|
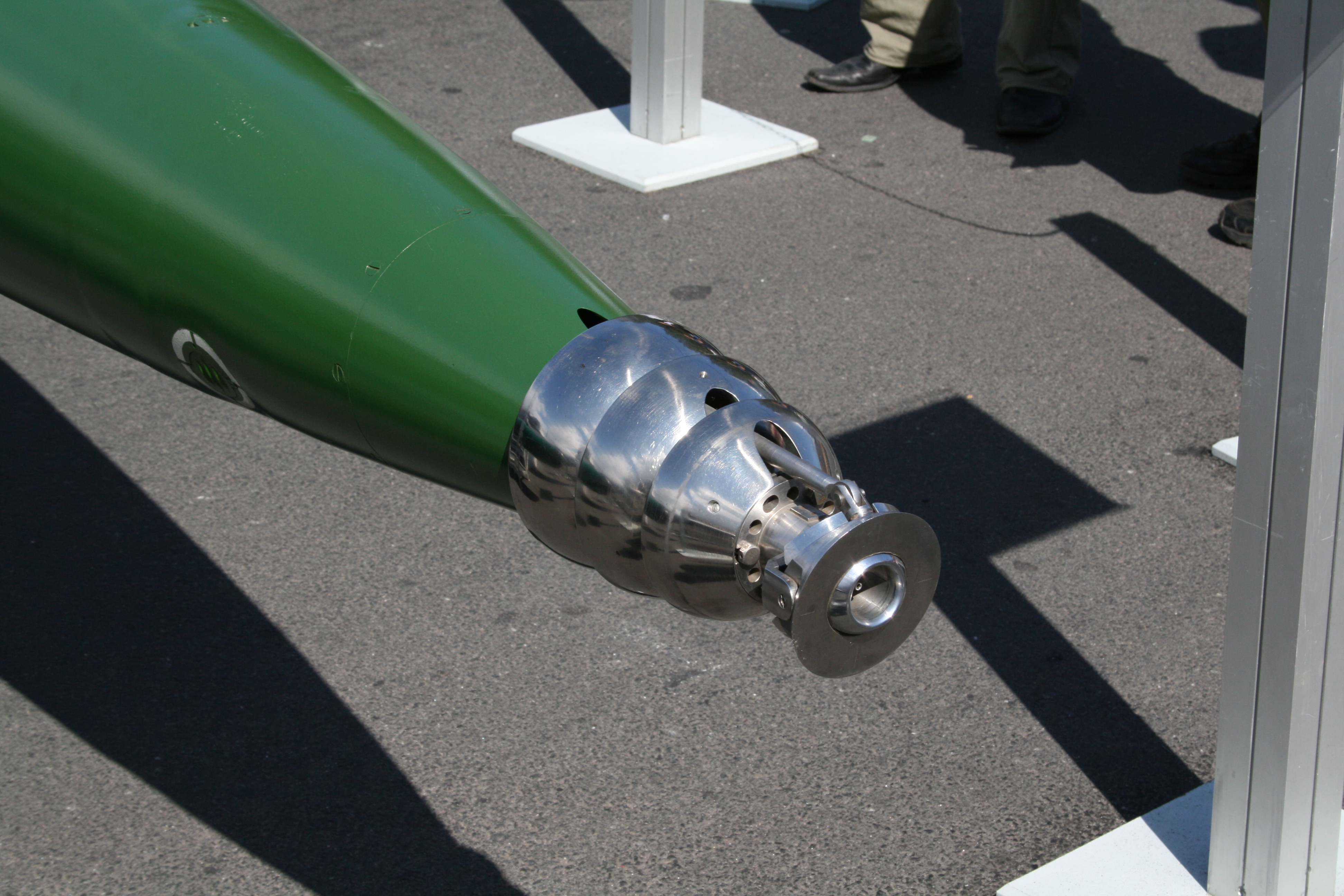
Supercavitation
Supercavitation is the phenomenon of a cavitation bubble reducing skin friction drag on a submerged object and enabling high speeds. Applications include torpedoes and propellers, but in theory, the technique could be extended to an entire underwater vessel. Physical principle Cavitation is the formation of vapour bubbles in liquid caused by flow around an object. Bubbles form when water accelerates around sharp corners and the pressure drops below the vapour pressure. Pressure increases upon deceleration, and the water generally reabsorbs the vapour; however, vapour bubbles can implode and apply small concentrated impulses that may damage surfaces like ship propellers and pump impellers. The potential for vapour bubbles to form in a liquid is given by the nondimensional cavitation number. It equals local pressure minus vapour pressure, divided by dynamic pressure. At increasing depths (or pressures in piping), the potential for cavitation is lower because the difference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cavitation
Cavitation in fluid mechanics and engineering normally is the phenomenon in which the static pressure of a liquid reduces to below the liquid's vapor pressure, leading to the formation of small vapor-filled cavities in the liquid. When subjected to higher pressure, these cavities, called "bubbles" or "voids", collapse and can generate shock waves that may damage machinery. These shock waves are strong when they are very close to the imploded bubble, but rapidly weaken as they propagate away from the implosion. Cavitation is a significant cause of wear in some engineering contexts. Collapsing voids that implode near to a metal surface cause cyclic stress through repeated implosion. This results in surface fatigue of the metal, causing a type of wear also called "cavitation". The most common examples of this kind of wear are to pump impellers, and bends where a sudden change in the direction of liquid occurs. Cavitation is usually divided into two classes of behavior. ''In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torpedo
A modern torpedo is an underwater ranged weapon launched above or below the water surface, self-propelled towards a target, with an explosive warhead designed to detonate either on contact with or in proximity to the target. Historically, such a device was called an automotive, automobile, locomotive, or fish torpedo; colloquially, a ''fish''. The term ''torpedo'' originally applied to a variety of devices, most of which would today be called mines. From about 1900, ''torpedo'' has been used strictly to designate a self-propelled underwater explosive device. While the 19th-century battleship had evolved primarily with a view to engagements between armored warships with large-caliber guns, the invention and refinement of torpedoes from the 1860s onwards allowed small torpedo boats and other lighter surface vessels, submarines/submersibles, even improvised fishing boats or frogmen, and later light aircraft, to destroy large ships without the need of large guns, though somet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Supercavitating Torpedoes
A supercavitating torpedo is a torpedo using the effect of supercavitation to create a bubble (physics), bubble around the torpedo to move at high velocity under water. Super cavitation has many variables, though. If the air stream is unstable, the torpedo could lose balance. The idea is to reduce drag on the torpedo while it sails underwater. This would make the speed greater and therefore the force of impact greater. The following is a list of supercavitating torpedoes which have been developed or are in development. * VA-111 Shkval, 1977 * Hoot (torpedo), Hoot, believed to be reverse-engineered from the VA-111 Shkval, 2006 * Superkavitierender Unterwasserlaufkörper (Supercavitating underwater-travelling munition) Barracuda, 2005 prototype * Unnamed prototype, mentioned 2004 * Supercavitating underwater vehicle, being developed by the Agency for Defense Development, ADD, undergoing trials since 2025 DARPA also considered building supercavitating minisubs dubbed "Underwater ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superkavitierender Unterwasserlaufkörper
The Superkavitierender Unterwasserlaufkörper (lit. ''Supercavitating Underwater Running Body,'' formerly known as Barracuda) was a German close-range supercavitating torpedo technology demonstrator designed by the ''Diehl BGT Defence'' (now '' Diehl Defence'') and developed in cooperation with the German Navy. The supercavitating torpedo for a "close-range defense of underwater targets" was presented to the public in 2005 as a prototype, but it never went into development and procurement. This form of torpedo solves the problem of high underwater drag by means of the supercavitation effect, where underwater at a velocity of around a cavity filled with steam surrounds the moving object. Only the tip is in contact with the water, as such the frictional resistance is greatly reduced. The propulsion of such a torpedo can no longer be done by a propeller but requires a rocket engine. Guidance is based on an inertial measurement unit (IMU) and a sonar antenna array integrated into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
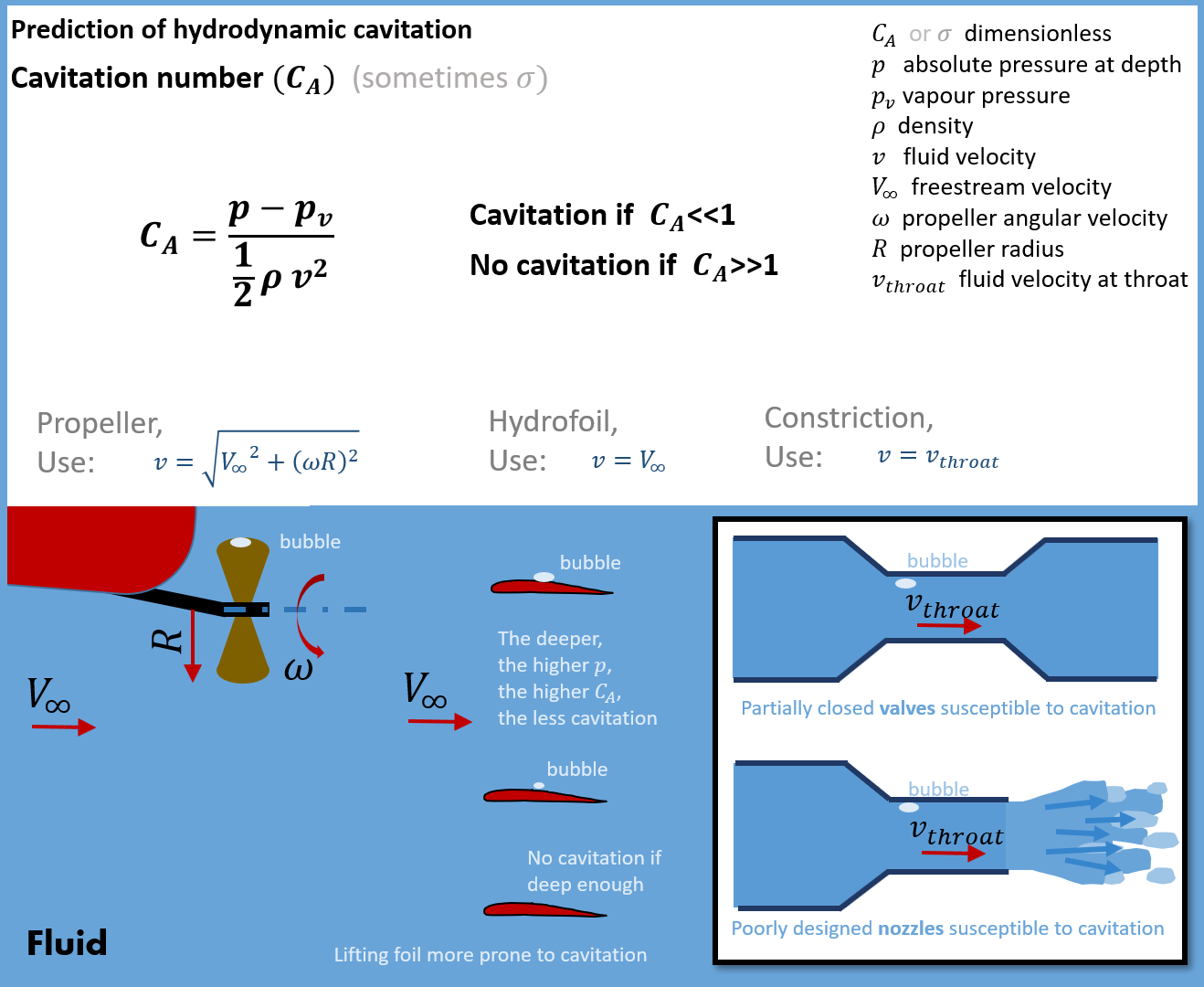
Cavitation Number
There are three dimensionless numbers that may be referred to as the cavitation number in various scenarios: the cavitation number for hydrodynamic cavitation, the Thoma number for cavitation in pumps, and the Garcia-Atance number for ultrasonic cavitation (named after Gonzalo Garcia-Atance Fatjo). Hydrodynamic cavitation The cavitation number (Ca) can be used to predict hydrodynamic cavitation. It has a similar structure as the Euler number, but a different meaning and use: The cavitation number expresses the relationship between the difference of a local absolute pressure from the vapor pressure and the kinetic energy per volume, and is used to characterize the potential of the flow to cavitate. It is defined as \mathrm = \frac where *\rho is the density of the fluid. *p is the local pressure. *p_\mathrm is the vapor pressure of the fluid. *v is a characteristic velocity of the flow. The cavitation number serves as one of the primary methods for characterizing cavitation w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoot (torpedo)
The Hoot (; ''Whale'') is an Iranian supercavitation torpedo claimed to travel at approximately , several times faster than a conventional torpedo. It was claimed to have been successfully test-fired from a surface ship against a dummy submarine during the Iranian military exercise "Great Prophet" () on 2 April 2006 and 3 April 2006. Iran test-fired the torpedo within its territorial waters in the Strait of Hormuz in May 2017. The official Iranian news agency IRNA claims the torpedo was produced and developed by the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (). Most military and industry analysts have concluded that the Hoot is reverse engineered from the Russian VA-111 Shkval supercavitation torpedo which travels at the same speed. See also * List of supercavitating torpedoes A supercavitating torpedo is a torpedo using the effect of supercavitation to create a bubble (physics), bubble around the torpedo to move at high velocity under water. Super cavitation has many variables, thoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VA-111 Shkval
The VA-111 ''Shkval'' (from , ''squall'') torpedo and its descendants are supercavitating torpedoes originally developed by the Soviet Union. They are capable of speeds in excess of 200 knots (370 km/h or 230 miles/h). Design and capabilities Design began in the 1960s when the NII-24 research institute was ordered to produce a new weapon capable of engaging nuclear submarines. The merger of the institute and GSKB-47 created the Research Institute of Applied Hydromechanics, who continued with the design and production of the Shkval. Previously operational as early as 1977, the torpedo was announced as being deployed in the 1990s. The ''Shkval'' is intended as a countermeasure against torpedoes launched by undetected enemy submarines. The VA-111 is launched from torpedo tubes at . A solid-fuel rocket accelerates it to cavitation speed, with a combined-cycle gas turbine in the nose creating the required gas bubble. Once accelerated, speed is maintained by an underwater ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juliet Marine Systems Ghost
Juliet Marine Systems ''Ghost'' is a super-cavitating stealth ship. The ship's experimental hull design can reduce hull friction to 1/900th that of conventional watercraft. ''Ghost'' was designed, developed, and built by the private American company Juliet Marine Systems. History Inventor Gregory Sancoff had decided to focus on small watercraft following the attack on USS ''Cole'' in 2000, after which he recalled saying: "Some yahoo terrorists in a cheap little boat and $500 worth of explosives can kill 17 sailors on a billion-dollar ship?" He also came across a 630-page United States Navy report on an exercise called Juliet, where the Navy attacked an enemy force of small, high-speed boats; after two days, the Navy had suffered over 20,000 simulated casualties. Sancoff gathered information on marine technology, including hydroplane racing boats and high-speed super-cavitating torpedoes. In 2007, Sancoff founded Juliet Marine Systems, named after the Navy exercise that insp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the northeast, Afghanistan to the east, Pakistan to the southeast, and the Gulf of Oman and the Persian Gulf to the south. With a Ethnicities in Iran, multi-ethnic population of over 92 million in an area of , Iran ranks 17th globally in both List of countries and dependencies by area, geographic size and List of countries and dependencies by population, population. It is the List of Asian countries by area, sixth-largest country entirely in Asia and one of the world's List of mountains in Iran, most mountainous countries. Officially an Islamic republic, Iran is divided into Regions of Iran, five regions with Provinces of Iran, 31 provinces. Tehran is the nation's Capital city, capital, List of cities in Iran by province, largest city and financial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sergey Lavrov
Sergey Viktorovich Lavrov (, ; born 21 March 1950) is a Russian diplomat who has served as Minister of Foreign Affairs (Russia), Minister of Foreign Affairs since 2004. He is the longest-serving Russian foreign minister since Andrei Gromyko during the Soviet Union. Lavrov was born in Moscow and graduated from the Moscow State Institute of International Relations (MGIMO) in 1972. He received his first Soviet diplomatic posting in Sri Lanka, and speaks fluent Sinhala language, Sinhala, Maldivian language, Dhivehi, English, and French, in addition to his native Russian. From 1981 to 1988 Lavrov held several posts in the Permanent Mission of Russia to the United Nations, Soviet Permanent Mission to the United Nations in New York City. Starting in the late 1980s he was deputy director and then director of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Russia), Foreign Ministry's Department of International Organizations before becoming a Deputy Minister of Foreign Affairs in 1992. Lavrov was the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DARPA
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) is a research and development agency of the United States Department of Defense responsible for the development of emerging technologies for use by the military. Originally known as the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA), the agency was created on February 7, 1958, by President Dwight D. Eisenhower in response to the Soviet Union, Soviet launching of Sputnik 1 in 1957. By collaborating with academia, industry, and government partners, DARPA formulates and executes research and development projects to expand the frontiers of technology and science, often beyond immediate U.S. military requirements.Dwight D. Eisenhower and Science & Technology, (2008). Dwight D. Eisenhower Memorial CommissionSource The name of the organization first changed from its founding name, ARPA, to DARPA, in March 1972, changing back to ARPA in February 1993, then reverted to DARPA in March 1996. ''The Economist'' has called DARPA "the agency that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |