|
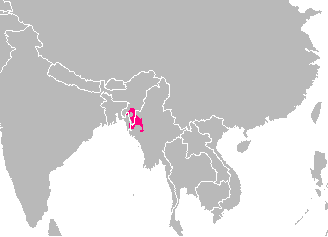
Sukte Clan
The Sukte are one of the clans of Tedim Chins (also called "Zomi") that mainly inhabit the Tedim district in Myanmar, with small numbers in India, in Manipur, Meghalaya and Assam states. They are recognized as a Scheduled Tribe in Manipur. From 1995, they have been part of the Zomi Re-unification Organisation in Manipur. Social status They were listed as Salhte in the 1947 Constitution where they are among the groups given Adivasi status. They are commonly referred to as the Zo by others, but they use the name Sukte for themselves. Population Only five people were counted in this ethnic group in the 1981 census. However the leader of the youth group for the Kuki/zo claims there are 3,500 Sukte currently. The Sukte are agriculturalists, growing primarily maize and rice. They are mainly Christian in religion. See also *Sukte language The Tedim language is a Tibeto-Burman language spoken mostly in the southern Indo-Burmese border. It is the native language of the Tedim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tedim Chins
The Tedim people, also called Tedim Chins and Tiddim (Hai-Dim) people, are a Zomi ethnic group, part of the Chin people, primarily inhabiting the Tedim Township in the Chin State of Myanmar. They speak the Tedim language The Tedim language is a Tibeto-Burman language spoken mostly in the southern Indo-Burmese border. It is the native language of the Tedim tribe of the Zomi people, and a form of standardized dialect merging from the Sukte and Kamhau dialects ..., a northeastern Kuki-Chin language. The Tedim people were early adopters of the Zomi identity, founding the Zomi Baptist Convention in 1953, after a careful discussion of nomenclature. According to Khup Za Go, most people called "Chins" by the Burmese do not recognize that name as their identifier, and also feel the Burmese use of it to be abusive or degrading. However, the Burmese government never accepted the term "Zomi" and most outsiders do not recognize it either, and so "Chin" is often added to the label " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manipur
Manipur () is a state in northeastern India with Imphal as its capital. It borders the Indian states of Assam to the west, Mizoram to the south, and Nagaland to the north and shares the international border with Myanmar, specifically the Sagaing Region to the east and Chin State to the southeast. Covering an area of 22,330 square kilometers (8,621 mi²), the state consists mostly of hilly terrain with the 1813-square-kilometre (700 mi²) Imphal Valley inhabited by the Meitei (Manipuri) community, historically a kingdom. Surrounding hills are home to Naga and Kuki-Zo communities, who speak Tibeto-Burman languages. The official language and lingua franca, Meitei (Manipuri), also belongs to the Tibeto-Burman family. During the days of the British Raj, Manipur was one of the princely states. Prior to the British departure in 1947, Manipur acceded to the Dominion of India, along with roughly 550 other princely states. In September 1949, the ruler of Manipur signed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meghalaya
Meghalaya (; "the abode of clouds") is a states and union territories of India, state in northeast India. Its capital is Shillong. Meghalaya was formed on 21 January 1972 by carving out two districts from the Assam: the United Khasi Hills and Jaintia Hills and the Garo Hills.History of Meghalaya State Government of India The estimated population of Meghalaya in 2014 was 3,211,474. Meghalaya covers an area of approximately 22,429 square kilometres, with a length-to-breadth ratio of about 3:1.Meghalaya IBEF, India (2013) The state is bound to the south by the Bangladeshi divisions of Mymensingh Division, Mymensingh and Sylhet Division, Sylhet, to the west by the Bangladeshi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assam
Assam (, , ) is a state in Northeast India, northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra Valley, Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of . It is the second largest state in Northeast India, northeastern India by area and the largest in terms of population, with more than 31 million inhabitants. The state is bordered by Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh to the north; Nagaland and Manipur to the east; Meghalaya, Tripura, Mizoram and Bangladesh to the south; and West Bengal to the west via the Siliguri Corridor, a strip of land that connects the state to the rest of India. Assamese language, Assamese and Bodo language, Bodo are two of the official languages for the entire state and Meitei language, Meitei (Manipuri language, Manipuri) is recognised as an additional official language in three districts of Barak Valley and Hojai district. in Hojai district and for the Barak valley region, alongside Bengali language, Bengali, which is also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zomi Re-unification Organisation
The Zomi Revolutionary Army (ZRA) is a Zomi nationalist militant group formed in 1997, following an increase in ethnic tensions between the Thadou-Kuki people and the Paite people in Churachandpur district of Manipur, India. Its parent organisation, the Zomi Re-unification Organisation, was founded in April 1993. The militant organization's leader is Thanglianpau Guite. Background The Zo identity for the Kuki-Chin language speaking people spread across Northeast India and Myanmar's Chin State began to take shape soon after World War II. The people of the then Lushai Hills district in India (present-day Mizoram) rallied behind a "Mizo" ("Zo people") identity in 1946. In 1953, the Baptist Associations of Tedim, Falam and Hakha in Myanmar's Chin State adopted Zomi ("Zo people") as their "national" name (subsuming the various tribal identities). In India's Manipur state, T. Gougin formed a "United Zomi Organisation" in 1961 and "Zomi National Congress" in 1972. The final s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adivasi
The Adivasi (also transliterated as Adibasi) are heterogeneous tribal groups across the Indian subcontinent. The term is a recent invention from the 20th century and is now widely used as a self-designation by groups classified as Scheduled Tribes by the Indian government. They are officially recognized as " Scheduled Tribes" in India and as " Ethnic Minorities" in Bangladesh. They comprise 8.6% of India's population and 1.1% of Bangladesh's; or 104.2 million in India, according to the 2011 census, and 2 million in Bangladesh according to the 2010 estimate. Claiming to be among the original inhabitants of the Indian subcontinent, many present-day Adivasi communities formed during the flourishing period of the Indus Valley Civilization or after the decline of the IVC, harboring various degrees of ancestry from ancient Dravidians, Indus Valley Civilization, Indo-Aryan, Austroasiatic and Tibeto-Burman language speakers. Adivasi studies is a new scholarly field, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sukte Language
The Tedim language is a Tibeto-Burman language spoken mostly in the southern Indo-Burmese border. It is the native language of the Tedim tribe of the Zomi people, and a form of standardized dialect merging from the Sukte and Kamhau dialects. It is a subject-object verb language, and negation follows the verb. It is mutually intelligible with the Paite language. History Zomi was the primary language spoken by Pau Cin Hau, a religious leader who lived from 1859 to 1948. He also devised a logographic and later simplified alphabetic script for writing materials in Zomi. Phonology The phonology of Zomi can be described as (C)V(V)(C)T order, where C represents a consonant, V represents a vowel, T represents a tone, and parentheses enclose optional constituents of a syllable. Consonants * Approximants , wcan be heard as allophones of vowels /i̯, u̯/ within diphthongs. * /x/ can also be heard as an aspirated velar stop ʰin free variation. Vowels * Sounds /ɛ, ɔ/ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnic Groups In Northeast India
Northeast India, officially the North Eastern Region (NER), is the easternmost region of India representing both a geographic and political administrative division of the country. It comprises eight states—Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland and Tripura (commonly known as the "Seven Sisters"), and the "brother" state of Sikkim. The region shares an international border of 5,182 kilometres (3,220 mi) (about 99 per cent of its total geographical boundary) with several neighbouring countries – it borders China to the north, Myanmar to the east, Bangladesh to the south-west, Nepal to the west, and Bhutan to the north-west. It comprises an area of , almost 8 per cent of that of India. The Siliguri Corridor connects the region to the rest of mainland India. The states of North Eastern Region are officially recognised under the North Eastern Council (NEC), constituted in 1971 as the acting agency for the development of the north eastern st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuki Tribes
The Kuki people, or Kuki-Zo people,Rakhi BoseIn Tense Manipur, Sub-Categorisation And 'Creamy Layer' Could Open A Pandora's Box Outlook, 11 September 2024. uoting general secretary of the Committee on Tribal Unity (COTU), Kangpokpi''At present, all tribal communities in Manipur (other than the Nagas) are united and organised under the banner of Kuki-Zo, and we want separate administration for our regions in Kangpokpi, Churachandpur and Tengnoupal.” are an ethnic group in the Northeastern Indian states of Manipur, Nagaland, Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura and Mizoram, as well as the neighbouring countries of Bangladesh and Myanmar. The Kukis form one of the largest hill tribe communities in this region. In Northeast India, they are present in all states except Arunachal Pradesh. The Chin people of Myanmar and the Mizo people of Mizoram are kindred tribes of the Kukis. Collectively, they are termed the Zo people. Some fifty tribes of Kuki peoples in India are recognised as sche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scheduled Tribes Of Manipur
A schedule (, ) or a timetable, as a basic time-management tool, consists of a list of times at which possible tasks, events, or actions are intended to take place, or of a sequence of events in the chronological order in which such things are intended to take place. The process of creating a schedule — deciding how to order these tasks and how to commit resources between the variety of possible tasks — is called scheduling,Ofer Zwikael, John Smyrk, ''Project Management for the Creation of Organisational Value'' (2011), p. 196: "The process is called scheduling, the output from which is a timetable of some form". and a person responsible for making a particular schedule may be called a scheduler. Making and following schedules is an ancient human activity. Some scenarios associate this kind of planning with learning life skills. Schedules are necessary, or at least useful, in situations where individuals need to know what time they must be at a specific location to rece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Groups Of Manipur
Social organisms, including human(s), live collectively in interacting populations. This interaction is considered social whether they are aware of it or not, and whether the exchange is voluntary or not. Etymology The word "social" derives from the Latin word ''socii'' ("allies"). It is particularly derived from the Italian ''Socii'' states, historical allies of the Roman Republic (although they rebelled against Rome in the Social War of 91–87 BC). Social theorists In the view of Karl Marx,Morrison, Ken. ''Marx, Durkheim, Weber. Formations of modern social thought'' human beings are intrinsically, necessarily and by definition social beings who, beyond being "gregarious creatures", cannot survive and meet their needs other than through social co-operation and association. Their social characteristics are therefore to a large extent an objectively given fact, stamped on them from birth and affirmed by socialization processes; and, according to Marx, in producing and reproduci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |