|
Suprascapular
The suprascapular artery is a branch of the thyrocervical trunk on the neck. Structure At first, it passes downward and laterally across the scalenus anterior and phrenic nerve, being covered by the sternocleidomastoid muscle; it then crosses the subclavian artery and the brachial plexus, running behind and parallel with the clavicle and subclavius muscle and beneath the inferior belly of the omohyoid to the superior border of the scapula. It passes over the superior transverse scapular ligament in most of the cases while below it through the suprascapular notch in some cases. The artery then enters the supraspinous fossa of the scapula. It travels close to the bone, running through the suprascapular canal underneath the supraspinatus muscle, to which it supplies branches. It then descends behind the neck of the scapula, through the great scapular notch and under cover of the inferior transverse ligament, to reach the infraspinatous fossa, where it supplies infraspinatus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suprascapular Notch
The suprascapular notch (or ''scapular notch'') is a notch in the superior border of the scapula, just medial to the base of the coracoid process. It forms the entrance site into the suprascapular canal. Structure This notch is converted into a foramen by the suprascapular ligament, and serves for the passage of the suprascapular nerve; sometimes the ligament is ossified. The suprascapular vessels varies in number as well as in their course as they run at the suprascapular notch site. The suprascapular artery pass above the suprascapular ligament in most cases. The suprascapular vein been found to pass above the suprascapular ligament as well as passing through the suprascapular notch. Types Two main classification systems exists with others being modified approaches of the same principle. Typing based on subjective observation of the suprascapular notch shape. Introduced by and modified by . There are six basic types of scapular notch: * Type I: Notch is absent. The sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
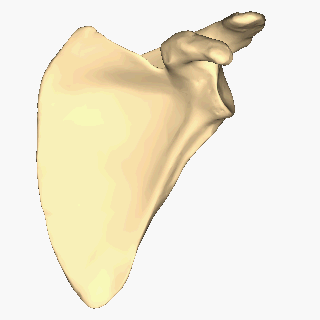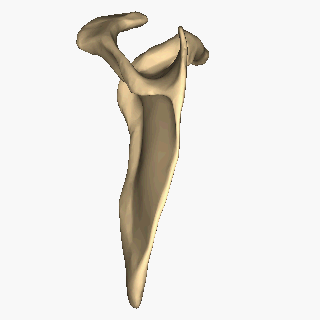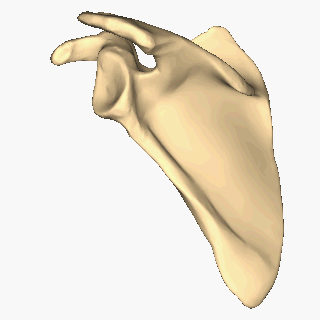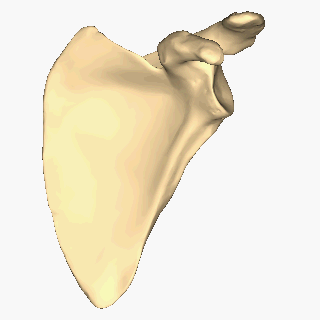
Scapula
The scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on either side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the other. The name derives from the Classical Latin word for trowel or small shovel, which it was thought to resemble. In compound terms, the prefix omo- is used for the shoulder blade in medical terminology. This prefix is derived from ὦμος (ōmos), the Ancient Greek word for shoulder, and is cognate with the Latin , which in Latin signifies either the shoulder or the upper arm bone. The scapula forms the back of the shoulder girdle. In humans, it is a flat bone, roughly triangular in shape, placed on a posterolateral aspect of the thoracic cage. Structure The scapula is a thick, flat bone lying on the thoracic wall that provides an attachment for three groups of muscles: i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neck Of The Scapula
The scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on either side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the other. The name derives from the Classical Latin word for trowel or small shovel, which it was thought to resemble. In compound terms, the prefix omo- is used for the shoulder blade in medical terminology. This prefix is derived from ὦμος (ōmos), the Ancient Greek word for shoulder, and is cognate with the Latin , which in Latin signifies either the shoulder or the upper arm bone. The scapula forms the back of the shoulder girdle. In humans, it is a flat bone, roughly triangular in shape, placed on a posterolateral aspect of the thoracic cage. Structure The scapula is a thick, flat bone lying on the thoracic wall that provides an attachment for three groups of muscles: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suprascapular Vein
The suprascapular vein is a vein running above the scapula. It drains into the external jugular vein. It drains the posterior region around the scapula. Structure The suprascapular vein runs above the scapula. It runs above the anterior coracospinal ligament. It lies close to the suprascapular artery. It drains into the external jugular vein. Variation The course of the suprascapular vein is not very variable. In nearly 20% of people, there may be 2 suprascapular veins lying next to each other. In a very small minority, there may be three. Function The suprascapular vein drains the posterior region around the scapula The scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on eithe .... References External links Nervous system {{circulatory-stub Veins of the head and neck ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suprascapular Canal
The suprascapular canal is an anatomical passage between two openings found on the upper dorsal aspect of the shoulder. It is found bilaterally running on superio-lateral aspect of the dorsal surface of the scapula underneath the supraspinatus muscle. Structure The suprascapular canal is an osteofibrous Canal (anatomy), canal situated in the spinoglenoid fossa conveying suprascapular nerve and vessels. Its passage covered by the Supraspinous fascia, supraspinatus fascia and connects between its entrance formed by the suprascapular notch (enclosed by the suprascapular ligament) and its exit formed by spinoglenoid notch (enclosed by the spinoglenoid ligament). Clinical significance As the suprascapular nerve travels through the suprascapular canal narrow sites, it can potentially get entrapped leading to suprascapular Nerve compression syndrome, nerve entrapment syndrome. The causes have different anatomical implications at each site. The mechanisms varies and range from anatomi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Scapular Notch
The great scapular notch (or ''spinoglenoid notch'') is a notch which serves to connect the supraspinous fossa and infraspinous fossa. It lies immediately medial to the attachment of the acromion to the lateral angle of the scapular spine. The Suprascapular artery and suprascapular nerve pass around the great scapular notch anteroposteriorly. Supraspinatus and infraspinatus are both supplied by the suprascapular nerve, which originates from the superior trunk of the brachial plexus (roots C5-C6). Additional images File:Great scapular notch - animation01.gif, Left scapula. Great scapular notch shown in red. File:Great scapular notch - animation04.gif, Animation. Great scapular notch shown in red. See also * Suprascapular notch * Suprascapular canal The suprascapular canal is an anatomical passage between two openings found on the upper dorsal aspect of the shoulder. It is found bilaterally running on superio-lateral aspect of the dorsal surface of the scapula underne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supraspinous Fossa
The supraspinous fossa (supraspinatus fossa, supraspinatous fossa) of the posterior aspect of the scapula (the shoulder blade) is smaller than the infraspinous fossa, concave, smooth, and broader at its vertebral than at its humeral end. Its medial two-thirds give origin to the Supraspinatus. Structure The fossa can be exposed by the removal of skin and the superficial fascia of the back and the trapezius muscle. The supraspinous fossa is bounded by the spine of scapula on the inferior side, acromion process on the lateral side and the superior angle of scapula on the superior side. Supraspinatus muscle originates from the supraspinous fossa. Distal attachment of the levator scapulae muscle is also on the medial aspect of the fossa. Function The suprascapular artery and nerve are found within the fossa. The posterior branch of the suprascapular artery supplies the supraspinatous muscle. Dorsal scapular artery also gives off a collateral branch and anastomoses with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyrocervical Trunk
The thyrocervical trunk is an artery of the neck. It is a branch of the subclavian artery. It arises from the first portion of this vessel, between the origin of the subclavian artery and the inner border of the scalenus anterior muscle. It is located distally to the vertebral artery and proximally to the costocervical trunk. It gives off a number of branches to the neck. It helps to supply blood to the muscles of the neck. Structure The thyrocervical trunk is a branch of the subclavian artery. It arises from the first portion of this vessel, between the origin of the subclavian artery and the inner border of the scalenus anterior muscle. It is located distally to the vertebral artery and proximally to the costocervical trunk. It is short and thick. Branches The thyrocervical trunk divides soon after its origin into a number of branches. * Inferior thyroid artery. * Suprascapular artery. * Transverse cervical artery. This is present in about 1/3 of cases. In the res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transverse Cervical Artery
The transverse cervical artery (transverse artery of neck or transversa colli artery) is an artery in the neck and a branch of the thyrocervical trunk, running at a higher level than the suprascapular artery. Structure It passes transversely below the inferior belly of the omohyoid muscle to the anterior margin of the trapezius, beneath which it divides into a superficial and a deep branch. It crosses in front of the phrenic nerve and the scalene muscles, and in front of or between the divisions of the brachial plexus, and is covered by the platysma and sternocleidomastoid muscles, and crossed by the omohyoid and trapezius. The transverse cervical artery originates from the thyrocervical trunk, it passes through the posterior triangle of the neck to the anterior border of the levator scapulae muscle, where it divides into deep and superficial branches. * Superficial branch ** Ascending branch ** Descending branch (also known as superficial cervical artery, which supplies th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infraspinatous Fossa
The infraspinous fossa (infraspinatus fossa or infraspinatous fossa) of the scapula is much larger than the supraspinatous fossa; toward its vertebral margin a shallow concavity is seen at its upper part; its center presents a prominent convexity, while near the axillary border is a deep groove which runs from the upper toward the lower part. The medial two-thirds of the fossa give origin to the Infraspinatus; the lateral third is covered by this muscle. Additional images File:Infraspinatus fossa of left scapula- animation.gif, Left scapula. Infraspinatous fossa shown in red. File:Infraspinatus fossa - animation.gif, Animation. Infraspinatous fossa shown in red. File:Infraspinatous fossa of scapula01.png, Still image. File:Gray203.png, Left scapula. Dorsal surface. ("Infra-spinatous" fossa visible at bottom right.) File:Scapula post.jpg, Left scapula. Dorsal surface. Infraspinatous fossa not labeled, but visible at center. File:Infraspinatus muscle back2.png, Infraspi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |