|
Suncook Lakes
The Suncook Lakes are a pair of lakes located in Belknap County in central New Hampshire, United States, in the town of Barnstead. Upper Suncook Lake encompasses , while Lower Suncook Lake covers . The lakes are connected by a channel, spanned by a road bridge. A dam at the outlet of Lower Suncook Lake controls the water level of both lakes. The lakes are located along the Suncook River, a tributary of the Merrimack River. There are three islands on Lower Lake. Lower Suncook Lake has an average depth of and a maximum depth of , while Upper Suncook Lake has a greater average depth and a maximum depth greater than . The lakes are classified as a warmwater fishery, with observed species including smallmouth and largemouth bass, chain pickerel, horned pout, and white perch. Rainbow trout The rainbow trout (''Oncorhynchus mykiss'') is a species of trout native to cold-water tributary, tributaries of the Pacific Ocean in North America and Asia. The steelhead (sometimes called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belknap County, New Hampshire
Belknap County () is a County (United States), county in the U.S. state of New Hampshire. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the population was 63,705. The county seat is Laconia, New Hampshire, Laconia. It is located in New Hampshire's Lakes Region (New Hampshire), Lakes Region, slightly southeast of the state's geographic center. Belknap County comprises the Laconia, NH Micropolitan Statistical Area, which in turn constitutes a portion of the Boston-Worcester, Massachusetts, Worcester-Providence, Rhode Island, Providence, Massachusetts, MA-Rhode Island, RI-NH-Connecticut, CT Greater Boston, Combined Statistical Area. The southwestern half of Lake Winnipesaukee lies in Belknap County, while several other major lakes such as Squam Lake and Lake Winnisquam lie partially or wholly within the county. The Belknap Mountains lie along the shore of Winnipesaukee east of Laconia and feature Mount Major, known for its numerous hiking trails and Gunstock Mountain, home of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suncook River
The Suncook River is a river located in central New Hampshire in the United States. It is a tributary of the Merrimack River, which flows to the Gulf of Maine. Course The Suncook River begins at the outlet of Crystal Lake in the town of Gilmanton, New Hampshire. The village of Gilmanton Ironworks is located at the lake's outlet. The Suncook flows south two miles to the Suncook Lakes (Upper and Lower) in Barnstead. Below the lakes, the river passes through the village of Center Barnstead and enters the town of Pittsfield, whose village is centered on a 19th century dam on the river. The river continues south through the towns of Chichester and Epsom, and then forms the town boundary between Pembroke and Allenstown. Shortly before reaching the Merrimack River, the Suncook drops in , a natural waterpower site that led to the growth of the village of Suncook. 2006 flood On May 16, 2006, the Suncook River, responding to the highest rainfall amounts in at least 70 years (m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barnstead, New Hampshire
Barnstead is a New England town, town in Belknap County, New Hampshire, United States. The population was 4,915 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, up from 4,593 at the 2010 United States census, 2010 census. Home to the Suncook Lakes, Barnstead includes the villages of Center Barnstead, New Hampshire, Center Barnstead, Barnstead Parade (identified as "Barnstead" on topographic maps) and South Barnstead. History The town was granted on May 20, 1727, by Lieutenant Governor John Wentworth (lieutenant governor, born 1671), John Wentworth to the Reverend Joseph Adams and others. Settlement commenced in 1765, and two years later Barnstead was incorporated as a town by Governor Sir John Wentworth, 1st Baronet, John Wentworth. Many of the settlers came from Barnstable, Massachusetts, and Hempstead (village), New York, Hempstead, New York—the name is taken from these two. Although not mountainous, the terrain forms large swells, good for grazing. By 1830, when the population ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Hampshire
New Hampshire ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec to the north. Of the List of states and territories of the United States, 50 U.S. states, New Hampshire is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, seventh-smallest by land area and the List of U.S. states and territories by population, tenth-least populous, with a population of 1,377,529 residents as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. Concord, New Hampshire, Concord is the List of capitals in the United States, state capital and Manchester, New Hampshire, Manchester is the List of municipalities in New Hampshire, most populous city. New Hampshire's List of U.S. state mottos, motto, "Live Free or Die", reflects its role in the American Revolutionary War; its state nickname, nickname, "The Granite State", refers to its ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merrimack River
The Merrimack River (or Merrimac River, an occasional earlier spelling) is a river in the northeastern United States. It rises at the confluence of the Pemigewasset and Winnipesaukee rivers in Franklin, New Hampshire, flows southward into Massachusetts, and then flows northeast until it empties into the Gulf of Maine at Newburyport. From Pawtucket Falls in Lowell, Massachusetts, onward, the Massachusetts–New Hampshire border is roughly calculated as the line three miles north of the river. The Merrimack is an important regional focus in both New Hampshire and Massachusetts. The central-southern part of New Hampshire and most of northeast Massachusetts is known as the Merrimack Valley. Several U.S. naval ships have been named and USS Merrimac in honor of this river. The river is also known for the early American literary classic '' A Week on the Concord and Merrimack Rivers'' by Henry David Thoreau. Etymology and spelling The etymology of the name of the Merrimac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
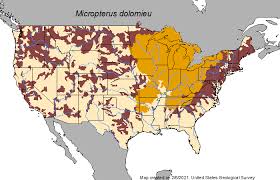
Smallmouth Bass
The smallmouth bass (''Micropterus dolomieu'') is a species of freshwater fish in the Centrarchidae, sunfish family (biology), family (Centrarchidae) of the order (biology), order Centrarchiformes. It is the type species of its genus ''Micropterus'' (black basses), and is a popular game fish sought by anglers throughout the temperate zones of North America, and has been spread by fish stocking, stocking —as well as illegal introduced species, introductions—to many cool-water tributaries and lakes in Canada and more so introduced in the United States. The maximum recorded size is approximately and . The smallmouth bass is native to the upper and middle Mississippi River basin, the Saint Lawrence River–Great Lakes system, the Champlain Valley, and the Hudson Bay basin. Its common names include smallmouth, bronzeback, brown bass, brownie, smallie, bronze bass, and bareback bass. Description Smallmouth have a slender but muscular fusiform body shape making them powerful ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Largemouth Bass
The largemouth bass (''Micropterus nigricans'') is a carnivorous, freshwater fish, freshwater, ray-finned fish in the Centrarchidae (sunfish) family, native to the eastern United States, eastern and central United States, southeastern Canada and northern Mexico. It is known by a variety of regional names, such as the widemouth bass, ''bigmouth bass'', ''black bass'', ''largie'', Potter's fish, Florida bass or ''Florida largemouth'', ''green bass'', bucketmouth bass, ''green trout'', growler, Gilsdorf bass, Oswego bass, LMB, and southern largemouth and northern largemouth. The largemouth bass, as it is known today, was first described by French naturalist Georges Cuvier in 1828. A recent study concluded that the correct scientific name for the Florida bass is ''Micropterus salmoides'', while the largemouth bass is ''Micropterus nigricans''. It is the largest species of the black bass, with a maximum recorded length of and an unofficial weight of . The largemouth bass is the Lis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chain Pickerel
The chain pickerel (''Esox niger'') is a species of freshwater fish in the pike family (biology), family (family Esocidae) of order (biology), order Esociformes. The chain pickerel and the American pickerel (''E. americanus'') belong to the ''Esox'' genus of pike. Taxonomy French naturalist Charles Alexandre Lesueur described the chain pickerel in 1818. Its species name is the Latin word ''niger'' "black". Nicknames include the "southern pike", "grass pike", "jack", "jackfish", "gunny" and "eastern pickerel". In central Florida the chain pickerel is known locally as "Gatorfish" Description The chain pickerel has a distinctive, dark, chain-like pattern on its greenish sides. There is a vertical dark marking underneath the eye, which helps to distinguish the chain pickerel from redfin pickerel (''Esox americanus americanus'') and grass pickerel (''E. americanus vermiculatus''), in which the mark curves posteriorly. Its body outline resembles that of the northern pike (''E. lucius ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brown Bullhead
The brown bullhead (''Ameiurus nebulosus'') is a fish of the family Ictaluridae that is widely distributed in North America. It is a species of bullhead catfish and is similar to the black bullhead (''Ameiurus melas'') and yellow bullhead (''Ameiurus natalis''). It was originally described as ''Pimelodus nebulosus'' by Charles Alexandre Lesueur in 1819, and is also referred to as ''Ictalurus nebulosus''. The brown bullhead is also widely known as the "mud pout", "horned pout", "hornpout", or simply "mud cat", a name also used with the other bullhead species. The brown bullhead is important as a clan symbol of the Ojibwe people. In their tradition, the bullhead or is one of six beings that came out of the sea to form the original clans. Appearance The brown bullhead grows to be approximately in length and is a darker brown-green dorsally, growing lighter green and yellow towards the ventral surface. The belly is off-white or cream, and the fish has no scales. Additionall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Perch
The white perch (''Morone americana'') is not a true Percidae, perch but is a fish of the temperate bass family, Moronidae, notable as a food and game fish in eastern North America. In some places it is referred to as "Silver Bass". The common name "white perch" is sometimes applied to the white crappie (''Pomoxis annularis''). Description Generally silvery-white in color, hence the name, depending upon habitat and size specimens have begun to develop a darker shade near the dorsal fin and along the top of the fish. This sometimes earns them the nickname "black-back". White perch have been reported up to in length and weighing . Ecology Although favoring brackish waters, it is also found in fresh water and coastal areas from the St. Lawrence River and Lake Ontario south to the Pee Dee River in South Carolina, and as far east as Nova Scotia. They are also found in the lower Great Lakes, Finger Lakes, Long Island Sound and nearby coastal areas, Hudson River, Hudson and Mohaw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rainbow Trout
The rainbow trout (''Oncorhynchus mykiss'') is a species of trout native to cold-water tributary, tributaries of the Pacific Ocean in North America and Asia. The steelhead (sometimes called steelhead trout) is an Fish migration#Classification, anadromous (sea-run) form of the coastal rainbow trout or Columbia River redband trout that usually returns to freshwater to Spawn (biology), spawn after living two to three years in the ocean. Adult freshwater stream rainbow trout average between , while lake-dwelling and anadromous forms may reach . Coloration varies widely based on subspecies, forms, and habitat. Adult fish are distinguished by a broad reddish stripe along the lateral line, from gills to the tail, which is most vivid in breeding males. Wild-caught and Fish hatchery, hatchery-reared forms of the species have been transplanted and introduced for food or sport in at least 45 countries and every continent except Antarctica. Introductions to locations outside their nativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Lakes In New Hampshire
This is a list of lakes and ponds in the U.S. state of New Hampshire. The New Hampshire Department of Environmental Services lists 944 lakes and impoundments in their ''Official List of Public Waters''. The water bodies that are listed include natural lakes and reservoirs, including areas on rivers impounded behind dams. Wikipedia articles have been written about the following New Hampshire lakes. Swimming, fishing, and/or boating are permitted in some of these lakes, but not all. References {{Authority control * Lakes New Hampshire New Hampshire ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec t ... Swimming venues in New Hampshire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |