|
Supreme Nasal Concha
The supreme nasal concha or highest nasal concha is a nasal concha (turbinate) that occurs in some cases. It is shaped like a seashell and found on the posterosuperior part of the lateral nasal wall.Supreme nasal concha. (n.d.) ''Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing.'' (2012). Retrieved April 16, 2015 fro/ref> It lies on the medial surface of the labyrinth of ethmoid above the superior nasal concha. This makes it the highest of the nasal conchae, and the highest of three on the ethmoid bone. It is often no more than a small, simple crest protruding from the nasal wall. The space below and the fissure lateral to the concha are known as the supreme nasal meatus. It was historically known as Santorini's concha, after Giovanni Domenico Santorini.Supreme nasal concha. (n.d.) ''Medical Eponyms''. (2012). Retrieved April 16, 2015 fro/ref> See also * Nasal concha In anatomy, a nasal concha (; : conchae; ; Latin for 'shell'), also called a nasal turbinate or turbi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethmoid Bone
The ethmoid bone (; from ) is an unpaired bone in the skull that separates the nasal cavity from the brain. It is located at the roof of the nose, between the two orbits. The cubical (cube-shaped) bone is lightweight due to a spongy construction. The ethmoid bone is one of the bones that make up the orbit of the eye. Structure The ethmoid bone is an anterior cranial bone located between the eyes. It contributes to the medial wall of the orbit, the nasal cavity, and the nasal septum. The ethmoid has three parts: cribriform plate, ethmoidal labyrinth, and perpendicular plate. The cribriform plate forms the roof of the nasal cavity and also contributes to formation of the anterior cranial fossa, the ethmoidal labyrinth consists of a large mass on either side of the perpendicular plate, and the perpendicular plate forms the superior two-thirds of the nasal septum. Between the orbital plate and the nasal conchae are the ethmoidal sinuses or ethmoidal air cells, which are a var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
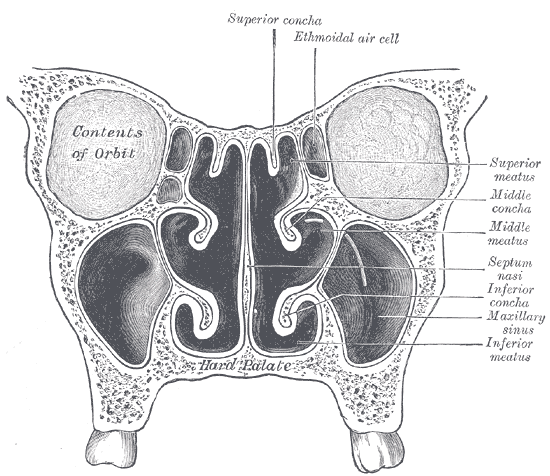
Nasal Concha
In anatomy, a nasal concha (; : conchae; ; Latin for 'shell'), also called a nasal turbinate or turbinal, is a long, narrow, curled shelf of bone tissue, bone that protrudes into the breathing passage of the nose in humans and various other animals. The conchae are shaped like an elongated seashell, which gave them their name (Latin ''concha'' from Greek ''κόγχη''). A concha is any of the scrolled spongy bones of the nasal cavity, nasal passages in vertebrates.''Anatomy of the Human Body'' Gray, Henry (1918) The Nasal Cavity. In humans, the conchae divide the nasal airway into four groove-like air passages, and are responsible for forcing inhaled air to flow in a steady, regular pattern around the largest possible surface area of nasal mucosa. As a cilium, ciliated mucous membrane with shallow blood supply, the nasal mucosa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labyrinth Of Ethmoid
The ethmoidal labyrinth or lateral mass of the ethmoid bone consists of a number of thin-walled cellular cavities, the ethmoid air cells, arranged in three groups, anterior, middle, and posterior, and interposed between two vertical plates of bone; the lateral plate forms part of the orbit, the medial plate forms part of the nasal cavity. In the disarticulated bone many of these cells are opened into, but when the bones are articulated, they are closed in at every part, except where they open into the nasal cavity. Surfaces The upper surface of the labyrinth presents a number of half-broken cells, the walls of which are completed, in the articulated skull, by the edges of the ethmoidal notch of the frontal bone. Crossing this surface are two grooves, converted into two openings by articulation with the frontal; they are the anterior and posterior ethmoidal foramina, and open on the inner wall of the orbit. The posterior surface presents large irregular cellular cavities, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Nasal Concha
The superior nasal concha is a small, curved plate of bone representing a medial bony process of the labyrinth of the ethmoid bone. The superior nasal concha forms the roof of the superior nasal meatus. Anatomy Anatomical relations The superior nasal concha is situated posterosuperiorly to the middle nasal concha. It forms the superior boundary of the superior nasal meatus. Superior to the superior nasal concha is the sphenoethmoidal recess where the sphenoid sinus communicates with the nasal cavity; the sphenoethmoidal recess is interposed between the superior nasal concha, and (the anterior aspect of) the body of sphenoid bone. The sphenoid sinus ostium exists medial to the superior turbinate. See also * Nasal concha In anatomy, a nasal concha (; : conchae; ; Latin for 'shell'), also called a nasal turbinate or turbinal, is a long, narrow, curled shelf of bone tissue, bone that protrudes into the breathing passage of the nose in humans and various other anim ... Add ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethmoid Bone
The ethmoid bone (; from ) is an unpaired bone in the skull that separates the nasal cavity from the brain. It is located at the roof of the nose, between the two orbits. The cubical (cube-shaped) bone is lightweight due to a spongy construction. The ethmoid bone is one of the bones that make up the orbit of the eye. Structure The ethmoid bone is an anterior cranial bone located between the eyes. It contributes to the medial wall of the orbit, the nasal cavity, and the nasal septum. The ethmoid has three parts: cribriform plate, ethmoidal labyrinth, and perpendicular plate. The cribriform plate forms the roof of the nasal cavity and also contributes to formation of the anterior cranial fossa, the ethmoidal labyrinth consists of a large mass on either side of the perpendicular plate, and the perpendicular plate forms the superior two-thirds of the nasal septum. Between the orbital plate and the nasal conchae are the ethmoidal sinuses or ethmoidal air cells, which are a var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasal Meatus
In anatomy, the term nasal meatus can refer to any of the three meatuses (passages) through the skulls nasal cavity: the superior meatus (''meatus nasi superior''), middle meatus (''meatus nasi medius''), and inferior meatus (''meatus nasi inferior''). The nasal meatuses are the spaces beneath each of the corresponding nasal conchae. In the case where a fourth, supreme nasal concha is present, there is a fourth supreme nasal meatus. Structure The superior meatus is the smallest of the three. It is a narrow cavity located obliquely below the superior concha. This meatus is short, lies above and extends from the middle part of the middle concha below. From behind, the sphenopalatine foramen opens into the cavity of the superior meatus and the meatus communicates with the posterior ethmoidal cells. Above and at the back of the superior concha is the sphenoethmoidal recess which the sphenoidal sinus opens into. The superior meatus occupies the middle third of the nasal cavity, nasal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giovanni Domenico Santorini
Giovanni Domenico Santorini (June 6, 1681 – May 7, 1737) was an Italian anatomist. He was a native of Venice, earning his medical doctorate at Pisa in 1701. He is remembered for conducting anatomical dissections of the human body. From 1705 until 1728, Santorini performed anatomical demonstrations in Venice. His best written work was the 1724 publication of ''Observationes anatomicae'', a detailed work involving anatomical aspects of the human body. He is credited for providing descriptions of several anatomical structures, including the following: * Santorini's cartilage: The corniculate cartilage of the larynx. * Santorini's concha: The supreme nasal concha (turbinate).Supreme nasal concha. (n.d.) ''Medical Eponyms''. (2012). Retrieved April 16 2015 fro/ref> * Duct of Santorini: An accessory duct of the pancreas. * Santorini's fissures: Vertical fissures in the anterior part of the cartilage of the external acoustic meatus (ear canal). * Santorini's minor caruncle: Locatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasal Concha
In anatomy, a nasal concha (; : conchae; ; Latin for 'shell'), also called a nasal turbinate or turbinal, is a long, narrow, curled shelf of bone tissue, bone that protrudes into the breathing passage of the nose in humans and various other animals. The conchae are shaped like an elongated seashell, which gave them their name (Latin ''concha'' from Greek ''κόγχη''). A concha is any of the scrolled spongy bones of the nasal cavity, nasal passages in vertebrates.''Anatomy of the Human Body'' Gray, Henry (1918) The Nasal Cavity. In humans, the conchae divide the nasal airway into four groove-like air passages, and are responsible for forcing inhaled air to flow in a steady, regular pattern around the largest possible surface area of nasal mucosa. As a cilium, ciliated mucous membrane with shallow blood supply, the nasal mucosa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |