|
Sumayyah Bint Khayyat
Sumeyah (; ), was the first member of the ''Umma'' (community) of the Islamic prophet Muhammad to become a martyr (). Shortly after she was martyred, her husband Yasir ibn Amir was also killed for his conversion to Islam, making him the first male martyr (). Her full name is said to be Sumayya bint Khabbat or Sumayya bint Khayyat. Her son was Ammar ibn Yasir. Early life She was a slave of Abu Hudhayfa ibn al-Mughira, a member of the Makhzum clan in Mecca.Muhammad ibn Jarir al-Tabari. ''Tarikh al-Rusul wa'l-Muluk''. Translated by Landau-Tasseron, E. (1998). ''Volume 39: Biographies of the Prophet's Companions and Their Successors'', pp. 29-30, 116-117. Albany: State University of New York Press. Her master gave her in marriage to Yasir ibn Amir, who was from the Malik clan of the Madh'hij tribe in Yemen. After coming to Mecca to look for a lost brother, he had decided to settle there under Abu Hudhayfa's protection. Sumayyah gave birth to their son Ammar c.566. Yasir also h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mecca
Mecca, officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, is the capital of Mecca Province in the Hejaz region of western Saudi Arabia; it is the Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow valley above sea level. Its metropolitan population in 2022 was 2.4million, making it the List of cities in Saudi Arabia by population, third-most populated city in Saudi Arabia after Riyadh and Jeddah. Around 44.5% of the population are Saudis, Saudi citizens and around 55.5% are Muslim world, Muslim foreigners from other countries. Pilgrims more than triple the population number every year during the Pilgrimage#Islam, pilgrimage, observed in the twelfth Islamic calendar, Hijri month of . With over 10.8 million international visitors in 2023, Mecca was one of the ten List of cities by international visitors, most visited cities in the world. Mecca is generally considered "the fountainhead and cradle of Islam". Mecca is revered in Islam as the birthp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khabbab Ibn Al-Aratt
(), , was a Companion of the Islamic prophet Muhammad whom Islamic tradition regards as one of the ten earliest converts to Islam.. Born as a slave in Mecca, he later became a swordsmith and was able to build up enough of a reputation to eventually get freed by his master. His beautiful recitation of the Quran is said to have been the direct cause of Umar ibn al-Khattab's (died 644, reigned as the second caliph 634–644) conversion to Islam in . Biography Khabbab ibn al-Aratt's background is uncertain, as medieval sources give widely different accounts. While some accounts regarded him in various ways as a (non-Arab client) of the Arab Banu Zuhra tribe, his descendants claimed that his father (whose name they gave as ) belonged to the Banu Sa'd branch of the Arab Banu Tamim tribe. However, he most likely was the son of a non-Arab inhabitant of the (southern Iraq), perhaps an Iraqi Nabataean, who was brought to Mecca as a slave and sold to someone belonging to the Arab Kh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khadija Bint Khuwaylid
Khadija bint Khuwaylid (November 619) was the first wife of Muhammad. Born into an aristocratic clan of the Quraysh, she was an affluent merchant in her own right and was known to have a noble personality within her tribe. In his early 20s, she employed Muhammad to manage a trade caravan to Syria and, impressed by his skills, subsequently offered him marriage, which he accepted. The couple had two sons, Qasim and Abd Allah, and four daughters, Zaynab, Ruqayya, Umm Kulthum and Fatima. In the aftermath of Muhammad's first revelation, Khadija is credited to have been the first convert to Islam. She continued to support her husband throughout her life and died in November 619 (Ramadan BH 3); the year was reportedly termed the " Year of Sorrow" by Muhammad. Her remains are located at the al-Mu'alla in Mecca and attract many Muslims for . Honored by Muslims as one of the " Mother of the Believers", Khadija is considered as one of the four "ladies of heaven" alongside Fatima, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibn Sa'd
Abū ‘Abd Allāh Muḥammad ibn Sa‘d ibn Manī‘ al-Baṣrī al-Hāshimī or simply Ibn Sa'd () and nicknamed ''Scribe of Waqidi'' (''Katib al-Waqidi''), was a scholar and Arabian biographer. Ibn Sa'd was born in 784/785 CE (168 AH) and died on 16 February 845 CE (230 AH). Ibn Sa'd was from Basra, but lived mostly in Baghdad, hence the ''nisba'' al-Basri and al-Baghdadi respectively. He is said to have died at the age of 62 in Baghdad and was buried in the cemetery of the Syrian gate. ''Kitāb al-Ṭabaqāt al-Kabīr'' The '' Kitāb al-Ṭabaqāt al-Kabīr'' () is a compendium of biographical information ('' tabaqāt'') about famous Islamic personalities. This eight-volume work contains the lives of Muhammad, his Companions and his Helpers, including those who fought at the Battle of Badr as a special class, and of the following generation, the Followers, who received their traditions from the Companions. Ibn Sa'd's authorship of this work is attested in a postscript ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibn Ishaq
Abu Abd Allah Muhammad ibn Ishaq ibn Yasar al-Muttalibi (; – , known simply as Ibn Ishaq, was an 8th-century Muslim historian and hagiographer who collected oral traditions that formed the basis of an important biography of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. His biography is known as the '' Al-Sirah al-Nabawiyyah'', and it has mainly survived through several recensions. Life Born in Medina circa A.H. 85 (A.D. 704),Mustafa al-Saqqa, Ibrahim al-Ibyari and Abdu l-Hafidh Shalabi, Tahqiq Kitab Sirah an-Nabawiyyah, Dar Ihya al-Turath, p. 20. ibn Isḥaq's grandfather was Yasār ibn Khiyar (according to some ibn Khabbar, Kuman or Kutan), one of forty Christian or Jewish boys who had been held captive in a monastery at Ayn al-Tamr. After being found in one of Khalid ibn al-Walid's campaigns, Yasār was taken to Medina and enslaved to Qays ibn Makhrama ibn al-Muṭṭalib ibn ʿAbd Manāf ibn Quṣayy. On his conversion to Islam, he was manumitted as " mawlā" (client), thus acquiri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th centuryAD, it endured until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. The term 'Byzantine Empire' was coined only after its demise; its citizens used the term 'Roman Empire' and called themselves 'Romans'. During the early centuries of the Roman Empire, the western provinces were Romanization (cultural), Latinised, but the eastern parts kept their Hellenistic culture. Constantine the Great, Constantine I () legalised Christianity and moved the capital to Constantinople. Theodosius I, Theodosius I () made Christianity the state religion and Greek gradually replaced Latin for official use. The empire adopted a defensive strategy and, throughout its remaining history, expe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Tabari
Abū Jaʿfar Muḥammad ibn Jarīr ibn Yazīd al-Ṭabarī (; 839–923 CE / 224–310 AH), commonly known as al-Ṭabarī (), was a Sunni Muslim scholar, polymath, historian, exegete, jurist, and theologian from Amol, Tabaristan, present-day Iran. Among the most prominent figures of the Islamic Golden Age, al-Tabari is widely known for his historical works and expertise in Quranic exegesis, and has been described as "an impressively prolific polymath".Lindsay Jones (ed.), ''Encyclopedia of religion'', volume 13, Macmillan Reference USA, 2005, p. 8943 He authored works on a diverse range of subjects, including world history, poetry, lexicography, grammar, ethics, mathematics, and medicine. Among his most famous and influential works are his Quranic commentary, '' Tafsir al-Tabari'', and historical chronicle, '' Tarikh al-Tabari''. Al-Tabari followed the Shafi'i school for nearly a decade before he developed his own interpretation of Islamic jurisprudence. His understand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
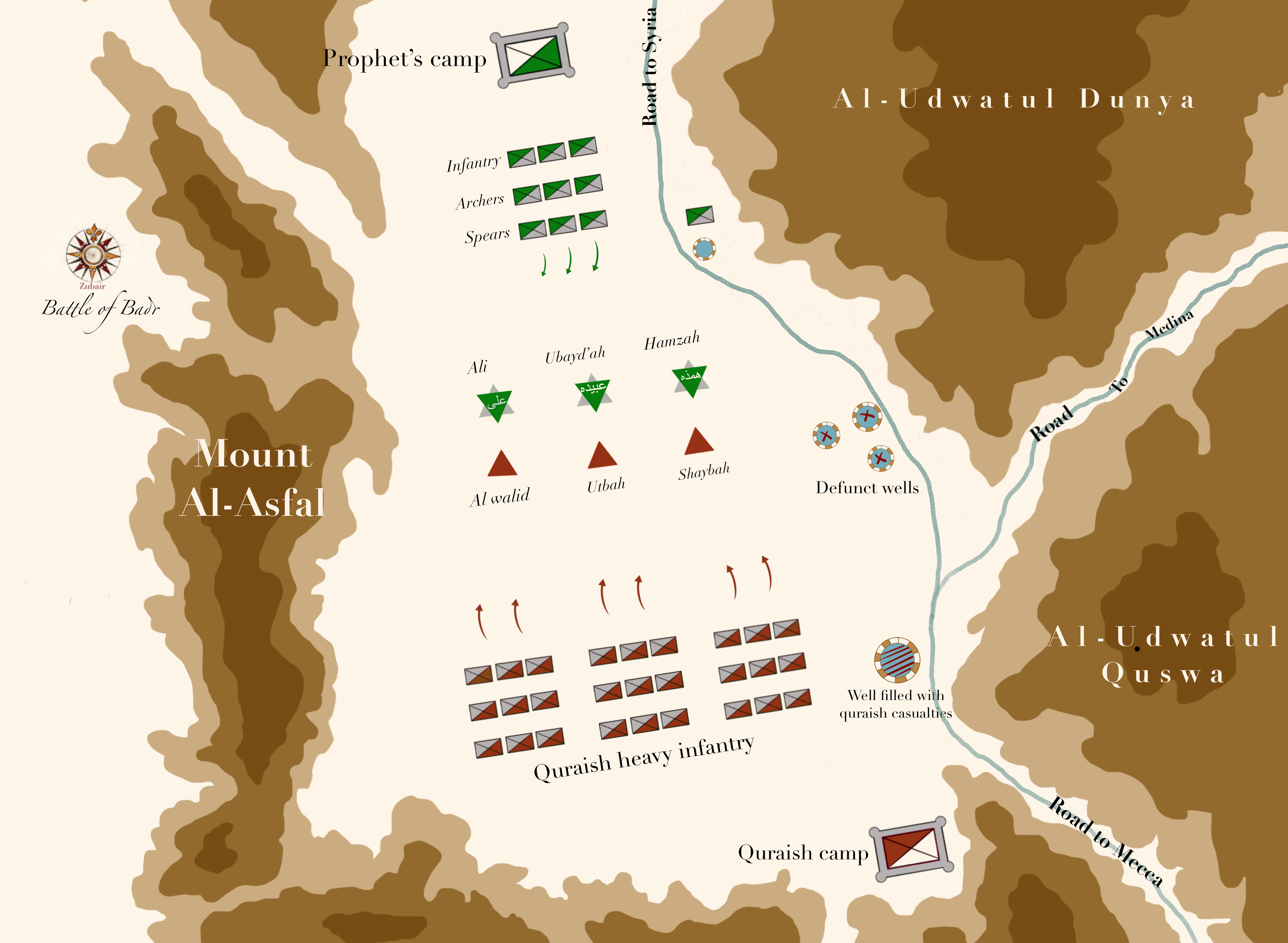
Battle Of Badr
The Battle of Badr or sometimes called The Raid of Badr ( ; ''Ghazwahu Badr''), also referred to as The Day of the Criterion (, ; ''Yawm al-Furqan'') in the Qur'an and by Muslims, was fought on 13 March 624 CE (17 Ramadan, 2 AH), near the present-day city of Badr, Al Madinah Province in Saudi Arabia. Muhammad, commanding an army of his Sahaba, defeated an army of the Quraysh led by Amr ibn Hishām, better known among Muslims as ''Abu Jahl''. The battle marked the beginning of the six-year war between Muhammad and his tribe. The Battle of Badr took place after five or six unsuccessful attempts by the Muslims to intercept and raid Meccan trade caravans between 623 and early 624 CE. Muhammad took keen interest in capturing Meccan caravans and their wealth after his migration to Medina. A few days before the battle, when he learnt of a Makkan caravan returning from the Levant led by Abu Sufyan ibn Harb, Muhammad gathered a small expeditionary force to raid it. Abu Sufyan, le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amr Ibn Hisham
Amr ibn Hisham (), better known as Abū Jahl (; ) was the Meccan Quraysh polytheist leader of the Mushrikites known for his opposition to the Islamic prophet Muhammad. He was the most prominent flag-bearer of opposition towards Islam. A prominent head of the Makhzum clan, Amr was known as ''Abu al-Hakam'' ('Father of Wisdom') among pre-Islamic Arabs. After Muhammad started preaching monotheism, Amr opposed him and often physically attacked early Muslims. He persecuted many Muslim converts, including Sumayya, and Yasir ibn Amir. His cruel torture methods towards Muslims made Muhammad give him the title ''Abu Jahl'' ('Father of Ignorance') and ''Firawn al-Umma'' ('Pharaoh of the Nation'). Following the migration to Medina, Amr gathered a large army of polytheists to attack Medina and kill Muslims. On 13 March 624, the Battle of Badr took place, in which Amr was a major leader. In the battle, Amr was fatally wounded by Mu'awwidh ibn Amr and Mu'ādh ibn 'Amr and eventually kille ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chain Mail
Mail (sometimes spelled maille and, since the 18th century, colloquially referred to as chain mail, chainmail or chain-mail) is a type of armour consisting of small metal rings linked together in a pattern to form a mesh. It was in common military use between the 3rd century BC and the 16th century AD in Europe, while it continued to be used militarily in Asia, Africa, and the Middle East as late as the 18th century. Even today it is still in use in industries such as Butcher, butchery and as protection against the powerful bites of creatures such as sharks. A coat of this armour is often called a hauberk or sometimes a byrnie. History The earliest examples of surviving mail were found in the Carpathian Basin at a burial in Horný Jatov, Slovakia dated in the 3rd century BC, and in a chieftain's burial located in Ciumești, Romania. Its invention is commonly credited to the Celts, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quraysh
The Quraysh () are an Tribes of Arabia, Arab tribe who controlled Mecca before the rise of Islam. Their members were divided into ten main clans, most notably including the Banu Hashim, into which Islam's founding prophet Muhammad was born. By the seventh century, they had become wealthy merchants, dominating trade between the Indian Ocean, East Africa, and the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean. The tribe ran caravans to Gaza City, Gaza and Damascus in summer and to Yemen (region), Yemen in winter, while also mining and pursuing other enterprises on these routes. When Muhammad Muhammad's first revelation, began preaching Islam in Mecca, the Quraysh initially showed little concern. However, their opposition to his activities quickly grew as he increasingly challenged Religion in pre-Islamic Arabia, Arab polytheism, which was prevalent throughout pre-Islamic Arabia. As relations deteriorated, Muhammad and Early Muslims, his followers migrated to Medina (the journey known as the Hij ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |