|
Sultans Of Sindh
This is a list of the monarchs of Sindh ( Sindhi: سنڌ جا بادشاهہَ, romanized: ''Sindh Jā Bādshāha''), from the establishment of the Ror dynasty around 450 BC until the conquest of Sindh from the Talpur dynasty by the East India Company in 1843. Ror dynasty (450 BC–489 AD) Known rulers of the Ror dynasty are: Rai dynasty (480–632 AD) Known rulers of the Rai dynasty are: Brahmin dynasty (632–712 AD) The known rulers of the Brahmin dynasty are: Vilayet As-Sindh (Umayyad Caliphate) (712–750 AD) In 712, Sind was conquered by the Umayyad Caliphate. The emirs appointed by the caliphate are as below; Vilayet As-Sindh (Abbasid Caliphate)(750–861 AD) Habbari dynasty (861–1010 AD) The Habbari rulers stylised themselves as Emirs. ''Note: the dates below are only approximate.'' Soomra dynasty (1010–1351 AD) The list of Soomra rulers is as follows; Samma dynasty (1336–1524 AD) The Samma dynasty which was a Muslim dynasty of Sindh who suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talpur Dynasty
The Talpur dynasty () was a Baloch people in Sindh, Baloch dynasty that ruled the Sind State (present-day Sindh, Pakistan) after overthrowing the Kalhora dynasty in 1783 until British conquest of Sindh in 1843. A branch of the family continued to rule Khairpur (princely state), Khairpur, under Suzerainty#India, British suzerainty and later as a Princely states of Pakistan, Pakistani princely state, until 1955 when it was amalgamated into West Pakistan. For most of their rule, they were subordinate to the Khanate of Kalat and subject to the Durrani Empire, being forced to pay tribute to them. History The Talpurs were ethnically Sindhi language, Sindhi-speaking Baloch people, and were descendants of Mir Sulaiman Kako Talpur, who had arrived in Sindh from Choti Bala in southern Punjab. The Talpurs had served the Kalhora dynasty until 1775, when the Kalhora ruler had ordered the assassination of the chief of the Talpur, Talpur clan, Mir Bahram Khan, leading to a revolt among th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kot Diji Fort
The Kot Diji Fort (; ; ''Fort of the Daughter''), formally known as Fort Ahmadabad, is an 18th-century Talpur-era fort located in the town of Kot Diji in Khairpur District, Pakistan, about 25 miles east of the Indus River at the edge of the Thar Desert. The fort sits above a pre- Harappan Civilization archaeological site dating to 2500 to 2800 B.C.E. Background The Kot Diji Fort was built by Mir Sohrab Khan Talpur, between 1785 and 1795. The site sits on a hill at the southern end of the Rohri Hills, and sits above a prehistoric mound of the same name, where remains of a pre- Harappan civilization have been found. Structure The fort sits atop a 110 foot tall high hill that rises above the city of Kot Diji. The fort's 30 foot tall walls encircle the uppermost portion of the fort, resulting a narrow-width fortress with perimeter of 1.8 kilometres. The fort contains three strategically placed towers that are each 50 feet tall. The fort contains several sites for cannon placement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rai Diyach
Dyas, also spelled Diyas, was an 11th-century Chudasama king of Saurashtra region of western India mentioned in bardic literature and folklore. In bardic literature and folklore During his reign, the Raja (king) of Patan invaded his dominions and conquered the capital town of Vamanasthali (now Vanthali). So Dyas fled to the Uparkot of Junagadh to which the Raja laid siege. Some sources name the Raja as Durlabhsen (possibly Durlabharaja). Different reasons are assigned for the war but the accounts are unanimous in representing Dyas to have insulted one of the ladies of the Raja's family while on a pilgrimage to Girnar near Junagadh. After much difficulty the Uparkot was taken. When Dyas died, his son Navagahana was a child and was secretly raised. After few years of reign by governors appointed from Patan, Navaghana regained the throne when he became an adult. Dates According to bardic tales and folklore, he was a son and the successor of Kavat and reigned from Vamanast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company that was founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to Indian Ocean trade, trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (South Asia and Southeast Asia), and later with East Asia. The company gained Company rule in India, control of large parts of the Indian subcontinent and British Hong Kong, Hong Kong. At its peak, the company was the largest corporation in the world by various measures and had its own armed forces in the form of the company's three presidency armies, totalling about 260,000 soldiers, twice the size of the British Army at certain times. Originally Chartered company, chartered as the "Governor and Company of Merchants of London Trading into the East-Indies," the company rose to account for half of the world's trade during the mid-1700s and early 1800s, particularly in basic commodities including cotton, silk, indigo dye, sugar, salt, spices, Potass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Hyderabad
The Battle of Hyderabad (), sometimes called the Battle of Dubbo, was one of the major campaigns of the British against Sindh, which was fought on 24 March 1843 between the forces of the British East India Company and the Talpur dynasty, Talpur Mirs of Sindh near Hyderabad, Sindh, Hyderabad, Sindh, Pakistan. A small British force, led by Captain Sir James Outram, 1st Baronet, James Outram, was attacked by the Talpurs and forced to make a fort of the British residence, which they successfully defended until they finally escaped to a waiting river steamer. After the British victory at Battle of Miani, Meeanee (also spelt Miani), Sir Charles James Napier continued his advance to the Indus River and attacked the Sindh capital of Hyderabad. Hyderabad was defended by 20,000 troops and Baloch people, Baloch tribes under the command oMir Sher Muhammad Khan Talpur "Sher-i-Sindh"and Hoshu Sheedi, Hosh Mohammad Sheedi. Charles Napier with a force of only 3,000 men but with artillery suppor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sindhi Language
Sindhi ( ; or , ) is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by more than 30 million people in the Pakistani province of Sindh, where it has official status, as well as by 1.7 million people in India, where it is a Scheduled languages of India, scheduled language without state-level official status. Sindhi is primarily written in the Perso-Arabic script in Pakistan, while in India, both the Perso-Arabic script and Devanagari are used. Sindhi is a Northwestern Indo-Aryan languages, Northwestern Indo-Aryan language, and thus related to, but not mutually intelligible with, Saraiki language, Saraiki and Punjabi language, Punjabi. Sindhi has several regional dialects. The earliest written evidence of modern Sindhi as a language can be found in a translation of the Qur’an into Sindhi dating back to 883 AD. Sindhi was one of the first Indo-Aryan languages to encounter influence from Persian language, Persian and Arabic following the Umayyad campaigns in India, Umayyad conquest in 712 AD. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
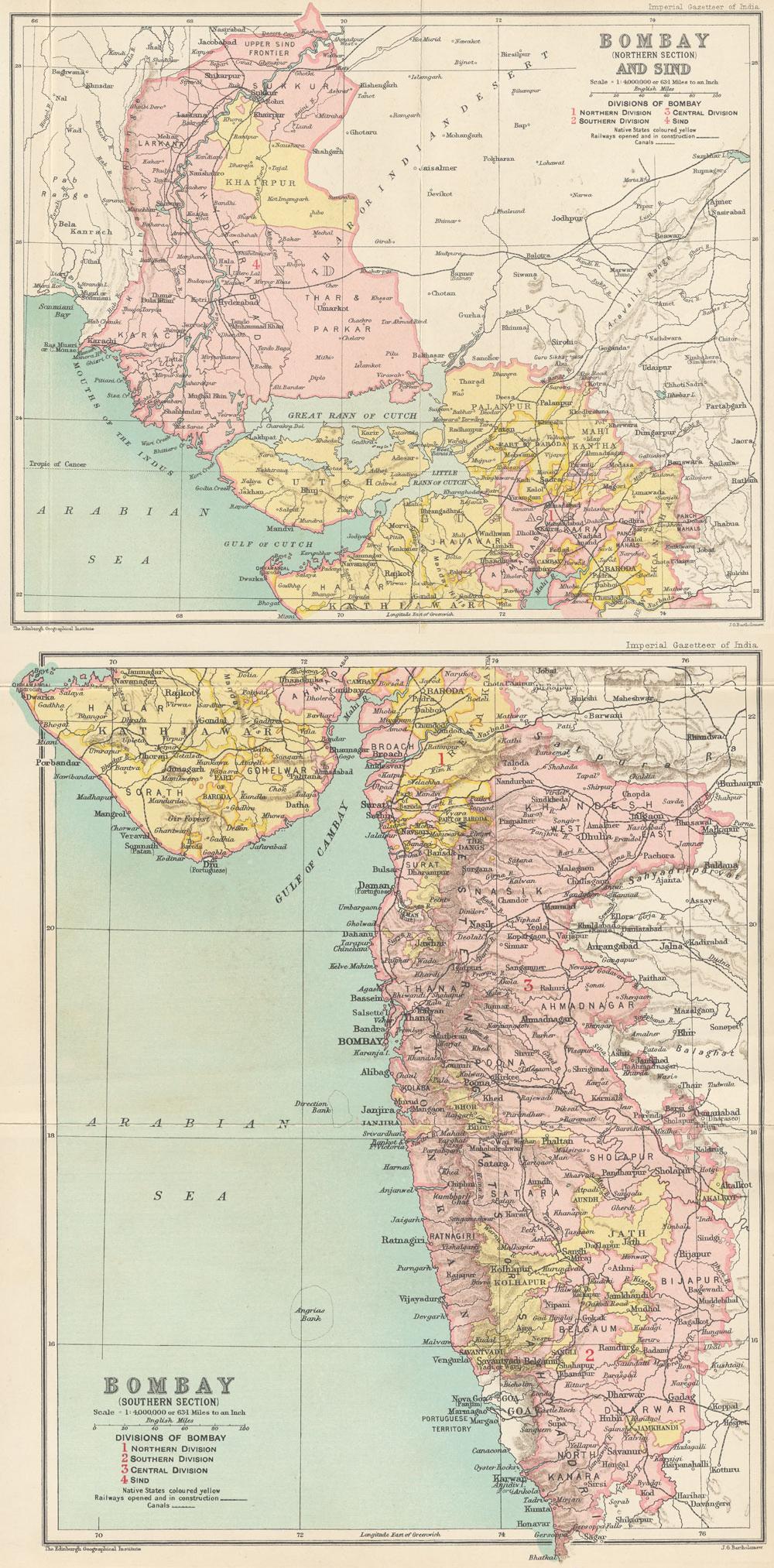
Sindh
Sindh ( ; ; , ; abbr. SD, historically romanized as Sind (caliphal province), Sind or Scinde) is a Administrative units of Pakistan, province of Pakistan. Located in the Geography of Pakistan, southeastern region of the country, Sindh is the third-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the Demographics of Pakistan, second-largest province by population after Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab. It is bordered by the Pakistani provinces of Balochistan, Pakistan, Balochistan to the west and north-west and Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab to the north. It shares an India-Pakistan border, International border with the Indian states of Gujarat and Rajasthan to the east; it is also bounded by the Arabian Sea to the south. Sindh's landscape consists mostly of alluvial plains flanking the Indus River, the Thar Desert of Sindh, Thar Desert in the eastern portion of the province along the India–Pakistan border, international border with India, and the Kirthar Mountains in the western portion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Ali Murad Khan
George Ali Murad Khan II Talpur (; born 29 June 1933) is a member of the Talpur dynasty who was the Mir (ruler) of Khairpur from 1947 to 1954. He was also Hon.Lieutenant-Colonel in Pakistan Army. Ascending to the throne after his father's removal from power, he chose to accede to the Dominion of Pakistan in the same year and was invested with full powers by Liaquat Ali Khan in 1951. Three years later, the state merged with Pakistan, removing Khan's sovereign status. Khan fathered two sons, Abbas Raza Khan and Mehdi Raza Khan and one daughter Zahra from his second wife. Early life Khan was born on 29 June 1933 at Brighton, Sussex in United Kingdom to Mir Faiz Muhammad Khan Talpur II and Dulhan Pasha Begum. He studied at St Bonaventure's High School in Hyderabad followed by Aitchison College, Lahore, before graduating from the University of Cambridge. At an age of nine months, Khan was mistakenly shot by his father. Although the bullet passed through his right lung and stomach, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sibi Fort
Sibi Fort, also known as Chakar Fort, is a ruined fort situated in Sibi city of Balochistan Province, Pakistan. Throughout its history, the ancient mud fort faced burning and destruction several times due to the tribal wars of the region. History Dating back to around 650 AD, the fort was constructed by a local Hindu tribe Sewis. Sibi (Siwi) was a popular place of the ''Chachnama'' that the King Chach defeated Sewis, pushing them out of this place captured Sibi Fort. The Hindu rulers Sewis had kept this for some time but lost to king Chach in 550 A.D. The Brahman rule continued here until the early part of eighth century A.D. When the young Arab general Muhammad bin Qasim conquered the whole of these areas, In the 11th century, Sibi was included in Ghaznavid Empire. The Muslims rule remained it included in the Suba Multan under Nasir ad-Din Qabacha (1210-1228 A.D.) According to the Persian book ''Ain-i-Akbari'', the Sibi Fort was in control by Jam Nizamuddin of Sindh as a pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umarkot Fort
Umarkot Fort (; Sindhi: ), also called Amarkot (), is a fort in Umerkot, Sindh ( Sindhi: ), Pakistan. Emperor Akbar was born in Umarkot Fort when his father Humayun fled from the military defeats at the hands of Sher Shah Suri on 15 October 1542. Rana Prasad Singh Sodha of Umarkot, who had risen to power, had given refuge to Mughal Emperor Humayun, and it was there that Hamida Bano Begum gave birth to young Akbar. Later the Mughal Emperor Akbar became the Shahenshah of Hindustan and was a popular figure with both Hindus and Muslims. Umerkot has many sites of historical significance such as Mughal emperor Akbar's birthplace near Umarkot Fort. Currently, Akbar's birthplace is an open land. In 1746, the Mughal Subahdar, Noor Mohammad Kalhoro, built a fort at the location. Later the British took over that area. Amarkot Fort was built by Rana Amar Singh in 11th century. It remained under control of Sodha Rajput dynasty known as the Ranas of Umerkot, but later was taken ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacco Qillo
Pakko Qillo (, ''Strong Fort'') is a fort in Hyderabad, Sindh, Pakistan. It was built in the 18th century, and served as a strategic military base and played a crucial role in the city's history. Etymology The fort is known as Pakko Qillo (Sindhi) and Pacco Qillo (English), Pakko means strong, intact and Qillo means fort. Construction The Fort was constructed on the hillock known locally as Ganjo Takkar or Ganji, by Mian Ghulam Shah Kalhoro, around 1768 when he founded the city of Hyderabad. History During Talpur rule over Sindh, Mir Fateh Ali Khan left Khudabad and moved his capital to Hyderabad Hyderabad is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Telangana. It occupies on the Deccan Plateau along the banks of the Musi River (India), Musi River, in the northern part of Southern India. With an average altitude of , much ... in 1789. He used the Hyderabad Fort as a residence and a place in which to hold his court. He added a harem and other buildings t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qasim Fort
Manora Fort is a fort that was built to protect the harbour of Karachi. Originally erected as a mud fortress by the Talpur Mirs in 1797, the fort was captured by the British in 1839 - after which they seized control of Karachi and lower Sindh. History Establishment Manora Fort was built by the Talpur dynasty in 1797 in order to protect the port, which handled trade with Oman and Bahrain. The fort was built at the top of cliffs that were in height, with a small mosque and a round tower. The fort was used to repel attacks by Qasimi pirates who threatened and sometimes raided Karachi Harbor in the early 19th century. Accounts and extent of piracy have been contested, and it has been suggested that piracy might have been used as a ''casus belli'' for the East India Company to seize control of the Persian Gulf region. Capture by the British On 1 February 1839 a British ship, HMS ''Wellesley'' (1815), anchored off the island of Manora. On 3 February, the ship opened fire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |