|
Sulfonylureas
Sulfonylureas or sulphonylureas are a class of organic compounds used in medicine and agriculture. The functional group consists of a sulfonyl group (-S(=O)2) with its sulphur atom bonded to a nitrogen atom of a ureylene group (N,N-dehydrourea, a dehydrogenated derivative of urea). The side chains R1 and R2 distinguish various sulfonylureas. Sulfonylureas are the most widely used herbicide. Agricultural uses Many sulfonylureas are also used as herbicides, because they can interfere with plant biosynthesis of certain amino acids. As herbicides sulfonylureas function by interfering with biosynthesis of the amino acids valine, isoleucine, and leucine, specifically via acetolactate synthase inhibition. Compounds in this class include amidosulfuron, azimsulfuron, bensulfuron-methyl, chlorimuron-ethyl, chlorsulfuron, ethametsulfuron-methyl, cinosulfuron, ethoxysulfuron, flazasulfuron, flupyrsulfuron-methyl-sodium, imazosulfuron, metsulfuron-methyl, nicosulfuron, oxasulfuron, primisu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antidiabetic Drug
Drugs used in diabetes treat types of diabetes mellitus by decreasing blood sugar level, glucose levels in the blood. With the exception of Insulin (medication), insulin, most GLP-1 receptor agonists (liraglutide, exenatide, and others), and pramlintide, all diabetes medications are administered orally and are thus called oral hypoglycemic agents or oral antihyperglycemic agents. There are different classes of hypoglycemic drugs, and selection of the appropriate agent depends on the nature of diabetes, age, and situation of the person, as well as other patient factors. Type 1 diabetes or Diabetes mellitus is an endocrine disorder characterized by hyperglycemia due to autoimmune destruction of insulin-secreting pancreatic beta cells or from variable degrees of insulin resistance and deficiency. Chronic hyperglycemia of diabetes can lead to multiorgan damage, resulting in renal, neurologic, cardiovascular, and other serious complications. The treatment for Type 1 diabetes is insul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metformin
Metformin, sold under the brand name Glucophage, among others, is the main first-line medication for the treatment of type2 diabetes, particularly in people who are overweight. It is also used in the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome, and is sometimes used as an off-label adjunct to lessen the risk of metabolic syndrome in people who take antipsychotic medication. It has been shown to inhibit inflammation, and is not associated with weight gain. Metformin is taken by mouth. Metformin is generally well tolerated. Common adverse effects include diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal pain. It has a small risk of causing low blood sugar. High blood lactic acid level (acidosis) is a concern if the medication is used in overly large doses or prescribed in people with severe kidney problems. Metformin is a biguanide anti- hyperglycemic agent. It works by decreasing glucose production in the liver, increasing the insulin sensitivity of body tissues, and increasing GDF15 s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
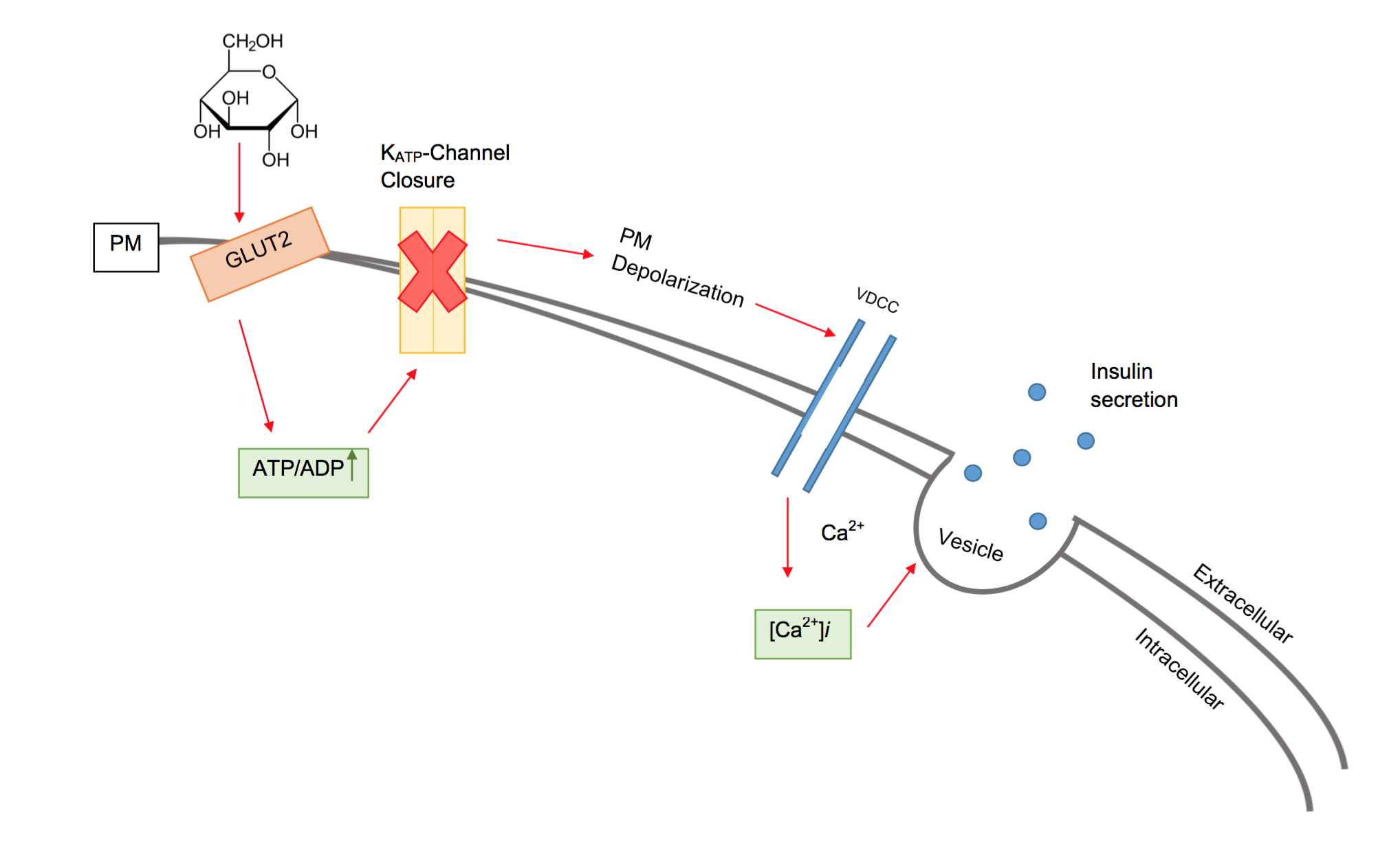
Neonatal Diabetes
Neonatal diabetes mellitus (NDM) is a disease that affects an infant and their body's ability to produce or use insulin. NDM is a kind of diabetes that is monogenic (regulated by a single gene) and arises in the first 6 months of life. Infants do not produce enough insulin, leading to an increase in glucose accumulation. It is a rare disease, occurring in only one in 100,000 to 500,000 live births. NDM can be mistaken for the much more common type 1 diabetes, but type 1 diabetes usually occurs later than the first 6 months of life. There are two types of NDM: permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus (PNDM), a lifelong condition, and transient neonatal diabetes mellitus (TNDM), a form of diabetes that disappears during the infant stage but may reappear later in life. Specific genes that can cause NDM have been identified. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Cell
Beta cells (β-cells) are specialized endocrine cells located within the pancreatic islets of Langerhans responsible for the production and release of insulin and amylin. Constituting ~50–70% of cells in human islets, beta cells play a vital role in maintaining blood glucose levels. Problems with beta cells can lead to disorders such as diabetes. Function The function of beta cells is primarily centered around the synthesis and secretion of hormones, particularly insulin and amylin. Both hormones work to keep blood glucose levels within a narrow, healthy range by different mechanisms. Insulin facilitates the uptake of glucose by cells, allowing them to use it for energy or store it for future use. Amylin helps regulate the rate at which glucose enters the bloodstream after a meal, slowing down the absorption of nutrients by inhibit gastric emptying. Insulin synthesis Beta cells are the only site of insulin synthesis in mammals. As glucose stimulates insulin secretion, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbicide
Herbicides (, ), also commonly known as weed killers, are substances used to control undesired plants, also known as weeds.EPA. February 201Pesticides Industry. Sales and Usage 2006 and 2007: Market Estimates. Summary in press releasMain page for EPA reports on pesticide use ihere Selective herbicides control specific weed species while leaving the desired crop relatively unharmed, while non-selective herbicides (sometimes called "total weed killers") kill plants indiscriminately. The combined effects of herbicides, nitrogen fertilizer, and improved cultivars has increased yields (per acre) of major crops by three to six times from 1900 to 2000. In the United States in 2012, about 91% of all herbicide usage, was determined by weight applied, in agriculture. In 2012, world pesticide expenditures totaled nearly US$24.7 billion; herbicides were about 44% of those sales and constituted the biggest portion, followed by insecticides, fungicides, and fumigants. Herbicide is also used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metsulfuron-methyl
Metsulfuron-methyl is an organic compound classified as a sulfonylurea herbicide, which kills broadleaf weeds and some annual grasses. It is a systemic compound with foliar and soil activity, that inhibits cell division in shoots and root In vascular plants, the roots are the plant organ, organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often bel ...s. It has residual activity in soils, allowing it to be used infrequently but requiring up to 22 months before planting certain crops (sunflowers, flax, corn, or safflower). It has very low toxicity to mammals, birds, fish, and insects but is a moderate eye irritant. References Sulfonylurea herbicides Benzenesulfonylureas Triazines Benzoate esters Methyl esters Group 2 herbicides {{ester-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfometuron-methyl
Sulfometuron methyl is an organic compound used as an herbicide. It is classed as a sulfonylurea. It functions via the inhibition of the enzyme acetolactate synthase, which catalyzes the first step in biosynthesis of the branched-chain amino acids valine, leucine, and isoleucine Isoleucine (symbol Ile or I) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the depro .... References {{Herbicides Benzenesulfonylureas Herbicides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribenuron-methyl
Tribenuron in the form of tribenuron-methyl is a sulfonylurea herbicide. Its mode of action is the inhibition of acetolactate synthase, group 2 of the Herbicide Resistance Action Committee's classification scheme. Chemistry In the 1970s, chemists at DuPont worked extensively on sulfonylurea herbicides, following the invention of this class of herbicides by George Levitt which had led to the commercialisation of chlorsulfuron. Tribenuron (the carboxylic acid) and its methyl ester were first disclosed in general terms in one of Levitt's patents and subsequently the ester was subject to further patenting and selected for development under the code name DPX L5300. In the final step of its synthesis, 2-methoxycarbonylbenzenesulfonyl isocyanate was condensed with 2-methylamino-4-methoxy-6-methyl-1,3,5-triazine to form the sulfonylurea product. : Mode of action Tribenuron is an herbicide that acts as an acetolactate synthase inhibitor. For the purposes of herbicide resistance manag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medicine
Medicine is the science and Praxis (process), practice of caring for patients, managing the Medical diagnosis, diagnosis, prognosis, Preventive medicine, prevention, therapy, treatment, Palliative care, palliation of their injury or disease, and Health promotion, promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention (medical), prevention and treatment of illness. Contemporary medicine applies biomedical sciences, biomedical research, medical genetics, genetics, and medical technology to diagnosis (medical), diagnose, treat, and prevent injury and disease, typically through pharmaceuticals or surgery, but also through therapies as diverse as psychotherapy, splint (medicine), external splints and traction, medical devices, biologic medical product, biologics, and Radiation (medicine), ionizing radiation, amongst others. Medicine has been practiced since Prehistoric medicine, prehistoric times, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop functioning properly. Signs and symptoms of stroke may include an hemiplegia, inability to move or feel on one side of the body, receptive aphasia, problems understanding or expressive aphasia, speaking, dizziness, or homonymous hemianopsia, loss of vision to one side. Signs and symptoms often appear soon after the stroke has occurred. If symptoms last less than 24 hours, the stroke is a transient ischemic attack (TIA), also called a mini-stroke. subarachnoid hemorrhage, Hemorrhagic stroke may also be associated with a thunderclap headache, severe headache. The symptoms of stroke can be permanent. Long-term complications may include pneumonia and Urinary incontinence, loss of b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myocardial Infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when Ischemia, blood flow decreases or stops in one of the coronary arteries of the heart, causing infarction (tissue death) to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is retrosternal Angina, chest pain or discomfort that classically radiates to the left shoulder, arm, or jaw. The pain may occasionally feel like heartburn. This is the dangerous type of acute coronary syndrome. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, nausea, presyncope, feeling faint, a diaphoresis, cold sweat, Fatigue, feeling tired, and decreased level of consciousness. About 30% of people have atypical symptoms. Women more often present without chest pain and instead have neck pain, arm pain or feel tired. Among those over 75 years old, about 5% have had an MI with little or no history of symptoms. An MI may cause heart failure, an Cardiac arrhythmia, irregular heartbeat, cardiogenic shock or cardiac arrest. Most MIs occur d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |