|
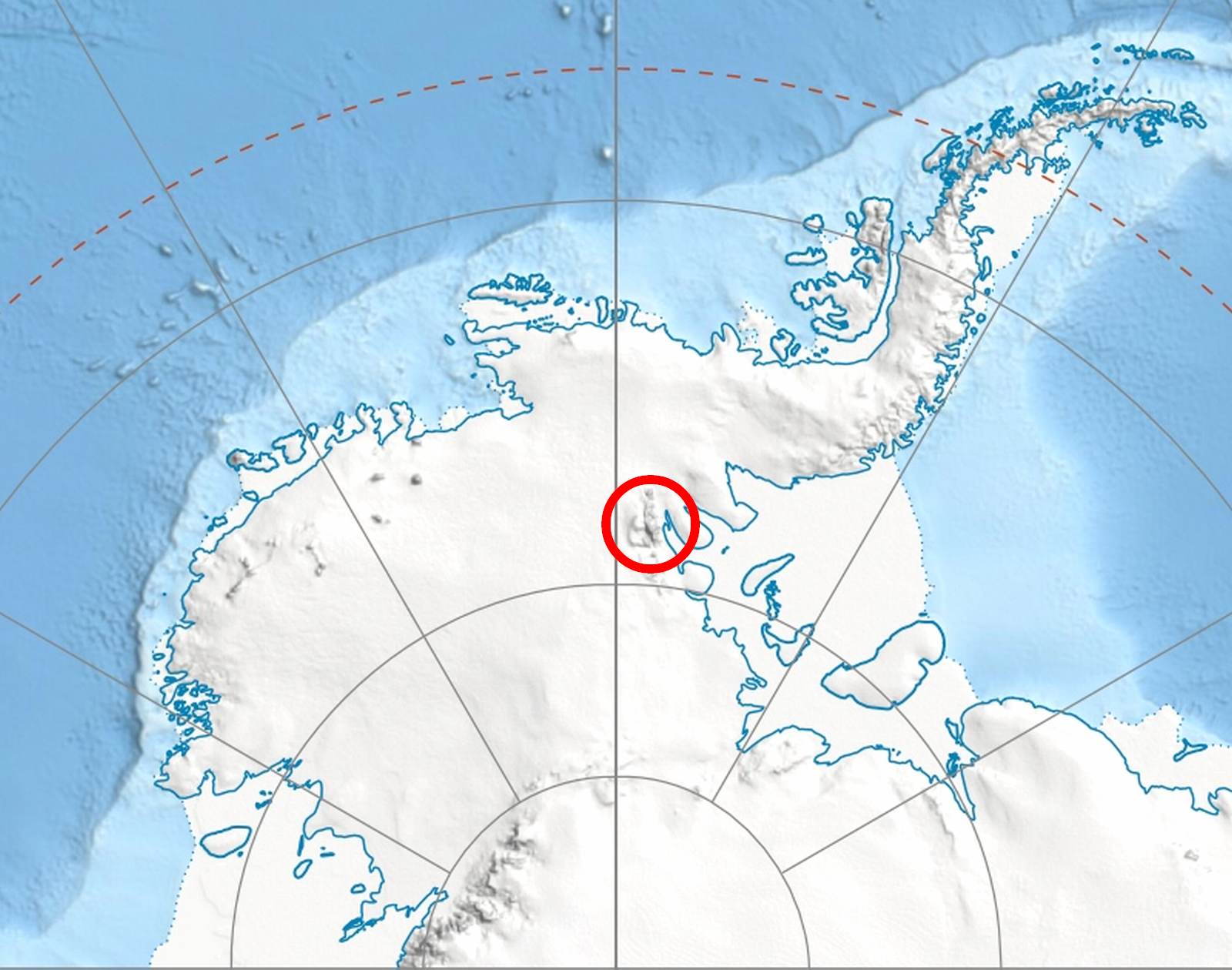
Sullivan Heights
Sullivan Heights () is a compact group of mountains in western Antarctica rising to in Mount Levack centered east-northeast of Mount Tyree in the Sentinel Range, Ellsworth Mountains. Roughly elliptical in plan and long, the feature includes sharp mountain peaks, rugged ridges, and steep peripheral scarps. The heights are encompassed by the flow of the Crosswell, Ellen, and Dater Glaciers, with their interior drained also by Pulpudeva and Strinava Glaciers. Separated from Vinson Massif to the south-southwest by Vranya Pass. The feature was named in 1997 by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) after Cornelius Wayne Sullivan (b. 1943), American oceanographer; United States Antarctic Program (USAP) field team leader for Sea Ice Microbial Communities (SIMCO) studies in McMurdo Sound, 1980–86, 1988, 1989; chief scientist and cruise coordinator for AMERIEZ ( Antarctic Marine Ecosystem Research at the Ice Edge Zone) projects in Weddell Sea, Nov–Dec 1983, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Ice Microbial Communities
Sea Ice Microbial Communities (SIMCO) refer to groups of microorganisms living within and at the interfaces of sea ice at the poles. The ice matrix they inhabit has strong vertical gradients of salinity, light, temperature and nutrients. Sea ice chemistry is most influenced by the salinity of the brine which affects the pH and the concentration of dissolved nutrients and gases. The brine formed during the melting sea ice creates pores and channels in the sea ice in which these microbes can live. As a result of these gradients and dynamic conditions, a higher abundance of microbes are found in the lower layer of the ice, although some are found in the middle and upper layers. Despite this extreme variability in environmental conditions, the taxonomical community composition tends to remain consistent throughout the year, until the ice melts. Much of the knowledge concerning the community diversity of the sea ice is known through genetic analyses and next-generation sequencing. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nebeska Peak
Nebeska Peak ( bg, връх Небеска, vrah Nebeska, ) is the rocky peak rising to 2450 m in Sullivan Heights on the east side of Sentinel Range in Ellsworth Mountains, Antarctica. It is surmounting Pulpudeva Glacier to the north and Hinkley Glacier to the south. The feature is named after the settlement of Nebeska in southern Bulgaria. Location Nebeska Peak is located at , which is 3.85 km west-southwest of Mount Farrell, 10.45 km northwest of Mount Waldron, 6.17 km northeast of Mount Segers, and 9.7 km east-southeast of Mount Bearskin. US mapping in 1988, and SCAR Antarctic Digital Database mapping in 2012. See also * Mountains in Antarctica Maps Vinson Massif. Scale 1:250 000 topographic map. Reston, Virginia: US Geological Survey, 1988. Antarctic Digital Database (ADD).Scale 1:250000 topographic map of Antarctica. Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR). Since 1993, regularly updated. References Nebeska PeakSCAR Composite Antarcti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Segers
Mount Segers () is a mountain at the south extremity of Sullivan Heights in the Sentinel Range, Ellsworth Mountains in Antarctica, separated from Vinson Massif to the southwest by Vranya Pass. It is situated 11 km (7 mi) east of Mount Tyree, on the east side of the head of Crosswell Glacier and surmounting Hinkley Glacier to the southeast. The peak was discovered by US Navy Squadron VX-6 on photographic flights of Dec. 14–15, 1959, and mapped by USGS from these photos. Named by US-ACAN for Chester W. Segers, a Navy cook and a member of the first wintering party at the South Pole Station South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west. Etymology The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sun� ... during the IGY in 1957. Maps Vinson Massif. Scale 1:250 000 topographic map. Reston, Virginia: US Geological Survey, 1988. Antarc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Farrell (Antarctica)
Mount Farrell is a mountain over high, rising just northwest of Dater Glacier and about east of Mount Shear, in the Sullivan Heights on the east side of Sentinel Range in the Ellsworth Mountains, Antarctica. It surmounts Pulpudeva Glacier to the northwest, Strinava Glacier to the northeast and Dater Glacier to the south, and is separated from the ridge of Mount Levack to the north by Zmeevo Pass. The mountain was first mapped by the United States Geological Survey from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1957–59, and was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Lieutenant Lawrence J. Farrell, U.S. Navy, who died in the crash of a UB-1 Otter airplane at Marble Point on January 4, 1959. See also * Mountains in Antarctica This is a list of all the Ultra prominent peaks (with topographic prominence greater than 1,500 metres) in Antarctica. Some islands in the South Atlantic have also been included and can be found at the end of the list. Antarctica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mamarchev Peak
Mamarchev Peak ( bg, Мамарчев връх, Mamarchev vrah, ) is the peak with tween heights both rising to Reference Elevation Model of Antarctica. Polar Geospatial Center. University of Minnesota, 2019 in the north part of in central in , |
Johnson Col
Johnson Col () is a col at about , located in the Sullivan Heights west-southwest of Mount Farrell in the central part of the Sentinel Range of the Ellsworth Mountains, Antarctica. It was first mapped by the United States Geological Survey from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1957–59, and was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Earl F. Johnson, a U.S. Navy utilitiesman at South Pole Station South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west. Etymology The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sun� ... in 1957. Maps Vinson Massif. Scale 1:250 000 topographic map. Reston, Virginia: US Geological Survey, 1988. Antarctic Digital Database (ADD).Scale 1:250000 topographic map of Antarctica. Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR). Since 1993, regularly updated. References Mountain passes of Ellsworth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Science Foundation
The National Science Foundation (NSF) is an independent agency of the United States government that supports fundamental research and education in all the non-medical fields of science and engineering. Its medical counterpart is the National Institutes of Health. With an annual budget of about $8.3 billion (fiscal year 2020), the NSF funds approximately 25% of all federally supported basic research conducted by the United States' colleges and universities. In some fields, such as mathematics, computer science, economics, and the social sciences, the NSF is the major source of federal backing. The NSF's director and deputy director are appointed by the President of the United States and confirmed by the United States Senate, whereas the 24 president-appointed members of the National Science Board (NSB) do not require Senate confirmation. The director and deputy director are responsible for administration, planning, budgeting and day-to-day operations of the foundation, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Studies
Marine is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the sea or ocean. Marine or marines may refer to: Ocean * Maritime (other) * Marine art * Marine biology * Marine debris * Marine habitats * Marine life * Marine pollution Military * Marines, a naval-based infantry force ** United States Marine Corps ** Royal Marines of the UK ** Brazilian Marine Corps ** Spanish Marine Infantry ** Fusiliers marins (France) ** Indonesian Marine Corps ** Republic of China Marine Corps ** Republic of Korea Marine Corps ** Royal Thai Marine Corps *"Marine" also means "navy" in several languages: ** Austro-Hungarian Navy () ** Belgian Navy (, , ) ** Royal Canadian Navy () *** Provincial Marine (1796–1910), a predecessor to the Royal Canadian Navy ** Navy of the Democratic Republic of the Congo () ** Royal Danish Navy () ** Finnish Navy (, ) ** French Navy () ** Gabonese Navy () ** German Navy () ** Royal Moroccan Navy () ** Royal Netherlands Navy () ** Swedish Navy () Places * Marines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hancock Institute
Hancock may refer to: Places in the United States * Hancock, Iowa * Hancock, Maine * Hancock, Maryland * Hancock, Massachusetts * Hancock, Michigan * Hancock, Minnesota * Hancock, Missouri * Hancock, New Hampshire ** Hancock (CDP), New Hampshire * Hancock, New York, a town ** Hancock (village), New York, in the town of Hancock * Hancock, Austin, Texas, a neighborhood * Hancock, Vermont * Hancock (town), Wisconsin ** Hancock, Wisconsin, a village within the town * Hancock County (other), a list of counties in ten U.S. states * Hancock Township (other) * Mount Hancock (other) * Hancock Park, Los Angeles, California People * Hancock (surname), with list of people with the surname Entertainment * ''Hancock'' (film), a 2008 superhero film starring Will Smith * ''Hancock's Half Hour'', a British BBC radio and TV comedy programme, eventually shortened to ''Hancock'' * ''Hancock'' (1963 TV series), a 1963 British ITV television series * ''Hancock'', a 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weddell Sea
The Weddell Sea is part of the Southern Ocean and contains the Weddell Gyre. Its land boundaries are defined by the bay formed from the coasts of Coats Land and the Antarctic Peninsula. The easternmost point is Cape Norvegia at Princess Martha Coast, Queen Maud Land. To the east of Cape Norvegia is the King Haakon VII Sea. Much of the southern part of the sea is covered by a permanent, massive ice shelf field, the Filchner-Ronne Ice Shelf. The sea is contained within the two overlapping Antarctic territorial claims of Argentine Antarctica, the British Antarctic Territory, and also resides partially within the Antarctic Chilean Territory. At its widest the sea is around across, and its area is around . Various ice shelves, including the Filchner-Ronne Ice Shelf, fringe the Weddell sea. Some of the ice shelves on the east side of the Antarctic Peninsula, which formerly covered roughly of the Weddell Sea, had completely disappeared by 2002. The Weddell Sea has been d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |