|
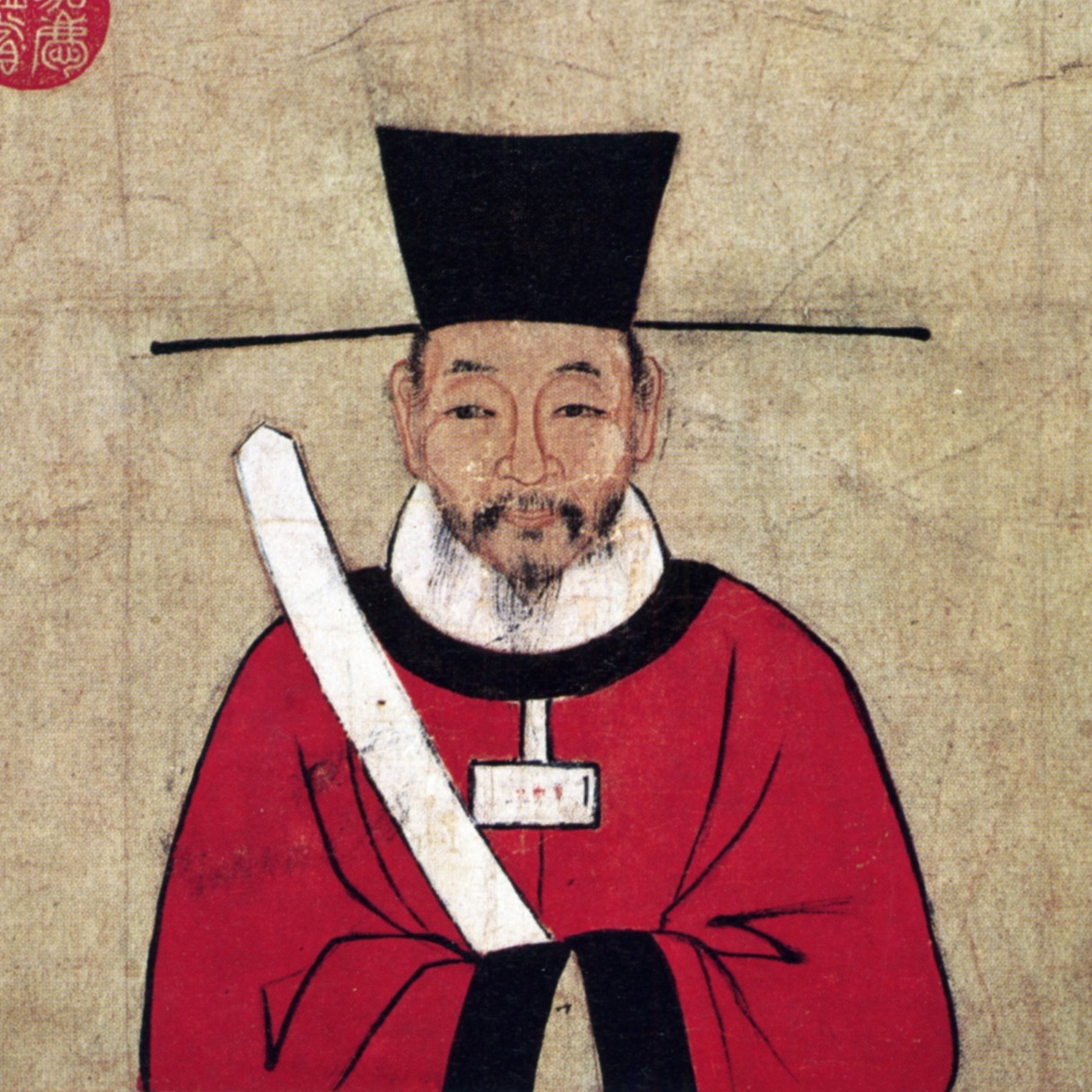
Sun Guangxian
Sun Guangxian (; died 968'' History of Song'', vol. 483.The Chinese Wikipedia article for Sun Guangxian gave his birth year as 900, but did not cite a source.), courtesy name Mengwen (), self-styled Baoguangzi (), was an official of the Chinese Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period Jingnan state (Nanping). He became the official who was most in charge of policies and governance after the retirement of Liang Zhen during the rule of Jingnan's second ruler Gao Conghui, and subsequently served in that role under Gao Conghui, his sons Gao Baorong and Gao Baoxu, and his grandson Gao Jichong. Background It is unclear when Sun Guangxian was born. Both the '' History of Song'' and the ''Spring and Autumn Annals of the Ten Kingdoms'' indicated that he was from Guiping (貴平, in modern Meishan, Sichuan)—although the ''Spring and Autumn Annals of the Ten Kingdoms'' acknowledged that one of Sun's own works, the ''Beimeng Suoyan'' (), stated that he was from Fuchun (富春, in modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sun (surname)
Sun () is a transliteration of a common Chinese surname (; pronounced ). It is the third name listed in the Song dynasty Chinese classics, classic text ''Hundred Family Surnames''. Other transliterations include Suen (Hong Kong and regions with Cantonese-speaking populations), Soon (Amoy dialect), Sng and Soon (Teochew dialect), Tôn (Vietnamese language, Vietnamese), Son (Korean surname), Son (Japanese language, Japanese/Korean language, Korean), Soon (regions with Hokkien-speaking populations), Sen/Suan/-son/-zon (Chinese Filipino in the Philippines), and Swen. In 2019, Sun was the twelfth most common surname in mainland China. A 2013 study found it to be the 12th most common name as well, shared by 18,300,000 people or 1.38% of the population, with the province with the most being Shandong. Note that in Hong Kong and regions with Cantonese-speaking populations, the surname Xin (surname), Xin (辛) is also transliterated as Sun. Origins *The name Sunshu Ao (孫叔敖) comes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhejiang
) , translit_lang1_type2 = , translit_lang1_info2 = ( Hangzhounese) ( Ningbonese) (Wenzhounese) , image_skyline = 玉甑峰全貌 - panoramio.jpg , image_caption = View of the Yandang Mountains , image_map = Zhejiang in China (+all claims hatched).svg , mapsize = 275px , map_caption = Location of Zhejiang in China , coordinates = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = China , named_for = Old name of Qiantang River , seat_type = Capital and largest city , seat = Hangzhou , established_title = Annexation by the Qin dynasty , established_date = 222 BC , established_title2 = Jiangnandong Circuit , established_date2 = 626 , established_title3 = Liangzhe Circuit , established_date3 = 997 , established_title4 = Zhejiang Province formed , established_date4 = 1368 , established_title5 = Republican Period , established_date5 = 1 January 1912 , established_title6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Of China
Throughout Chinese history, "Emperor" () was the superlative title held by the monarchs of imperial China's various dynasties. In traditional Chinese political theory, the emperor was the " Son of Heaven", an autocrat with the divine mandate to rule all under Heaven. Emperors were worshiped posthumously under an imperial cult. The lineage of emperors descended from a paternal family line constituted a dynasty, and succession in most cases theoretically followed agnatic primogeniture. The emperor of China was an absolute monarch. During the Han dynasty, Confucianism gained sanction as the official political theory. The absolute authority of the emperor came with a variety of governing duties and moral obligations; failure to uphold these was thought to remove the dynasty's Mandate of Heaven and to justify its overthrow. In practice, emperors sometimes avoided the strict rules of succession and dynasties' purported "failures" were detailed in official histories written by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
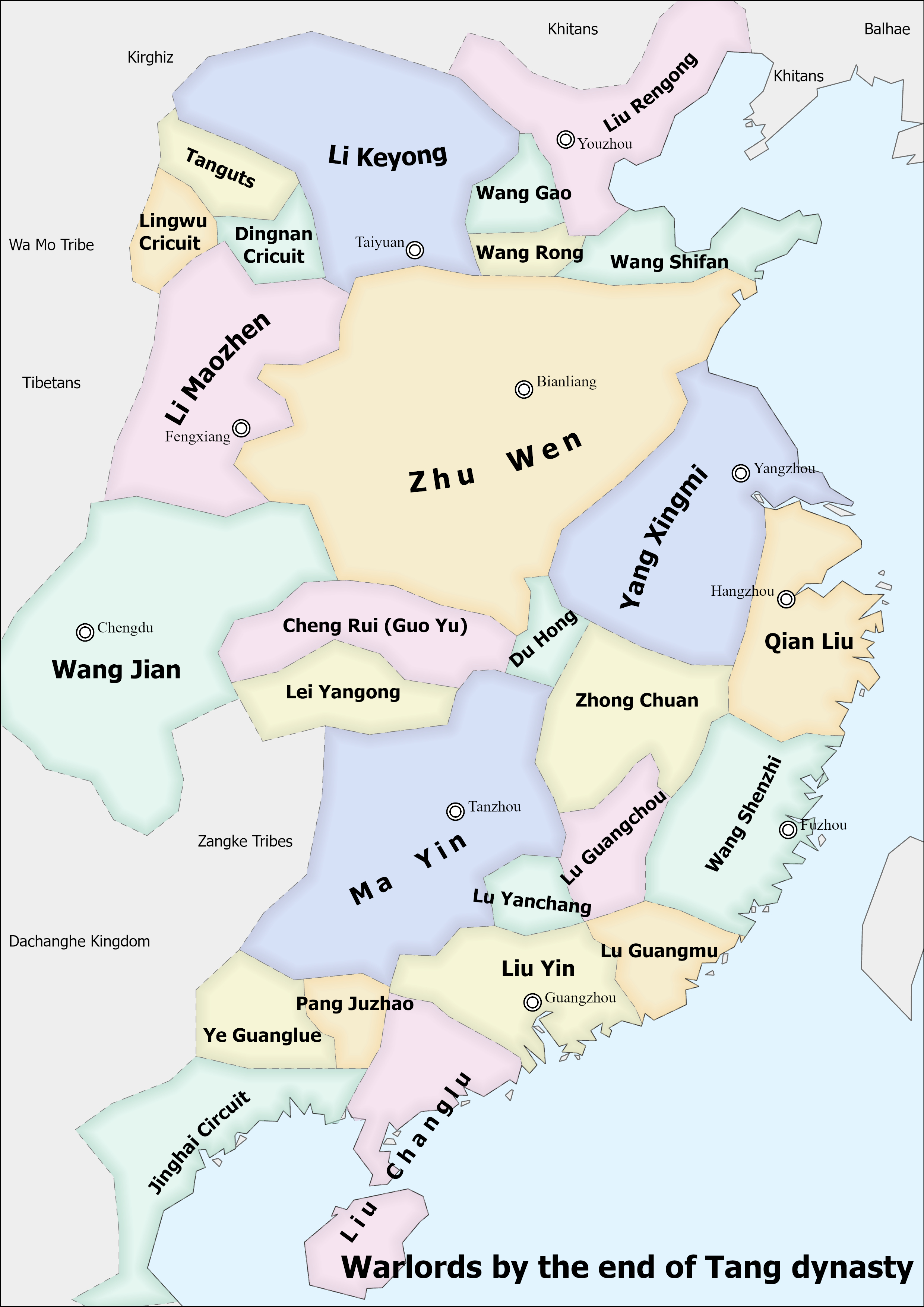
Ma Xifan
Ma Xifan (; 899 – 30 May 947), courtesy name Baogui (寶規), also known by his posthumous name as the Prince Wenzhao of Chu (楚文昭王), was the third ruler of the Ma Chu, Ma Chu dynasty of China during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. Background Ma Xifan was born in 899, during the reign of Emperor Zhaozong of Tang, as the fourth son of the warlord Ma Yin. At that time, Ma Yin had just taken control of Tanzhou (in modern Hunan), Tan Prefecture (in modern Changsha, Hunan) following the assassination of Ma Yin's predecessor Liu Jianfeng (Tang dynasty), Liu Jianfeng, and was not yet fully in control of Wu'an Circuit (武安, headquartered at Tan Prefecture), which would eventually become the central circuit for the Chu state, but was in the process of gradually consolidating his control. Ma Xifan's mother was a Lady Chen, who was Ma Yin's concubine, not his wife—as Ma Yin's first son, Ma Xizhen (), was said to be born of his wife, who was not named in historic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chu (Ten Kingdoms)
Chu (), known in historiography as Ma Chu () or Southern Chu (), was a dynastic state of China that existed from 907 to 951. It is counted as one of the Ten Kingdoms during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period of Chinese history. Founding Ma Yin was named regional governor by the Tang court in 896 after fighting against a rebel named Yang Xingmi. He declared himself as the Prince of Chu with the fall of the Tang dynasty in 907. Ma's position as Prince of Chu was confirmed by the Later Tang in the north in 927 and was given the posthumous title of King Wumu of Chu. Territories The capital of the Chu Kingdom was Changsha ( Tanzhou). The kingdom ruled over present-day Hunan and northeastern Guangxi. Economy Chu was peaceful and prosperous under Ma Yin's rule, exporting horses, silk and tea. Silk and lead coinage were often used as currency, particularly with external communities which would not accept other coinage of the land. Taxation was low for the peasantry and mer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ma Yin
Ma Yin (; c. 853 – December 2, 930), courtesy name Batu (霸圖), also known by his posthumous name as the King Wumu of Chu (楚武穆王), was a Chinese military general and politician who became the founding ruler of the Chinese Ma Chu dynasty during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. He was the only monarch who carried the title of "king" in his dynasty.Ma Yin's title was ''Wang'' (王) in Chinese, which could be translated as either "Prince" or "King" in English. The translation of "Prince" will be used here during the time that he carried the title of ''Wang'' of Chu during Later Liang and most of Later Tang. The translation of "King" will be used after he was created the ''Guowang'' (literally, "State King/Prince") of Chu by Li Siyuan, a title that carried for the rest of his life. He initially took control of the Changsha region in 896 after the death of his predecessor Liu Jianfeng, and subsequently increased his territorial hold to roughly modern Hunan and n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zizhi Tongjian
The ''Zizhi Tongjian'' (1084) is a chronicle published during the Northern Song dynasty (960–1127) that provides a record of Chinese history from 403 BC to 959 AD, covering 16 dynasties and spanning almost 1400 years. The main text is arranged into 294 scrolls (), each equivalent to a chapter—totaling around 3 million Chinese characters. In 1065, Emperor Yingzong of Song commissioned his official, Sima Guang (1019–1086), to lead a project to compile a Universal history (genre), universal history of China, and granted him funding and the authority to appoint his own staff. His team took 19 years to complete the work and in 1084 it was presented to Emperor Yingzong's successor Emperor Shenzong of Song. It was well-received and has proved to be immensely influential among both scholars and the general public. Endymion Wilkinson regards it as reference quality: "It had an enormous influence on later Chinese historical writing, either directly or through its many a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gao Jixing
Gao Jixing () (858 – January 28, 929), born Gao Jichang (高季昌), known for some time as Zhu Jichang (朱季昌), courtesy name Yisun (貽孫), also known by his posthumous name as the Prince Wuxin of Chu (楚武信王), was the founding prince of Jingnan during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period of China. During Tang Dynasty Background Gao Jichang was born in 858, during the reign of Emperor Xuānzong. He was from Shanshi (陝石, in modern Sanmenxia, Henan), and, in his youth, became a servant of a rich man at Bian Prefecture (汴州, in modern Kaifeng, Henan) — although the identity of his master received divergent reports in traditional sources. According to the '' History of the Five Dynasties'', which the ''Zizhi Tongjian'' also adopted, he became a servant of Li Qilang (), who later became an adoptive son of Zhu Quanzhong the military governor (''Jiedushi'') of Xuanwu Circuit (宣武, headquartered at Bian Prefecture) and had his name changed to Zhu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hubei
Hubei is a province of China, province in Central China. It has the List of Chinese provincial-level divisions by GDP, seventh-largest economy among Chinese provinces, the second-largest within Central China, and the third-largest among inland provinces. Its provincial capital at Wuhan serves as a major political, cultural, and economic hub for the region. Hubei is associated with the historical state of E that existed during the Western Zhou dynasty (771 BCE). Its name means 'north of the lake', referring to Dongting Lake. It borders Henan to the north, Anhui and Jiangxi to the east, Hunan to the south, and Chongqing and Shaanxi to the west. The high-profile Three Gorges Dam is located at Yichang in the west of the province. History The Hubei region was home to sophisticated Neolithic cultures. By the Spring and Autumn period (770–476 BC), the territory of today's Hubei formed part of the powerful Chu (state), State of Chu. Chu, nominally a tributary state of the Zh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jingzhou
Jingzhou ( zh, s=, c=荆州, t=, p=Jīngzhōu) is a prefecture-level city in southern Hubei province, China, located on the banks of the Yangtze River. Its total residential population was 5,231,180 based on the Seventh National Population Census of the People's Republic of China, 2020 census, 1,068,291 of whom resided in the built-up (''or metro'') area comprising two urban District (China), districts. Jingzhou's central urban area has grown out of Shashi City and Jingzhou Town (historically also known as Jiangling); their names were preserved in the names of Shashi District and Jingzhou District, which include the city's historical center, as well as Jiangling County, which administers the suburban areas of the larger historical area of Jiangling. The name "Shashi" also remains in the names of a number of local facilities, such as Jingzhou Shashi Airport and a railway freight station. Toponymy The contemporary city of Jingzhou is named after Jingzhou (ancient China), ancient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |