|
Sulfinate
Sulfinic acids are oxoacids of sulfur with the structure RSO(OH). In these organosulfur compounds, sulfur is Molecular geometry, pyramidal. Structure and properties Sulfinic acids RSO2H are typically more acidic than the corresponding carboxylic acid RCO2H. Sulfur is pyramidal, consequently sulfinic acids are chiral. The free acids are typically unstable, disproportionating to the sulfonic acid RSO3H and thiosulfonate RSSO2R. The formal anhydride of a sulfinic acid has no oxygen atom bridge, but is instead a sulfinyl sulfone (R–S+(–O−)–S2+(–O−)2–), and disproportionation is believed to occur through the free-radical fission of this intermediate. Alkylation of sulfinic acids can give either sulfones or sulfinate esters, depending on the solvent and reagent. Strongly polarized reactants (e.g. trimethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate) give esters, whereas relatively unpolarized reactants (e.g. an alkyl halide or enone) give sulfones. Sulf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfone
In organic chemistry, a sulfone is a organosulfur compound containing a sulfonyl () functional group attached to two carbon atoms. The central hexavalent sulfur atom is double-bonded to each of two oxygen atoms and has a single bond to each of two carbon atoms, usually in two separate hydrocarbon substituents. Synthesis and reactions By oxidation of thioethers and sulfoxides Sulfones are typically prepared by organic oxidation of thioethers, often referred to as sulfides. Sulfoxides are intermediates in this route. For example, dimethyl sulfide oxidizes to dimethyl sulfoxide and then to dimethyl sulfone. From SO2 : Sulfur dioxide is a convenient and widely used source of the sulfonyl functional group. Specifically, Sulfur dioxide participates in cycloaddition reactions with dienes. The industrially useful solvent sulfolane is prepared by addition of sulfur dioxide to buta-1,3-diene followed by hydrogenation of the resulting sulfolene. From sulfonyl and sulfuryl halides Sulf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disulfide
In chemistry, a disulfide (or disulphide in British English) is a compound containing a functional group or the anion. The linkage is also called an SS-bond or sometimes a disulfide bridge and usually derived from two thiol groups. In inorganic chemistry, the anion appears in a few rare minerals, but the functional group has tremendous importance in biochemistry. Disulfide bridges formed between thiol groups in two cysteine residues are an important component of the tertiary and quaternary structure of proteins. Compounds of the form are usually called ''persulfides'' instead. Organic disulfides Structure Disulfides have a C–S–S–C dihedral angle approaching 90°. The S–S bond length is 2.03 Å in diphenyl disulfide, similar to that in elemental sulfur. Disulfides are usually symmetric but they can also be unsymmetric. Symmetrical disulfides are compounds of the formula . Most disulfides encountered in organosulfur chemistry are symmetrical disulfides. Unsymme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organosulfur Compound
Organosulfur chemistry is the study of the properties and synthesis of organosulfur compounds, which are organic compounds that contain sulfur. They are often associated with foul odors, but many of the sweetest compounds known are organosulfur derivatives, e.g., saccharin. Nature is abound with organosulfur compounds—sulfur is vital for life. Of the 20 common amino acids, two ( cysteine and methionine) are organosulfur compounds, and the antibiotics penicillin and sulfa drugs both contain sulfur. While sulfur-containing antibiotics save many lives, sulfur mustard is a deadly chemical warfare agent. Fossil fuels, coal, petroleum, and natural gas, which are derived from ancient organisms, necessarily contain organosulfur compounds, the removal of which is a major focus of oil refineries. Sulfur shares the chalcogen group with oxygen, selenium, and tellurium, and it is expected that organosulfur compounds have similarities with carbon–oxygen, carbon–selenium, and car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiosulfonate
Thiosulfonate esters are organosulfur compounds with the formula . The parent member ''S''-methyl methanethiosulfonate is a colorless liquid. Thiosulfonate esters are usually produced by oxidation of disulfides or the nucleophilic attack of thiolates on organosulfonyl halides. The simplest thiosulfonate, can however be prepared from dimethyl sulfoxide by treatment with oxalyl chloride. Thiosulfonate also refers to the thiosulfonate anion and its salts. Alkali metal organylthiosulfonates are the salts of organylthiosulfonic acids (e.g., sodium methanethiosulfonate ). They are prepared by the reaction of organosulfonyl chlorides with sources of sulfide. Oxidation with mCPBA gives disulfones. See also *Bunte salts are related organosulfur compounds containing the anion with the formula *Thiosulfinate In organosulfur chemistry, thiosulfinate is a functional group consisting of the linkage (R refers to organic substituents). Thiolsulfinates are also named as alkanethiosulf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur Dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless gas with a pungent smell that is responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is released naturally by volcanic activity and is produced as a by-product of metals refining and the burning of Sour gas, sulfur-Sour crude oil, bearing fossil fuels. Sulfur dioxide is somewhat toxic to humans, although only when inhaled in relatively large quantities for a period of several minutes or more. It was known to medieval alchemy, alchemists as "volatile spirit of sulfur". Structure and bonding SO2 is a bent molecule with ''C''2v Point groups in three dimensions, symmetry point group. A valence bond theory approach considering just ''s'' and ''p'' orbitals would describe the bonding in terms of resonance (chemistry), resonance between two resonance structures. The sulfur–oxygen bond has a bond order of 1.5. There is support f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
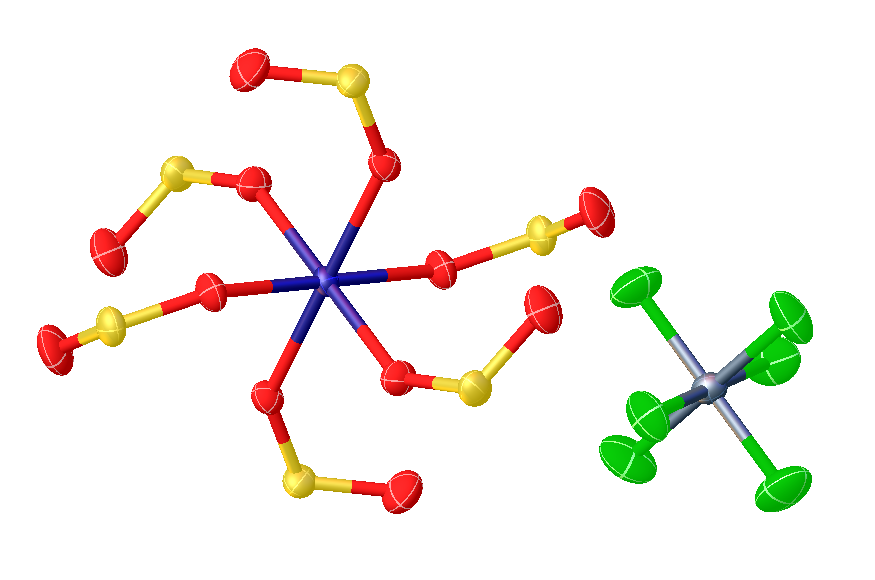
Metal Sulfur Dioxide Complex
In organometallic chemistry, metal sulfur dioxide complexes are complexes that contain sulfur dioxide, , bonded to a transition metal. Such compounds are common but are mainly of theoretical interest. Historically, the study of these compounds has provided insights into the mechanisms of migratory insertion reactions. Bonding modes Sulfur dioxide forms complexes with many transition metals. Most numerous are complexes with metals in oxidation state 0 or +1. In most cases SO2 binds in monodentate fashion, attaching to the metal through sulfur. Such complexes are further subdivided according to the planarity or pyramidalization at sulfur. The various bonding modes are: * η1-SO2, planar (meaning that the MSO2 subunit forms a plane). In such complexes, SO2 is classified as a 2e donor complemented by pi- back bonding into the empty pz orbital localized on sulfur. * η1-SO2, pyramidal (meaning that the MSO2 subunit is pyramidal at sulfur). In such complexes, SO2 is classifie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleophile
In chemistry, a nucleophile is a chemical species that forms bonds by donating an electron pair. All molecules and ions with a free pair of electrons or at least one pi bond can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they are Lewis bases. ''Nucleophilic'' describes the affinity of a nucleophile to bond with positively charged Atomic nucleus, atomic nuclei. Nucleophilicity, sometimes referred to as nucleophile strength, refers to a substance's nucleophilic character and is often used to compare the affinity of atoms. Neutral nucleophilic reactions with solvents such as Alcohol (chemistry), alcohols and water are named solvolysis. Nucleophiles may take part in nucleophilic substitution, whereby a nucleophile becomes attracted to a full or partial positive charge, and nucleophilic addition. Nucleophilicity is closely related to basicity. The difference between the two is, that basicity is a thermodynamic property (i.e. relates to an equilibrium state), but nucleop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Cyanide
Sodium cyanide is a compound with the formula Na C N and the structure . It is a white, water-soluble solid. Cyanide has a high affinity for metals, which leads to the high toxicity of this salt. Its main application, in gold mining, also exploits its high reactivity toward metals. It is a moderately strong base. Production and chemical properties Sodium cyanide is produced by treating hydrogen cyanide with sodium hydroxide: : Worldwide production was estimated at 500,000 tons in the year 2006. Formerly it was prepared by the Castner process involving the reaction of sodium amide with carbon at elevated temperatures. : The structure of solid NaCN is related to that of sodium chloride. The anions and cations are each six-coordinate. Potassium cyanide (KCN) adopts a similar structure. When treated with acid, it forms the toxic gas hydrogen cyanide: : Because the salt is derived from a weak acid, sodium cyanide readily reverts to HCN by hydrolysis; the moist solid emits smal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiolate
In organic chemistry, a thiol (; ), or thiol derivative, is any organosulfur compound of the form , where R represents an alkyl or other organic substituent. The functional group itself is referred to as either a thiol group or a sulfhydryl group, or a sulfanyl group. Thiols are the sulfur analogue of alcohols (that is, sulfur takes the place of oxygen in the hydroxyl () group of an alcohol), and the word is a blend of "''thio-''" with "alcohol". Many thiols have strong odors resembling that of garlic, cabbage or rotten eggs. Thiols are used as odorants to assist in the detection of natural gas (which in pure form is odorless), and the smell of natural gas is due to the smell of the thiol used as the odorant. Nomenclature Thiols are sometimes referred to as mercaptans () or mercapto compounds, a term introduced in 1832 by William Christopher Zeise and is derived from the Latin ('capturing mercury')''Oxford American Dictionaries'' ( Mac OS X Leopard). because the thiolate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |