|
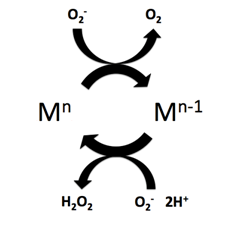
Superoxide Dismutase Mimetics
Superoxide dismutase (SOD) mimetics are synthetic compounds that mimic the native superoxide dismutase enzyme. SOD mimetics effectively convert the superoxide, superoxide anion (O), a reactive oxygen species, into hydrogen peroxide, which is further converted into water by catalase.Baudry, M; Etienne, S; Bruce, A; Palucki, M; Jacobsen, E; Malfroy, B (30 April 1993). "Salen-Manganese Complexes Are Superoxide Dismutase-Mimics". ''Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications'' 192 (2): 964–68. Retrieved 10 January 2015. Reactive oxygen species are natural byproducts of cellular respiration and cause oxidative stress and cell damage, which has been linked to causing cancers, neurodegeneration, age-related declines in health, and inflammatory diseases. SOD mimetics are a prime interest in therapeutic treatment of oxidative stress because of their smaller size, longer half-life, and similarity in function to the native enzyme. The chemical structure of SOD mimetics generally con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superoxide Dismutase
Superoxide dismutase (SOD, ) is an enzyme that alternately catalyzes the dismutation (or partitioning) of the superoxide () radical into ordinary molecular oxygen (O2) and hydrogen peroxide (). Superoxide is produced as a by-product of oxygen metabolism and, if not regulated, causes many types of cell damage. Hydrogen peroxide is also damaging and is degraded by other enzymes such as catalase. Thus, SOD is an important antioxidant defense in nearly all living cells exposed to oxygen. One exception is '' Lactobacillus plantarum'' and related lactobacilli, which use a different mechanism to prevent damage from reactive . Chemical reaction SODs catalyze the disproportionation of superoxide: : 2 HO2 → O2 + H2O2 In this way, is converted into two less damaging species. The pathway by which SOD-catalyzed dismutation of superoxide may be written, for Cu,Zn SOD, with the following reactions: * Cu2+-SOD + → Cu+-SOD + O2 (reduction of copper; oxidation of superoxide) * Cu+-S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porphyrin
Porphyrins ( ) are a group of heterocyclic macrocycle organic compounds, composed of four modified pyrrole subunits interconnected at their α carbon atoms via methine bridges (=CH−). The parent of porphyrin is porphine, a rare chemical compound of exclusively theoretical interest. Substituted porphines are called porphyrins. With a total of 26 π-electrons, of which 18 π-electrons form a planar, continuous cycle, the porphyrin ring structure is often described as aromatic. One result of the large conjugated system is that porphyrins typically absorb strongly in the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum, i.e. they are deeply colored. The name "porphyrin" derives from the Greek word πορφύρα (''porphyra''), meaning ''purple''. Complexes of porphyrins Concomitant with the displacement of two N-''H'' protons, porphyrins bind metal ions in the N4 "pocket". The metal ion usually has a charge of 2+ or 3+. A schematic equation for these syntheses is shown: :H2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Deficit
Cognitive deficit is an inclusive term to describe any characteristic that acts as a barrier to the cognition process. The term may describe * deficits in overall intelligence Intelligence has been defined in many ways: the capacity for abstraction, logic, understanding, self-awareness, learning, emotional knowledge, reasoning, planning, creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving. It can be described as the ... (as with intellectual disabilities), * specific and restricted deficits in cognitive abilities (such as in learning disorders like dyslexia), * neuropsychological deficits (such as in attention, working memory or executive function), * or it may describe drug-induced impairment in cognition and memory (such as that seen with alcohol, glucocorticoids, and the benzodiazepines.) Cause It usually refers to a durable characteristic, as opposed to altered level of consciousness, which may be acute and reversible. Cognitive deficits may be inborn or cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitochondrion
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used throughout the cell as a source of chemical energy. They were discovered by Albert von Kölliker in 1857 in the voluntary muscles of insects. The term ''mitochondrion'' was coined by Carl Benda in 1898. The mitochondrion is popularly nicknamed the "powerhouse of the cell", a phrase coined by Philip Siekevitz in a 1957 article of the same name. Some cells in some multicellular organisms lack mitochondria (for example, mature mammalian red blood cells). A large number of unicellular organisms, such as microsporidia, parabasalids and diplomonads, have reduced or transformed their mitochondria into other structures. One eukaryote, '' Monocercomonoides'', is known to have completely lost its mitochondria, and one multicellular organ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SOD2
Superoxide dismutase 2, mitochondrial (SOD2), also known as manganese-dependent superoxide dismutase (MnSOD), is an enzyme which in humans is encoded by the ''SOD2'' gene on chromosome 6. A related pseudogene has been identified on chromosome 1. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. This gene is a member of the iron/manganese superoxide dismutase family. It encodes a mitochondrial protein that forms a homotetramer and binds one manganese ion per subunit. This protein binds to the superoxide byproducts of oxidative phosphorylation and converts them to hydrogen peroxide and diatomic oxygen. Mutations in this gene have been associated with idiopathic cardiomyopathy (IDC), premature aging, sporadic motor neuron disease, and cancer. Structure The ''SOD2'' gene contains five exons interrupted by four introns, an uncharacteristic 5′-proximal promoter that possesses a GC-rich region in place of the TATA or CAAT, and an enhancer in the second ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caenorhabditis Elegans
''Caenorhabditis elegans'' () is a free-living transparent nematode about 1 mm in length that lives in temperate soil environments. It is the type species of its genus. The name is a blend of the Greek ''caeno-'' (recent), ''rhabditis'' (rod-like) and Latin ''elegans'' (elegant). In 1900, Maupas initially named it ''Rhabditides elegans.'' Osche placed it in the subgenus ''Caenorhabditis'' in 1952, and in 1955, Dougherty raised ''Caenorhabditis'' to the status of genus. ''C. elegans'' is an unsegmented pseudocoelomate and lacks respiratory or circulatory systems. Most of these nematodes are hermaphrodites and a few are males. Males have specialised tails for mating that include spicules. In 1963, Sydney Brenner proposed research into ''C. elegans,'' primarily in the area of neuronal development. In 1974, he began research into the molecular and developmental biology of ''C. elegans'', which has since been extensively used as a model organism. It was the first multice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nematode
The nematodes ( or grc-gre, Νηματώδη; la, Nematoda) or roundworms constitute the phylum Nematoda (also called Nemathelminthes), with plant- parasitic nematodes also known as eelworms. They are a diverse animal phylum inhabiting a broad range of environments. Less formally, they are categorized as Helminths, but are taxonomically classified along with arthropods, tardigrades and other moulting animals in the clade Ecdysozoa, and unlike flatworms, have tubular digestive systems with openings at both ends. Like tardigrades, they have a reduced number of Hox genes, but their sister phylum Nematomorpha has kept the ancestral protostome Hox genotype, which shows that the reduction has occurred within the nematode phylum. Nematode species can be difficult to distinguish from one another. Consequently, estimates of the number of nematode species described to date vary by author and may change rapidly over time. A 2013 survey of animal biodiversity published in the mega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salen Ligand
Salen refers to a tetradentate C2-symmetric ligand synthesized from salicylaldehyde (sal) and ethylenediamine (en). It may also refer to a class of compounds, which are structurally related to the classical salen ligand, primarily bis- Schiff bases. Salen ligands are notable for coordinating a wide range of different metals, which they can often stabilise in various oxidation states. For this reason salen-type compounds are used as metal deactivators. Metal salen complexes also find use as catalysts. Synthesis and properties H2salen may be synthesized by the condensation of ethylenediamine and salicylaldehyde. : Complexes of salen with metal cations may be made without isolating it from the reaction mixture. This is possible because the stability constant for the formation of the metal complexes are very high, due to the chelate effect. :H2L + Mn+ → ML(n−2)+ + 2 H+ where L stands for the ligand. The pyridine adduct of the cobalt(II) complex Co(salen)(py) ( salcomi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotating Model Of M40401 Edit
Rotation, or spin, is the circular movement of an object around a '' central axis''. A two-dimensional rotating object has only one possible central axis and can rotate in either a clockwise or counterclockwise direction. A three-dimensional object has an infinite number of possible central axes and rotational directions. If the rotation axis passes internally through the body's own center of mass, then the body is said to be ''autorotating'' or ''spinning'', and the surface intersection of the axis can be called a '' pole''. A rotation around a completely external axis, e.g. the planet Earth around the Sun, is called ''revolving'' or ''orbiting'', typically when it is produced by gravity, and the ends of the rotation axis can be called the ''orbital poles''. Mathematics Mathematically, a rotation is a rigid body movement which, unlike a translation, keeps a point fixed. This definition applies to rotations within both two and three dimensions (in a plane and in space ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitric Oxide
Nitric oxide (nitrogen oxide or nitrogen monoxide) is a colorless gas with the formula . It is one of the principal oxides of nitrogen. Nitric oxide is a free radical: it has an unpaired electron, which is sometimes denoted by a dot in its chemical formula (•N=O or •NO). Nitric oxide is also a heteronuclear diatomic molecule, a class of molecules whose study spawned early modern theories of chemical bonding. An important intermediate in industrial chemistry, nitric oxide forms in combustion systems and can be generated by lightning in thunderstorms. In mammals, including humans, nitric oxide is a signaling molecule in many physiological and pathological processes. It was proclaimed the "Molecule of the Year" in 1992. The 1998 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was awarded for discovering nitric oxide's role as a cardiovascular signalling molecule. Nitric oxide should not be confused with nitrogen dioxide (NO2), a brown gas and major air pollutant, or with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peroxynitrite
Peroxynitrite (sometimes called peroxonitrite) is an ion with the formula ONOO−. It is a structural isomer of nitrate, Preparation Peroxynitrite can be prepared by the reaction of superoxide with nitric oxide: : It is prepared by the reaction of hydrogen peroxide with nitrite: : H2O2 + → ONOO− + H2O Its presence is indicated by the absorbance at 302 nm (pH 12, ''ε''302 = 1670 M−1 cm−1). Reactions Peroxynitrite is weakly basic with a p''K''a of ~6.8. It is reactive toward DNA and proteins. ONOO− reacts nucleophilically with carbon dioxide. ''In vivo'', the concentration of carbon dioxide is about 1 mM, and its reaction with ONOO− occurs quickly. Thus, under physiological conditions, the reaction of ONOO− with carbon dioxide to form nitrosoperoxycarbonate () is by far the predominant pathway for ONOO−. homolyzes to form carbonate radical and nitrogen dioxide, again as a pair of caged radicals. Approximately 66 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytotoxicity
Cytotoxicity is the quality of being toxic to cells. Examples of toxic agents are an immune cell or some types of venom, e.g. from the puff adder (''Bitis arietans'') or brown recluse spider (''Loxosceles reclusa''). Cell physiology Treating cells with the cytotoxic compound can result in a variety of cell fates. The cells may undergo necrosis, in which they lose membrane integrity and die rapidly as a result of cell lysis. The cells can stop actively growing and dividing (a decrease in cell viability), or the cells can activate a genetic program of controlled cell death (apoptosis). Cells undergoing necrosis typically exhibit rapid swelling, lose membrane integrity, shut down metabolism, and release their contents into the environment. Cells that undergo rapid necrosis in vitro do not have sufficient time or energy to activate apoptotic machinery and will not express apoptotic markers. Apoptosis is characterized by well defined cytological and molecular events including a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |