|
Sulfametoxydiazine
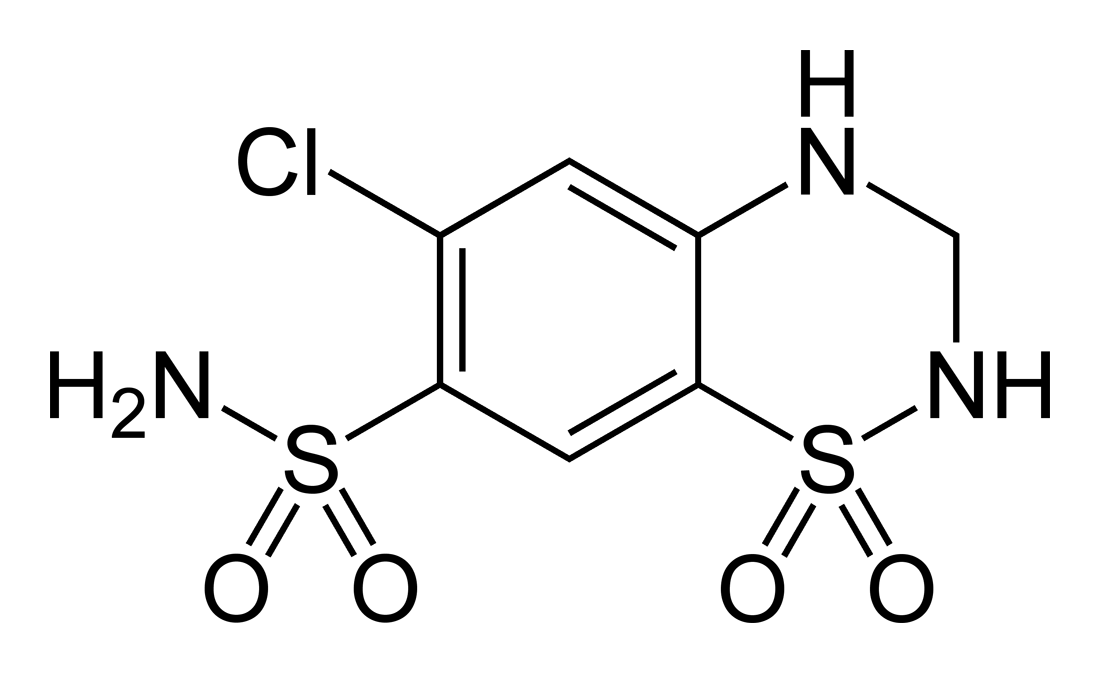
Sulfametoxydiazine (INN) or sulfamethoxydiazine (USAN: sulfameter) is a long-acting sulfonamide antibacterial. It is used as a leprostatic agent and in the treatment of urinary tract infections. Sulfamethoxydiazine is also used to treat and prevent diseases in animals. Because of its relatively long persistence, sulfamethoxydiazine residue can be detected in meat, dairy, and eggs, and is considered hazardous to human health. The United States and Japan both prohibit sulfamethoxydiazine residue in food, whereas the Codex Alimentarius Commission The is a collection of internationally recognized standards, codes of practice, guidelines, and other recommendations published by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and World Health Organization (WHO) of the United Nations relating to f ... states that the maximum limit for sulfonamides in animal tissues is 100 μg/kg. References Pyrimidines Sulfonamide antibiotics Phenol ethers 4-Aminophenyl compounds {{antiinfe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Adopted Name
A United States Adopted Name (USAN) is a unique nonproprietary name assigned to a medication marketed in the United States. Each name is assigned by the USAN Council, which is co-sponsored by the American Medical Association (AMA), the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP), and the American Pharmacists Association (APhA). The USAN Program states that its goal is to select simple, informative, and unique nonproprietary names (also called generic names) for drugs by establishing logical nomenclature classifications based on pharmacological or chemical relationships. In addition to drugs, the USAN Council names agents for gene therapy and cell therapy, contact lens polymers, surgical materials, diagnostics, carriers, and substances used as an excipient. The USAN Council works in conjunction with the World Health Organization (WHO) international nonproprietary name (INN) Expert Committee and national nomenclature groups to standardize drug nomenclature and establish rule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfonamide (medicine)
Sulfonamide is a functional group (a part of a molecule) that is the basis of several groups of medication, drugs, which are called sulphonamides, sulfa drugs or sulpha drugs. The original antibacterial sulfonamides are synthetic antimicrobial agents that contain the Sulfonamide (chemistry), sulfonamide group. Some sulfonamides are also devoid of antibacterial activity, e.g., the anticonvulsant sultiame. The sulfonylureas and thiazide diuretics are newer drug groups based upon the antibacterial sulfonamides. Drug allergy, Allergies to sulfonamides are common. The overall incidence of adverse drug reactions to sulfa antibiotics is approximately 3%, close to penicillin; hence medications containing sulfonamides are prescribed carefully. Sulfonamide drugs were the first broadly effective antibacterials to be used systemically, and paved the way for the antibiotic revolution in medicine. Function In bacteria, antibacterial sulfonamides act as competitive inhibitors of the enz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibacterial
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of such infections. They may either kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the ones which cause the common cold or influenza. Drugs which inhibit growth of viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals. Antibiotics are also not effective against fungi. Drugs which inhibit growth of fungi are called antifungal drugs. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against microbes, but in the usual medical usage, antibiotics (such as penicillin) are those produced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leprostatic Agent
A leprostatic agent is a drug that interferes with proliferation of the bacterium that causes leprosy. The following agents are leprostatic agents: * acedapsone * clofazimine * dapsone * desoxyfructo-serotonin * diucifon * ethionamide * rifampicin * rifapentine * sulfameter * thalidomide Leprosy is a chronic infectious disease caused by ''Mycobacterium leprae''. Host defenses are crucial in determining the patient's response to the disease, the clinical presentation, and the bacillary load. These factors also influence the length of therapy and the risk of adverse reactions to medication. ''M. leprae'' cannot be grown on routine laboratory culture media, so drug sensitivity testing in vitro is not possible. Growth and drug susceptibility testing are done by injecting into animal models. One description of a clinical picture that results from tuberculoid leprosy is characterized by intact cell-mediated immunity, a positive lepromin skin reaction, granuloma formation, and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urinary Tract Infection
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that affects a part of the urinary tract. Lower urinary tract infections may involve the bladder (cystitis) or urethra (urethritis) while upper urinary tract infections affect the kidney (pyelonephritis). Symptoms from a lower urinary tract infection include suprapubic pain, painful urination (dysuria), frequency and urgency of urination despite having an empty bladder. Symptoms of a kidney infection, on the other hand, are more systemic and include fever or Abdominal pain, flank pain usually in addition to the symptoms of a lower UTI. Rarely, the urine may appear Hematuria, bloody. Symptoms may be vague or non-specific at the extremities of age (i.e. in patients who are very young or old). The most common cause of infection is ''Escherichia coli'', though other bacteria or fungi may sometimes be the cause. Risk factors include female anatomy, sexual intercourse, diabetes mellitus, diabetes, obesity, catheterisation, and famil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Codex Alimentarius Commission
The is a collection of internationally recognized standards, codes of practice, guidelines, and other recommendations published by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and World Health Organization (WHO) of the United Nations relating to food, food production, food labeling, and food safety. History and governance Its name is derived from the Codex Alimentarius Austriacus. Its texts are developed and maintained by the Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC), a body established in early November 1961 by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Joined by the World Health Organization (WHO) in June 1962, the CAC held its first session in Rome in October 1963. The Commission's main goals are to protect the health of consumers, to facilitate international trade, and to ensure fair practices in the international food trade.Understanding Codex', World Health Organization and the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (5th ed. Sept. 2018) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrimidines
Pyrimidine (; ) is an aromatic, heterocyclic, organic compound similar to pyridine (). One of the three diazines (six-membered heterocyclics with two nitrogen atoms in the ring), it has nitrogen atoms at positions 1 and 3 in the ring. The other diazines are pyrazine (nitrogen atoms at the 1 and 4 positions) and pyridazine (nitrogen atoms at the 1 and 2 positions). In nucleic acids, three types of nucleobases are pyrimidine derivatives: cytosine (C), thymine (T), and uracil (U). Occurrence and history The pyrimidine ring system has wide occurrence in nature as substituted and ring fused compounds and derivatives, including the nucleotides cytosine, thymine and uracil, thiamine (vitamin B1) and alloxan. It is also found in many synthetic compounds such as barbiturates and the HIV drug zidovudine. Although pyrimidine derivatives such as alloxan were known in the early 19th century, a laboratory synthesis of a pyrimidine was not carried out until 1879, when Grimaux reported the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfonamide Antibiotics
Sulfonamide is a functional group (a part of a molecule) that is the basis of several groups of medication, drugs, which are called sulphonamides, sulfa drugs or sulpha drugs. The original antibacterial sulfonamides are synthetic antimicrobial agents that contain the Sulfonamide (chemistry), sulfonamide group. Some sulfonamides are also devoid of antibacterial activity, e.g., the anticonvulsant sultiame. The sulfonylureas and thiazide diuretics are newer drug groups based upon the antibacterial sulfonamides. Drug allergy, Allergies to sulfonamides are common. The overall incidence of adverse drug reactions to sulfa antibiotics is approximately 3%, close to penicillin; hence medications containing sulfonamides are prescribed carefully. Sulfonamide drugs were the first broadly effective antibacterials to be used systemically, and paved the way for the antibiotic revolution in medicine. Function In bacteria, antibacterial sulfonamides act as competitive inhibitors of the enz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenol Ethers
Phenol (also known as carbolic acid, phenolic acid, or benzenol) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile and can catch fire. The molecule consists of a phenyl group () bonded to a hydroxy group (). Mildly acidic, it requires careful handling because it can cause chemical burns. It is acutely toxic and is considered a health hazard. Phenol was first extracted from coal tar, but today is produced on a large scale (about 7 million tonnes a year) from petroleum-derived feedstocks. It is an important industrial commodity as a precursor to many materials and useful compounds, and is a liquid when manufactured. It is primarily used to synthesize plastics and related materials. Phenol and its chemical derivatives are essential for production of polycarbonates, epoxies, explosives such as picric acid, Bakelite, nylon, detergents, herbicides such as phenoxy herbicides, and numerous pharmaceutical drugs. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |