|
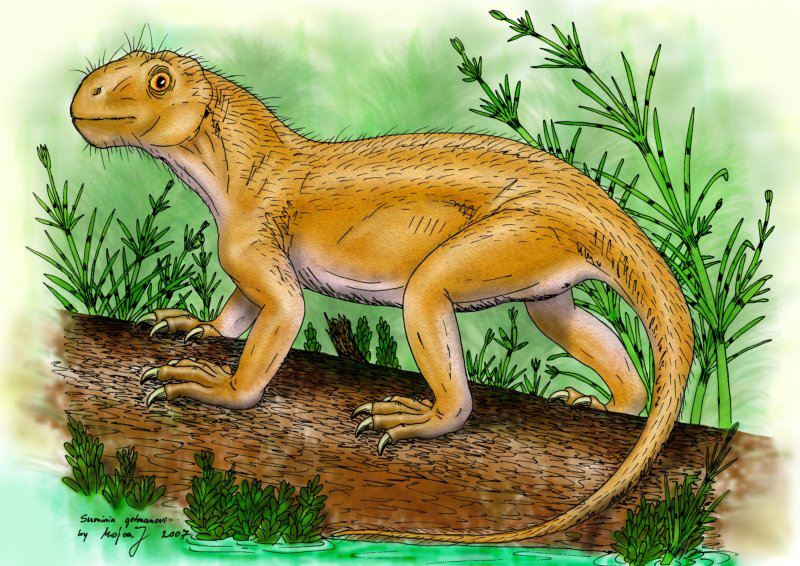
Suminia Scale
''Suminia'' is an extinct genus of basal anomodont that lived during the Tatarian age of the late Permian, spanning approximately from 268-252 Ma.Rybczynski N. 2000. Cranial anatomy and phylogenetic position of Suminia getmanovi, a basal anomodont (Amniota: Therapsida) from the Late Permian of Eastern Europe. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 130:329–73 ''Suminia'' is recognized the youngest non-dicynodont anomodont.Ivachnenko MF. 1994. A new Late Permian dromasaurian (Anomodontia) from Eastern Europe. Paleontological Journal 28: 96- 103. Its fossil localities are primarily derived from the Kotel’nich locality of the Kirov region in Russia. However, there have been some isolated specimen found in a few different localities, all from eastern European regions of Russia.Fröbisch, J. and Reisz, R. R. 2011. The postcranial anatomy of Suminia getmanovi (Synapsida: Anomodontia), the earliest known arboreal tetrapod. Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society, 162: 661–698. ''Suminia'', along wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Permian
Late may refer to: * LATE, an acronym which could stand for: ** Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy, a proposed form of dementia ** Local-authority trading enterprise, a New Zealand business law ** Local average treatment effect, a concept in econometrics Music * ''Late'' (album), a 2000 album by The 77s * Late!, a pseudonym used by Dave Grohl on his ''Pocketwatch'' album * Late (rapper), an underground rapper from Wolverhampton * "Late" (song), a song by Blue Angel * "Late", a song by Kanye West from ''Late Registration'' Other * Late (Tonga), an uninhabited volcanic island southwest of Vavau in the kingdom of Tonga * "Late" (''The Handmaid's Tale''), a television episode * LaTe, Oy Laivateollisuus Ab, a defunct shipbuilding company * Late may refer to a person who is Dead See also * * * ''Lates'', a genus of fish in the lates perch family * Later (other) * Tardiness * Tardiness (scheduling) In scheduling, tardiness is a measure of a delay in exe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an object or position in space such as a planet, moon, asteroid, or Lagrange point. Normally, orbit refers to a regularly repeating trajectory, although it may also refer to a non-repeating trajectory. To a close approximation, planets and satellites follow elliptic orbits, with the center of mass being orbited at a focal point of the ellipse, as described by Kepler's laws of planetary motion. For most situations, orbital motion is adequately approximated by Newtonian mechanics, which explains gravity as a force obeying an inverse-square law. However, Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity, which accounts for gravity as due to curvature of spacetime, with orbits following geodesics, provides a more accurate calculation and understanding of the exact mechanics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colobodectes
''Colobodectes'' is an extinct genus of dicynodont therapsid from the Tapinocephalus Assemblage Zone in the Abrahamskraal Formation (Beaufort Group), South Africa. See also * List of therapsids This list of therapsids is an attempt to create a comprehensive listing of all genera that have ever been included in the Therapsida excluding mammals and purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted genera, but also genera tha ... References External links The main groups of non-mammalian synapsids at Mikko's Phylogeny Archive Dicynodonts Permian synapsids of Africa Fossils of South Africa Fossil taxa described in 2003 Anomodont genera {{anomodont-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eodicynodon
''Eodicynodon'' (''eo-,'' early or primitive, dicynodont) is an extinct genus of dicynodont therapsids, a highly diverse group of herbivorous synapsids that were widespread during the middle-late Permian and early Triassic. As its name suggests, ''Eodicynodon'' is the oldest and most primitive dicynodont yet identified, ranging from the middle to late Permian and possessing a mix of ancestral Anomodont/therapsid features and derived dicynodont synapomorphies. First described by paleontologist T. H. Barry in 1974, its only associated species, ''E. oosthuizeni'', is named after Roy Oosthuizeni, the South African farmer who discovered the type specimen (a partial skull without the mandible) on his Cape Province farm between 1964 and 1970. Description ''Eodicynodon'' was a medium-sized dicynodont, at about 450 mm long and 150 mm high. While it had many features common to all dicynodonts, such as canine tusks and jaw structures related to the "cheek pivot system" of mas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galeops
''Galeops'' is an extinct genus of anomodont therapsids from the Middle-Late Permian of South Africa. It was described by Robert Broom Robert Broom FRS FRSE (30 November 1866 6 April 1951) was a British- South African doctor and palaeontologist. He qualified as a medical practitioner in 1895 and received his DSc in 1905 from the University of Glasgow. From 1903 to 1910, he ... in 1912. Some cladistic analyses have recovered it as closely related to dicynodonts. See also * List of therapsids References Anomodont genera Fossil taxa described in 1912 Taxa named by Robert Broom {{anomodont-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galechirus
''Galechirus'' is an extinct genus of anomodont therapsids. It was about 30 cm (1 ft) long. Description ''Galechirus'' was lizard-like in appearance. It is considered to be a dicynodont by some paleontologists; others think ''Galechirus'' is a younger form of a larger therapsid. Judging from its teeth, it was an insectivore. See also * List of therapsids This list of therapsids is an attempt to create a comprehensive listing of all genera that have ever been included in the Therapsida excluding mammals and purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted genera, but also genera tha ... References Anomodont genera Lopingian genus first appearances Lopingian genus extinctions Lopingian synapsids of Africa Permian South Africa Fossils of South Africa Fossil taxa described in 1907 Taxa named by Robert Broom {{anomodont-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galepus
''Galepus'' is an extinct genus of anomodont therapsids. See also * List of therapsids This list of therapsids is an attempt to create a comprehensive listing of all genera that have ever been included in the Therapsida excluding mammals and purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted genera, but also genera tha ... References Anomodont genera Permian synapsids Prehistoric synapsids of Africa Fossil taxa described in 1910 Taxa named by Robert Broom {{anomodont-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patranomodon
''Patranomodon'' (from Greek ''patr-'' “father”, thus “father of anomodonts”) is an extinct genus belonging to the group of Anomodontia. Rubidge and Hopson named this anomodont in 1990 after discovering its skull.Rubidge, B. S., & Hopson, J. A. (1990). A new anomodont therapsid from South Africa and its bearing on the ancestry of Dicynodontia. ''South African Journal of Science'', ''86''(1), 43-45. ''Patranomodon'' is known to have ranged in the Karoo of Southern Africa. Discovery and history The skull fossil of ''Patranomodon'' was found in the ''Eodicynodon'' Assemblage Zone of South Africa, belonging to the lowest biozone of the Beaufort Group. The Beaufort Group time period extends from the middle of the Permian to the early Triassic period. It is one of the three main subdivisions of the Karoo Supergroup in what today is southern Africa. Rubidge and Hopson were the first to discover the skull of ''Patranomodon''. These paleobiologists also named ''Patranomodon'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiarajudens
''Tiarajudens'' (" Tiaraju tooth") is an extinct genus of saber-toothed herbivorous anomodonts which lived during the Middle Permian period ( Capitanian stage) in what is now Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. It is known from the holotype UFRGS PV393P, a nearly complete skull. The type species ''T. eccentricus'' was named in 2011. Description ''Tiarajudens'' is a member of Anomodontia, a suborder of therapsids. Like other anomodonts, it was a quadrupedal herbivore about the size of a wild boar. The single fragmented holotype skull is short and robust at about in length. The most prominent features of ''Tiarajudens'' are its two large saber-like canine teeth. These teeth are unlike the tusks of dicynodonts, a later group of anomodonts. Twenty-one high- crowned teeth are present on either side of the upper jaw, including spoon-shaped incisors. Wide palatal teeth are also present. The top and bottom sets of teeth fit closely together, much like the teeth of mammals, allowing it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anomocephalus
''Anomocephalus'' is an extinct genus of primitive anomodonts and belongs to the clade Anomocephaloidea. The name is said to be derived from the Greek word ''anomos'' meaning lawless and ''cephalos'' meaning head. The proper word for head in Greek is however κεφαλή (''kephalē'').Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon. revised and augmented throughout by Sir Henry Stuart Jones. with the assistance of. Roderick McKenzie.'' Oxford: Clarendon Press. It is primitive in that it retains a complete set of teeth in both jaws, in contrast to its descendants, the dicynodonts, whose dentition is reduced to only a single pair of tusks (and in many cases no teeth at all), with their jaws covered by a horny beak similar to that of a modern tortoise. However, they are in no way closely related. Its discovery in 1999 from the earliest terrestrial rocks of Gondwana (from Williston in the Karoo of the Northern Cape Province of South Africa) has shown that this group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biseridens
''Biseridens'' ("two rows of teeth") is an extinct genus of anomodont therapsid, and one of the most basal anomodont genera known. Originally known from a partial skull misidentified as an eotitanosuchian in 1997, another well-preserved skull was found in the Qingtoushan Formation in the Qilian Mountains of Gansu, China, in 2009 that clarified its relationships to anomodonts, such as the dicynodonts. Among tetrapod taxa, the therapsid clade anomodontia in which ''Biseridens'' belong has one of the largest population sizes, highest levels of diversity, and longest stratigraphic range (Middle Permian to the Triassic, possibly into the Cretaceous), as well as being one of the only clades known from all the continents. Primarily understood from the recently discovered, most-well preserved specimen, ''Biseridens'' is most notably distinguishable as an anomodont due to its short snout, dorsally elevated zygomatic arch, and presence of a septomaxilla that distinctly lacks a facia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehensile
Prehensility is the quality of an appendage or organ that has adapted for grasping or holding. The word is derived from the Latin term ''prehendere'', meaning "to grasp". The ability to grasp is likely derived from a number of different origins. The most common are tree-climbing and the need to manipulate food. Examples Appendages that can become prehensile include: Uses Prehensility affords animals a great natural advantage in manipulating their environment for feeding, climbing, digging, and defense. It enables many animals, such as primates, to use tools to complete tasks that would otherwise be impossible without highly specialized anatomy. For example, chimpanzees have the ability to use sticks to obtain termites and grubs in a manner similar to human fishing Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment, but may also be caught from stocked bodies of water such as ponds, canals, park wetlan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |