|
Super High Altitude Research Project
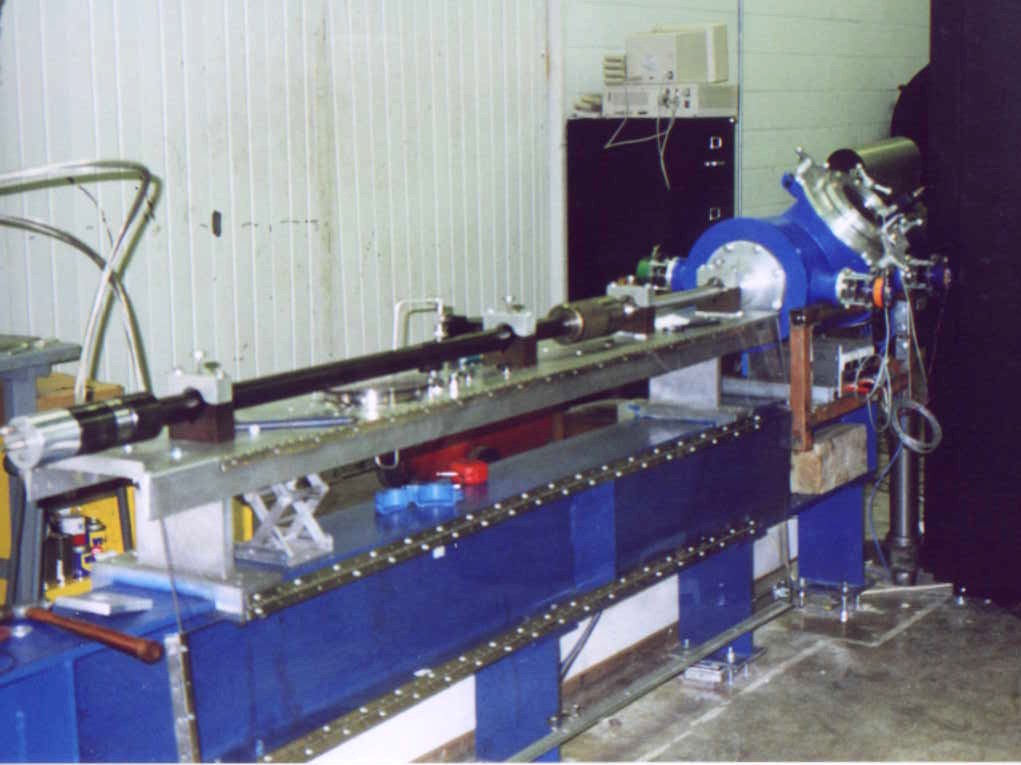
The Super High Altitude Research Project (Super HARP, SHARP) was a U.S. government project conducting research into the firing of high-velocity projectiles high into the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere using a two-stage light-gas gun, with the ultimate goal of propelling satellites into Geocentric orbit, Earth orbit. Design work on the prototype space gun began as early as 1985 at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory in California and became operational in December 1992. It is the largest gas gun in the world. Design and operation Rather than a single straight barrel, the SHARP gun uses an L-shape design with two separate sections; the long steel combustion section & pump tube section is connected to the long launch tube (or barrel) at a right angle. rail-mounted sleds sit at both ends of the pump tube to absorb recoil energy from firing and a smaller sled is mounted on a perpendicular set of tracks at the aft-end of the launch-tube near the junction point. The firing seque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth's Atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is composed of a layer of gas mixture that surrounds the Earth's planetary surface (both lands and oceans), known collectively as air, with variable quantities of suspended aerosols and particulates (which create weather features such as clouds and hazes), all retained by Earth's gravity. The atmosphere serves as a protective buffer between the Earth's surface and outer space, shields the surface from most meteoroids and ultraviolet solar radiation, keeps it warm and reduces diurnal temperature variation (temperature extremes between day and night) through heat retention (greenhouse effect), redistributes heat and moisture among different regions via air currents, and provides the chemical and climate conditions allowing life to exist and evolve on Earth. By mole fraction (i.e., by quantity of molecules), dry air contains 78.08% nitrogen, 20.95% oxygen, 0.93% argon, 0.04% carbon dioxide, and small amounts of other trace gases (see Composition below ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scramjet
A scramjet (supersonic combustion ramjet) is a variant of a ramjet airbreathing jet engine in which combustion takes place in supersonic airflow. As in ramjets, a scramjet relies on high vehicle speed to compress the incoming air forcefully before combustion (hence ''ram''jet), but whereas a ramjet decelerates the air to speed of sound, subsonic velocities before combustion using shock cones, a scramjet has no shock cone and slows the airflow using shockwaves produced by its ignition source in place of a shock cone. This allows the scramjet to operate efficiently at extremely high speeds. Although scramjet engines have been used in a handful of operational military vehicles, scramjets have so far mostly been demonstrated in research test articles and experimental vehicles. History Before 2000 The Bell X-1 attained Supersonic speed#Supersonic flight, supersonic flight in 1947 and, by the early 1960s, rapid progress toward faster aircraft suggested that operational aircraft wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Guns
A space gun, sometimes called a Verne gun because of its appearance in ''From the Earth to the Moon'' by Jules Verne, is a method of launching an object into space using a large gun- or cannon-like structure. Space guns could thus potentially provide a method of non-rocket spacelaunch. It has been conjectured that space guns could place satellites into Earth's orbit (although after-launch propulsion of the satellite would be necessary to achieve a stable orbit), and could also launch spacecraft beyond Earth's gravitational pull and into other parts of the Solar System by exceeding Earth's escape velocity of about . However, these speeds are too far into the hypersonic range for most practical propulsion systems and also would cause most objects to burn up due to aerodynamic heating or be torn apart by aerodynamic drag. Therefore, a more likely future use of space guns would be to launch objects into Low Earth orbit, at which point attached rockets could be fired or the objects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Scientist
''New Scientist'' is a popular science magazine covering all aspects of science and technology. Based in London, it publishes weekly English-language editions in the United Kingdom, the United States and Australia. An editorially separate organisation publishes a monthly Dutch-language edition. First published on 22 November 1956, ''New Scientist'' has been available in online form since 1996. Sold in retail outlets (paper edition) and on subscription (paper and/or online), the magazine covers news, features, reviews and commentary on science, technology and their implications. ''New Scientist'' also publishes speculative articles, ranging from the technical to the philosophical. ''New Scientist'' was acquired by Daily Mail and General Trust (DMGT) in March 2021. History Ownership The magazine was founded in 1956 by Tom Margerison, Max Raison and Nicholas Harrison as ''The New Scientist'', with Issue 1 on 22 November 1956, priced at one shilling (). An article in the magazi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Plumbbob
Operation Plumbbob was a series of nuclear tests that were conducted between May 28 and October 7, 1957, at the Nevada Test Site, following ''Project 57'', and preceding '' Project 58/58A''. Background The operation consisted of 29 explosions, of which only two did not produce any nuclear yield. Twenty-one laboratories and government agencies were involved. While most ''Operation Plumbbob'' tests contributed to the development of warheads for intercontinental and intermediate range missiles, they also tested air defense and anti-submarine warheads with smaller yields. They included 43 military effects tests on civil and military structures, radiation and bio-medical studies, and aircraft structural tests. ''Operation Plumbbob'' had the tallest tower tests to date in the U.S. nuclear testing program as well as high-altitude balloon tests. One nuclear test involved the largest troop maneuver ever associated with U.S. nuclear testing. Approximately 18,000 members of the U.S. Ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verneshot
A verneshot (named after French author Jules Verne) is a hypothetical volcanic eruption event caused by the buildup of gas deep underneath a craton. Such an event may be forceful enough to launch an extreme amount of material from the crust and mantle into a sub-orbital trajectory, leading to significant further damage after the material crashes back down to the surface. Connection with mass extinctions Verneshots have been proposed as a causal mechanism explaining the statistically unlikely contemporaneous occurrence of continental flood basalts, mass extinctions, and "impact signals" (such as planar deformation features, shocked quartz, and iridium anomalies) traditionally considered definitive evidence of hypervelocity impact events. (First submitted 17 April 2003). For an informal introduction ''see'Professor Jason Phipps Morgan's faculty biography at Cornell University from May 2004: ''I became interested in the causes of mass-extinctions, in particular worrying about t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Project HARP
Project HARP, for high altitude research project, was a joint venture of the United States Department of Defense and Canada's Department of National Defence created with the goal of studying ballistics of re-entry vehicles and collecting upper atmospheric data for research. Unlike conventional space launching methods that rely on rockets, HARP instead used very large guns to fire projectiles into the atmosphere at extremely high speeds. A HARP gun operated by the U.S. Army's Ballistic Research Laboratory (now called the U.S. Army Research Laboratory) at Yuma Proving Ground currently holds the world record for the highest altitude that a gun-fired projectile has achieved: . History Preparations Project HARP originated as the brainchild of Gerald Bull, a renowned but controversial ballistic engineer specializing in high-velocity guns and gun propulsion systems. In the mid-1950s, Bull was working on anti-ballistic missile (ABM) and intercontinental ballistic missile (IC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-rocket Spacelaunch
Non-rocket spacelaunch refers to theoretical concepts for launch into space where much of the speed and altitude needed to achieve orbit is provided by a propulsion technique that is not subject to the limits of the rocket equation. Although all space launches to date have been rockets, a number of alternatives to rockets have been proposed. In some systems, such as a combination launch system, skyhook, rocket sled launch, rockoon, or air launch, a portion of the total delta-v may be provided, either directly or indirectly, by using rocket propulsion. Present-day launch costs are very high – $2,500 to $25,000 per kilogram from Earth to low Earth orbit (LEO). As a result, launch costs are a large percentage of the cost of all space endeavors. If launch can be made cheaper, the total cost of space missions will be reduced. Due to the exponential nature of the rocket equation, providing even a small amount of the velocity to LEO by other means has the potential of greatly redu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quicklaunch
Quicklaunch is an inactive US company attempting to use a type of space gun to launch payloads into low Earth orbit. It is a university spin-off of the SHARP project which ended 2005. Quicklauncher The Quicklaunch proposed firing apparatus was a light-gas gun using hydrogen as the working gas and natural gas as the explosive heat source. Heating and pre-pressurizing the hydrogen working gas takes 10 minutes before the shot and most of the hydrogen is recovered by a muzzle muffler at the end of the launch tube to be reused for subsequent launches. The gun would be, for the most part, submerged in the ocean. Its horizontal and vertical direction (azimuth and elevation) could be adjusted based on customer launch requirements. The proposed launcher was designed to give projectiles an initial speed of while the Earth orbital speed is . The projectile design therefore included a one-stage rocket which ignites some time after launch. The designed payloads could include spacecraft, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escape Velocity
In celestial mechanics, escape velocity or escape speed is the minimum speed needed for an object to escape from contact with or orbit of a primary body, assuming: * Ballistic trajectory – no other forces are acting on the object, such as propulsion and friction * No other gravity-producing objects exist. Although the term ''escape velocity'' is common, it is more accurately described as a speed than as a velocity because it is independent of direction. Because gravitational force between two objects depends on their combined mass, the escape speed also depends on mass. For artificial satellites and small natural objects, the mass of the object makes a negligible contribution to the combined mass, and so is often ignored. Escape speed varies with distance from the center of the primary body, as does the velocity of an object traveling under the gravitational influence of the primary. If an object is in a circular or elliptical orbit, its speed is always less than the es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite
A satellite or an artificial satellite is an object, typically a spacecraft, placed into orbit around a celestial body. They have a variety of uses, including communication relay, weather forecasting, navigation ( GPS), broadcasting, scientific research, and Earth observation. Additional military uses are reconnaissance, early warning, signals intelligence and, potentially, weapon delivery. Other satellites include the final rocket stages that place satellites in orbit and formerly useful satellites that later become defunct. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs). Most satellites also have a method of communication to ground stations, called transponders. Many satellites use a standardized bus to save cost and work, the most popular of which are small CubeSats. Similar satellites can work together as groups, forming constellatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light-gas Gun
The light-gas gun is an apparatus for physics experiments. It is a highly specialized gun designed to generate extremely high velocities. It is usually used to study high-speed impact phenomena ( hypervelocity research), such as the formation of impact craters by meteorites or the erosion of materials by micrometeoroids. Some basic material research relies on projectile impact to create high pressure; such systems are capable of forcing liquid hydrogen into a metallic state. Operation A light-gas gun works on the same principle as a spring piston airgun. A large-diameter piston is used to force a gaseous working fluid through a smaller-diameter barrel containing the projectile to be accelerated. This reduction in diameter acts as a lever, increasing the speed while decreasing the pressure. In an airgun, the large piston is powered by a spring or compressed air, and the working fluid is atmospheric air. In a light-gas gun, the piston is powered by a chemical reaction (usually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |