|
Sultanian
Pre-Pottery Neolithic A (PPNA) denotes the first stage of the Pre-Pottery Neolithic, in early Levantine and Anatolian Neolithic culture, dating to years ago, that is, 10,000–8800 BCE. Archaeological remains are located in the Levantine and Upper Mesopotamian region of the Fertile Crescent. The time period is characterized by tiny circular mud-brick dwellings, the cultivation of crops, the hunting of wild game, and unique burial customs in which bodies were buried below the floors of dwellings. The Pre-Pottery Neolithic A and the following Pre-Pottery Neolithic B (PPNB) were originally defined by Kathleen Kenyon in the type site of Jericho, State of Palestine. During this time, pottery was not yet in use. They precede the ceramic Neolithic Yarmukian culture. PPNA succeeds the Natufian culture of the Epipalaeolithic Near East. Settlements PPNA archaeological sites are much larger than those of the preceding Natufian hunter-gatherer culture, and contain traces of communal s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khiamian
The Khiamian culture is a Neolithic archaeological culture of Southwest Asia, dating to the earliest part of the Pre-Pottery Neolithic A (PPNA), around 9700 to 8600 BC. It is primarily characterised by a distinctive type of stone arrowhead—the "El Khiam point"—first found at the type site of El Khiam. Overview The Khiamian owes its name to the site of El Khiam, situated on banks of the Dead Sea, where researchers have recovered the oldest chert arrows heads, with lateral notches, the so-called "El Khiam points".. 2007. ''Zivilisationen – wie die Kultur nach Sumer kam.'' Munich. p126 They have served to identify sites of this period, which are found in Israel, as well as in Jordan (Azraq), Sinai ( Abu Madi), and to the north as far as the Middle Euphrates ( Mureybet). El Khiam points and other chert stone tools alike are often referred to as projectile points or arrowheads. While it is true that they were used as arrowheads, the given names imply function and are therefo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tower Of Jericho
The Tower of Jericho () is an stone structure built in the Pre-Pottery Neolithic A period around 8000 BC. It is part of Tell es-Sultan, a UNESCO World Heritage Site in the State of Palestine, in the city of Jericho, consisting of the remains of the oldest fortified city in the world. The Tower of Jericho has been described as one of the world's oldest towers, one of the world's oldest stone buildings, and one of the oldest works of monumental architecture. The ancient wall of Jericho was discovered by John Garstang during the excavations of 1930 to 1936, which he suggested were those described in the Book of Joshua in the Bible and dated to around 1400 BC. Kathleen Kenyon discovered the tower built against the wall inside the town during excavations between 1952 and 1958. Kenyon provided evidence that both constructions dated to much earlier, to the Neolithic, the most recent era of the Stone Age, and were part of an early proto-city. The tower highlights the importance of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gesher (archaeological Site)
Gesher is an archaeological site located on the southern bank of Nahal Tavor, near kibbutz Gesher in the central Jordan Valley of Israel. It bears signs of occupation from two periods, the very early Neolithic and the Middle Bronze Age. The site was first excavated between 1986 and 1987 by Yosef Garfinkel of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem and between 2002 and 2004 by Susan Cohen of Montana State University. The average of 4 radiocarbon dating results suggested inhabitation of the settlement around 8000 BC. History Pre-Pottery Neolithic A During the Pre-Pottery Neolithic A the site was a small village composed of a few rounded structures. Typical flint finds included a high number of el-Khiam points which Garfinkel argued, along with the relatively early date could class Gesher as a Khiamian site. One outstanding discovery, unknown from any other Neolithic site of the period in the Near East, is a workshop for the production of basalt artifacts. The workshop produced basa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jericho
Jericho ( ; , ) is a city in the West Bank, Palestine, and the capital of the Jericho Governorate. Jericho is located in the Jordan Valley, with the Jordan River to the east and Jerusalem to the west. It had a population of 20,907 in 2017. From the end of the era of Mandatory Palestine, the city was Jordanian annexation of the West Bank, annexed and ruled by Jordan from 1949 to 1967 and, with the rest of the West Bank, has been subject to Israeli occupation of the West Bank, Israeli occupation since 1967; administrative control was handed over to the Palestinian Authority in 1994. Jericho is among the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world,Murphy-O'Connor, 1998, p. 288.Freedman et al., 2000, p. 689–671. and it is also the city with the oldest known defensive wall.Michal Strutin, ''Discovering Natural Israel'' (2001), p. 4. Archaeology, Archaeologists have unearthed the remains of more than 20 successive settlements in Jericho, the first of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the History of agriculture, introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of sedentism, settlement. The term 'Neolithic' was coined by John Lubbock, 1st Baron Avebury, Sir John Lubbock in 1865 as a refinement of the three-age system. The Neolithic began about 12,000 years ago, when farming appeared in the Epipalaeolithic Near East and Mesopotamia, and later in other parts of the world. It lasted in the Near East until the transitional period of the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) from about 6,500 years ago (4500 BCE), marked by the development ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
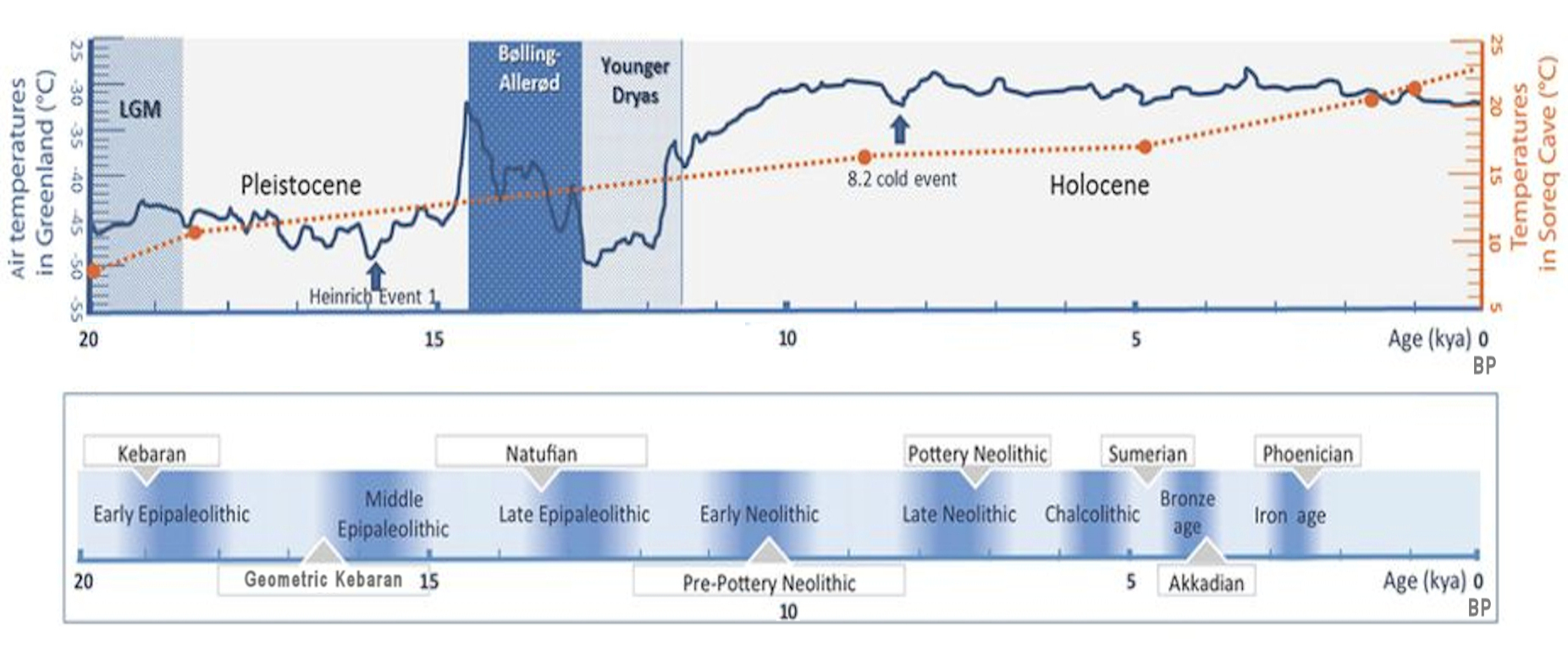
Climate And Post-Glacial Expansion In The Near East
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in a region, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorological variables that are commonly measured are temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind, and precipitation. In a broader sense, climate is the state of the components of the climate system, including the atmosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere, lithosphere and biosphere and the interactions between them. The climate of a location is affected by its latitude, longitude, terrain, altitude, land use and nearby water bodies and their currents. Climates can be classified according to the average and typical variables, most commonly temperature and precipitation. The most widely used classification scheme is the Köppen climate classification. The Thornthwaite system, in use since 1948, incorporates evapotranspiration along with temperature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yarmukian Culture
The Yarmukian culture was a Pottery Neolithic A (PNA) culture of the ancient Levant. It was the first culture in prehistoric Syria and one of the oldest in the Levant to make use of pottery. The Yarmukian derives its name from the Yarmuk River, which flows near its type site of Sha'ar Hagolan at the foot of the Golan Heights. This culture existed alongside the Lodian, or Jericho IX culture and the Nizzanim culture to the south. Recent theory In 2015, a salvage excavation brought to light a prehistoric site near Beit Hilkia and the Revivim quarry, with findings from the Yarmukian, Late Chalcolithic, and the Middle Bronze Age IIA–IIB. Somewhat surprising was the discovery of a typical Yarmukian-style fired clay figurine of a fertility goddess, the southernmost such finding. Of 163 sites found up to that date, the vast majority had been discovered in the main area known for its Yarmukian settlements, in and around the northern type-site of Sha'ar Hagolan, with just tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natufian Culture
The Natufian culture ( ) is an archaeological culture of the late Epipalaeolithic Near East in West Asia from 15–11,500 Before Present. The culture was unusual in that it supported a sedentism, sedentary or semi-sedentary population even before the Origins of agriculture in West Asia, introduction of agriculture. Natufian communities may be the ancestors of the builders of the region's first List of Neolithic settlements, Neolithic settlements, which may have been the earliest in the world. Some evidence suggests deliberate cultivation of cereals, specifically rye, by the Natufian culture at Tell Abu Hureyra, the site of the earliest evidence of agriculture in the world. The world's oldest known evidence of the production of bread-like foodstuff has been found at Shubayqa 1, a 14,400-year-old site in Jordan, Jordan's northeastern desert, 4,000 years before the Origins of agriculture in West Asia, emergence of agriculture in Southwest Asia. In addition, the oldest known evidence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epipalaeolithic Near East
The Epipalaeolithic Near East designates the Epipalaeolithic ("Final Old Stone Age") in the History of the Middle East#Prehistoric Near East, prehistory of the Near East. It is the period after the Upper Paleolithic, Upper Palaeolithic and before the Neolithic, between approximately 25,000 and 11,500 years Before Present. The people of the Epipalaeolithic were nomadic hunter-gatherers who generally lived in small, seasonal camps rather than permanent villages. They made sophisticated stone tools using microliths—small, finely-produced blades that were hafted in wooden implements. These are the primary artifacts by which archaeologists recognise and classify Epipalaeolithic sites. Although the appearance of microliths is an arbitrary boundary, the Epipalaeolithic does differ significantly from the preceding Upper Palaeolithic. Epipalaeolithic sites are more numerous, better preserved, and can be accurately Radiocarbon dating, radiocarbon dated. The period coincides with the gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calibrated Carbon 14 Dates For Gesher As Of 2013
In measurement technology and metrology, calibration is the comparison of measurement values delivered by a device under test with those of a calibration standard of known accuracy. Such a standard could be another measurement device of known accuracy, a device generating the quantity to be measured such as a voltage, a sound tone, or a physical artifact, such as a meter ruler. The outcome of the comparison can result in one of the following: * no significant error being noted on the device under test * a significant error being noted but no adjustment made * an adjustment made to correct the error to an acceptable level Strictly speaking, the term "calibration" means just the act of comparison and does not include any subsequent adjustment. The calibration standard is normally traceable to a national or international standard held by a metrology body. BIPM Definition The formal definition of calibration by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM) is the follo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reliefs Of Animals, Göbekli Tepe Layer III, Circa 9000 BCE
Relief is a sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces remain attached to a solid background of the same material. The term ''relief'' is from the Latin verb , to raise (). To create a sculpture in relief is to give the impression that the sculpted material has been raised above the background plane. When a relief is carved into a flat surface of stone (relief sculpture) or wood (relief carving), the field is actually lowered, leaving the unsculpted areas seeming higher. The approach requires chiselling away of the background, which can be time-intensive. On the other hand, a relief saves forming the rear of a subject, and is less fragile and more securely fixed than a sculpture in the round, especially one of a standing figure where the ankles are a potential weak point, particularly in stone. In other materials such as metal, clay, plaster stucco, ceramics or papier-mâché the form can be simply added to or raised up from the background. Monumental bronze reliefs are m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |