|
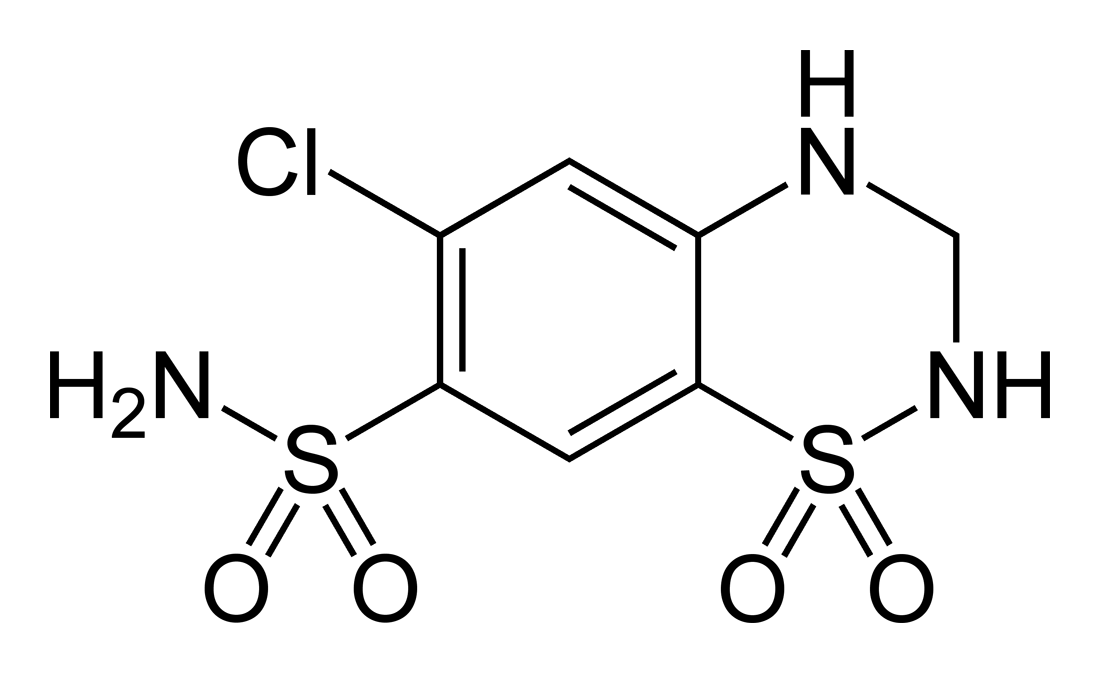
Sulfamerazine
Sulfamerazine is a sulfonamide antibacterial. Synthesis See also *Sulfadiazine *Sulfamethazine *Sulfamethizole References External links Sulfamerazine(DrugBank) Sulfamerazine(NIST The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce whose mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into physical sci ...) Sulfonamide antibiotics Pyrimidines {{dermatologic-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfamerazine Synthesis
Sulfamerazine is a sulfonamide (medicine), sulfonamide antibacterial. Synthesis See also *Sulfadiazine *Sulfamethazine *Sulfamethizole References External links Sulfamerazine(DrugBank) Sulfamerazine (NIST) Sulfonamide antibiotics Pyrimidines {{dermatologic-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
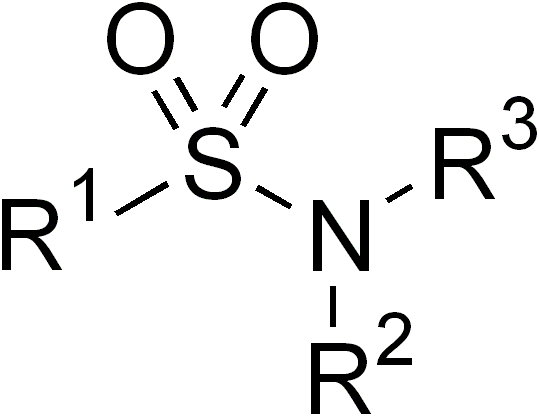
Sulfonamide (medicine)
Sulfonamide is a functional group (a part of a molecule) that is the basis of several groups of drugs, which are called sulphonamides, sulfa drugs or sulpha drugs. The original antibacterial sulfonamides are synthetic (nonantibiotic) antimicrobial agents that contain the sulfonamide group. Some sulfonamides are also devoid of antibacterial activity, e.g., the anticonvulsant sultiame. The sulfonylureas and thiazide diuretics are newer drug groups based upon the antibacterial sulfonamides. Allergies to sulfonamides are common. The overall incidence of adverse drug reactions to sulfa antibiotics is approximately 3%, close to penicillin; hence medications containing sulfonamides are prescribed carefully. Sulfonamide drugs were the first broadly effective antibacterials to be used systemically, and paved the way for the antibiotic revolution in medicine. Function In bacteria, antibacterial sulfonamides act as competitive inhibitors of the enzyme dihydropteroate synthas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibacterial
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of such infections. They may either kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the common cold or influenza; drugs which inhibit viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals rather than antibiotics. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against microbes, but in the usual medical usage, antibiotics (such as penicillin) are those produced naturally (by one microorganism fighting another), whereas non-antibiotic antibacterials (such as sulfonamides and anti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfadiazine
Sulfadiazine is an antibiotic. Used together with pyrimethamine, a dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor, it is the treatment of choice for toxoplasmosis, which is caused by a protozoan parasite. It is a second-line treatment for otitis media, prophylaxis of rheumatic fever, chancroid, chlamydia, and infections by '' Haemophilus influenzae''. It is also used as adjunct therapy for chloroquine-resistant malaria and several forms of bacterial meningitis. It is taken by mouth. Sulfadiazine is available in multiple generic tablets of 500 mg. For urinary tract infections, the usual dose is 4 to 6 grams daily in 3 to 6 divided doses. Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, headache, fever, rash, depression, and pancreatitis. It should not be used in people who have severe liver problems, kidney problems, or porphyria. If used during pregnancy, it may increase the risk of kernicterus in the baby. While the company that makes it does not recommend use during breastfeedi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfamethazine
Sulfadimidine or sulfamethazine is a sulfonamide antibacterial. There are non-standardized abbreviations for it as "sulfadimidine" (abbreviated SDI and more commonly but less reliably SDD) and as "sulfamethazine" (abbreviated SMT and more commonly but less reliably SMZ). Other names include sulfadimerazine, sulfadimezine, and sulphadimethylpyrimidine. References Further reading * ChemDB"Sulfamethazine" ''ChemDB'', National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), National Institutes of Health (NIH) * * PubChem"Sulfamethazine - Substance Summary" ''PubChem'', National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), National Library of Medicine (NLM), National Institutes of Health The National Institutes of Health, commonly referred to as NIH (with each letter pronounced individually), is the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and public health research. It was founded in the late ... (NIH) Sulfonamide antibiotics P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfamethizole
Sulfamethizole is a sulfonamide antibiotic An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy, .... References * * * Sulfonamide antibiotics Thiadiazoles {{dermatologic-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DrugBank
The DrugBank database is a comprehensive, freely accessible, online database containing information on drugs and drug targets created and maintained by the University of Alberta and The Metabolomics Innovation Centre located in Alberta, Canada. As both a bioinformatics and a cheminformatics resource, DrugBank combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. DrugBank has used content from Wikipedia; Wikipedia also often links to Drugbank, posing potential circular reporting issues. The DrugBank Online website is available to the public as a free-to-access resource. However, use and re-distribution of content from DrugBank Online or the underlying DrugBank Data, in whole or part, and for any purpose requires a license. Academic users can apply for a free license for certain use cases while all other users require a paid license. The latest release of the database (vers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NIST
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce whose mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into physical science laboratory programs that include nanoscale science and technology, engineering, information technology, neutron research, material measurement, and physical measurement. From 1901 to 1988, the agency was named the National Bureau of Standards. History Background The Articles of Confederation, ratified by the colonies in 1781, provided: The United States in Congress assembled shall also have the sole and exclusive right and power of regulating the alloy and value of coin struck by their own authority, or by that of the respective states—fixing the standards of weights and measures throughout the United States. Article 1, section 8, of the Constitution of the United States, ratified in 1789, granted these powers to the new Congr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfonamide Antibiotics
Sulfonamide is a functional group (a part of a molecule) that is the basis of several groups of drugs, which are called sulphonamides, sulfa drugs or sulpha drugs. The original antibacterial sulfonamides are synthetic (nonantibiotic) antimicrobial agents that contain the sulfonamide group. Some sulfonamides are also devoid of antibacterial activity, e.g., the anticonvulsant sultiame. The sulfonylureas and thiazide diuretics are newer drug groups based upon the antibacterial sulfonamides. Allergies to sulfonamides are common. The overall incidence of adverse drug reactions to sulfa antibiotics is approximately 3%, close to penicillin; hence medications containing sulfonamides are prescribed carefully. Sulfonamide drugs were the first broadly effective antibacterials to be used systemically, and paved the way for the antibiotic revolution in medicine. Function In bacteria, antibacterial sulfonamides act as competitive inhibitors of the enzyme dihydropteroate synthase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |