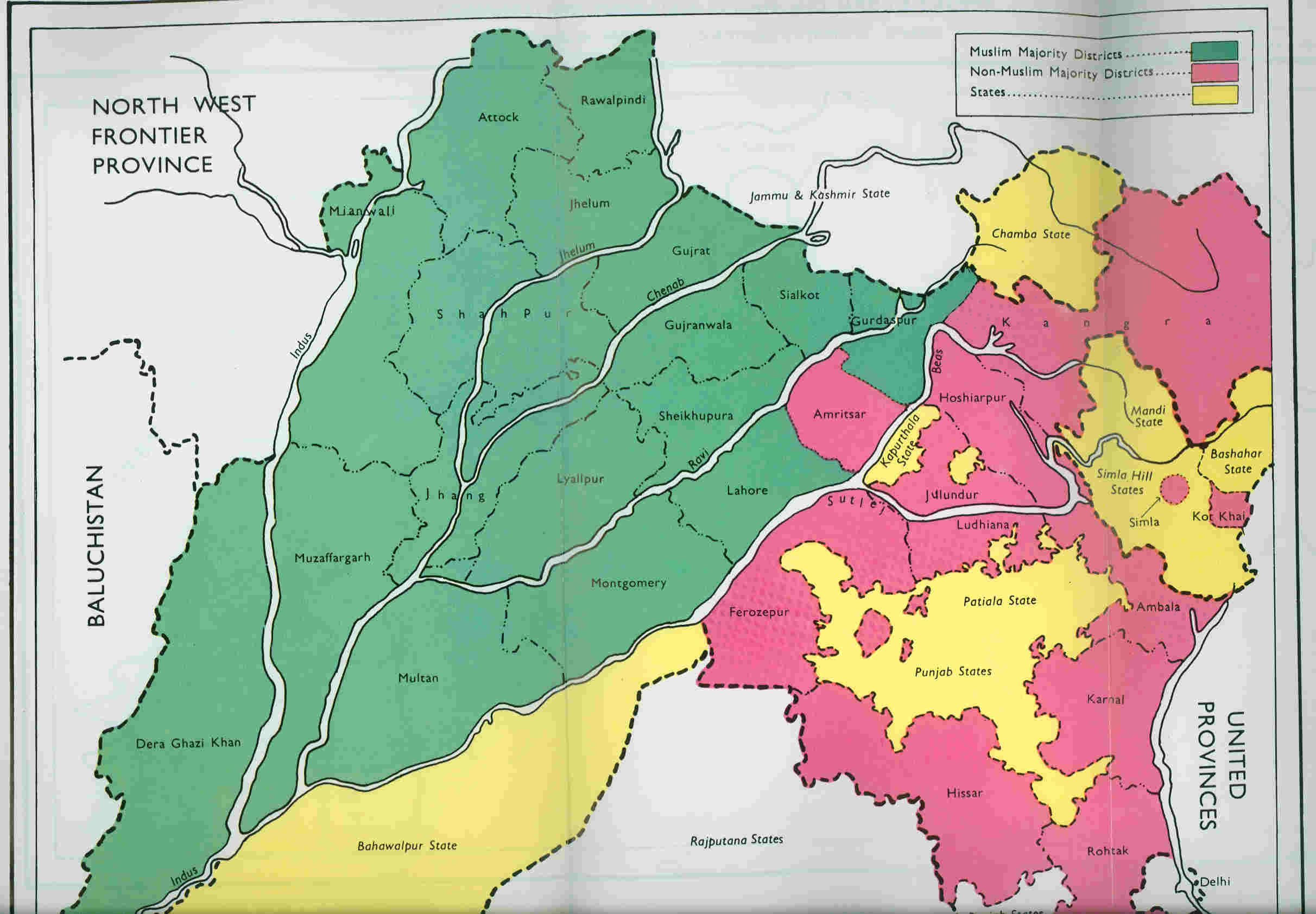
Punjab Province (British India)
The Punjab Province, officially the Province of the Punjab, was a Presidencies and provinces of British India, province of British India, with its capital in Lahore and summer capitals in Murree and Simla. At its greatest extent, it stretched from the Khyber Pass to Delhi; and from the Babusar Pass and the borders of Tibet to the borders of Sind Division, Sind. Established in 1849 following #History, Punjab's annexation, the province was Partition of India#Punjab, partitioned in 1947 into West Punjab, West and East Punjab; and incorporated into Pakistan and India, respectively. Most of the Punjab, Punjab region was annexed by the East India Company on Second Anglo-Sikh War, 29 March 1849 following the company's victory at the Battle of Gujrat, battle of Gujrat in northern Punjab, a month prior. The Punjab was the last major region of the Indian subcontinent to fall to British imperialism. Immediately following its annexation, the Punjab was annexed into the Bengal Presidency a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partition Of India
The partition of India in 1947 was the division of British India into two independent dominion states, the Dominion of India, Union of India and Dominion of Pakistan. The Union of India is today the Republic of India, and the Dominion of Pakistan is the Islamic Republic of Pakistan and the People's Republic of Bangladesh. The Partition (politics), partition involved the division of two provinces, Bengal and the Punjab Province (British India), Punjab, based on district-wise Hindu or Muslim majorities. It also involved the division of the British Indian Army, the Royal Indian Navy, the Indian Civil Service, the History of rail transport in India, railways, and the central treasury, between the two new dominions. The partition was set forth in the Indian Independence Act 1947 and resulted in the dissolution of the British Raj, or Crown rule in India. The two self-governing countries of India and Pakistan legally came into existence at midnight on 14–15 August 1947. The partiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |