|
Sugarscape
Sugarscape is a model for artificially intelligent agent-based social simulation following some or all rules presented by Joshua M. Epstein & Robert Axtell in their book ''Growing Artificial Societies''. Origin Fundaments of Sugarscape models can be traced back to the University of Maryland where economist Thomas Schelling presented his paper titled '' Models of Segregation''. Written in 1969, Schelling and the rest of the social environment modelling fraternity had their options limited by a lack of adequate computing power and an applicable programming mechanism to fully develop the potential of their model. John Conway's agent-based simulation " Game of Life" was enhanced and applied to Schelling's original idea by Joshua M. Epstein and Robert Axtell in their book ''Growing Artificial Societies''. To demonstrate their findings on the field of agent-based simulation, a model was created and distributed with their book on CD-ROM. The concept of this model has come to be know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agent-based Social Simulation
Agent-based social simulation (or ABSS) consists of social simulations that are based on agent-based modeling, and implemented using artificial agent technologies. Agent-based social simulation is a scientific discipline concerned with simulation of social phenomena, using computer-based multiagent models. In these simulations, persons or group of persons are represented by agents. MABSS is a combination of social science, multiagent simulation and computer simulation. ABSS models the different elements of the social systems using artificial agents, (varying on scale) and placing them in a computer simulated society to observe the behaviors of the agents. From this data it is possible to learn about the reactions of the artificial agents and translate them into the results of non-artificial agents and simulations. Three main fields in ABSS are agent-based computing, social science, and computer simulation. Agent-based computing is the design of the model and agents, while the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Simulation
Social simulation is a research field that applies computational methods to study issues in the social sciences. The issues explored include problems in computational law, psychology, organizational behavior, sociology, political science, economics, anthropology, geography, engineering, archaeology and linguistics . Social simulation aims to cross the gap between the descriptive approach used in the social sciences and the formal approach used in the natural sciences, by moving the focus on the processes/mechanisms/behaviors that build the social reality. In social simulation, computers support human reasoning activities by executing these mechanisms. This field explores the simulation of societies as complex non-linear systems, which are difficult to study with classical mathematical equation-based models. Robert Axelrod regards social simulation as a third way of doing science, differing from both the deductive and inductive approach; generating data that can be analysed ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
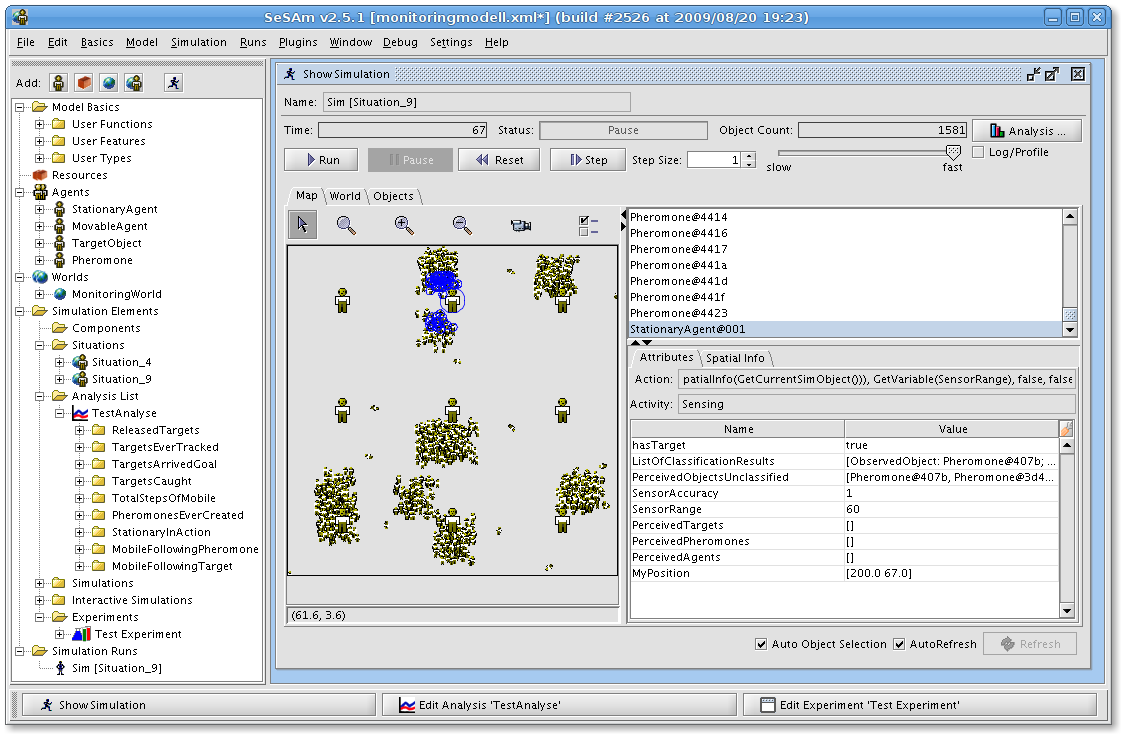
Agent-based Model
An agent-based model (ABM) is a computational model for simulating the actions and interactions of autonomous agents (both individual or collective entities such as organizations or groups) in order to understand the behavior of a system and what governs its outcomes. It combines elements of game theory, complex systems, emergence, computational sociology, multi-agent systems, and evolutionary programming. Monte Carlo methods are used to understand the stochasticity of these models. Particularly within ecology, ABMs are also called individual-based models (IBMs). A review of recent literature on individual-based models, agent-based models, and multiagent systems shows that ABMs are used in many scientific domains including biology, ecology and social science. Agent-based modeling is related to, but distinct from, the concept of multi-agent systems or multi-agent simulation in that the goal of ABM is to search for explanatory insight into the collective behavior of agents ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Axtell
Robert Axtell is a professor at George Mason University, Krasnow Institute for Advanced Study, where he is departmental chair of the Department of Computational Social Science. He is also a member of the External Faculty of the Santa Fe Institute. Axtell is also the co-director of the new Computational Public Policy Lab at Mason. Early life and education Axtell received his first degree at the University of Detroit in 1983 and earned his Ph.D. in Carnegie Mellon University in 1992, where he studied computing, social science, and public policy. Career In the early 1990s, whilst still a graduate student, he met Joshua M. Epstein who was to become a key collaborator. This led to Axtell joining Epstein at the Brookings Institution in 1992. The pair developed a keen interest in mathematical modeling influenced by the work of Thomas Schelling, with their primary research interest the modeling of complex social, economic, and biological systems using computational agent based models ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mason (Java)
MASON is a multi-agent simulation environment developed in Java. Development MASON is developed at George Mason University's Evolutionary Computation Laboratory in conjunction with the GMU Center for Social Complexity. First released in 2003, the environment continues to be maintained and kept up to date. The name, as well as referring to the parent institution, derives from the acronym Multi-Agent Simulator Of Neighborhoods (or Networks). MASON development started within the Java.net environment, then moved to Google Code and is now at GitHub. Whilst MASON is less extensive than other similar libraries it is designed with simplicity and execution speed as a priority. Applets Applets developed using MASON include Craig Reynolds' Boids algorithm, ''Balls and Bands'', a simulation of Hooke's law, an L-system generator, Conway's Game of Life, Sugarscape and autonomous multi-robot systems. MASON may be used with the Eclipse Integrated development environment An int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agent-based Model
An agent-based model (ABM) is a computational model for simulating the actions and interactions of autonomous agents (both individual or collective entities such as organizations or groups) in order to understand the behavior of a system and what governs its outcomes. It combines elements of game theory, complex systems, emergence, computational sociology, multi-agent systems, and evolutionary programming. Monte Carlo methods are used to understand the stochasticity of these models. Particularly within ecology, ABMs are also called individual-based models (IBMs). A review of recent literature on individual-based models, agent-based models, and multiagent systems shows that ABMs are used in many scientific domains including biology, ecology and social science. Agent-based modeling is related to, but distinct from, the concept of multi-agent systems or multi-agent simulation in that the goal of ABM is to search for explanatory insight into the collective behavior of agents ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Simulation
Social simulation is a research field that applies computational methods to study issues in the social sciences. The issues explored include problems in computational law, psychology, organizational behavior, sociology, political science, economics, anthropology, geography, engineering, archaeology and linguistics . Social simulation aims to cross the gap between the descriptive approach used in the social sciences and the formal approach used in the natural sciences, by moving the focus on the processes/mechanisms/behaviors that build the social reality. In social simulation, computers support human reasoning activities by executing these mechanisms. This field explores the simulation of societies as complex non-linear systems, which are difficult to study with classical mathematical equation-based models. Robert Axelrod regards social simulation as a third way of doing science, differing from both the deductive and inductive approach; generating data that can be analysed ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moore's Law
Moore's law is the observation that the Transistor count, number of transistors in an integrated circuit (IC) doubles about every two years. Moore's law is an observation and Forecasting, projection of a historical trend. Rather than a law of physics, it is an empirical relationship. It is an experience-curve law, a type of law quantifying efficiency gains from experience in production. The observation is named after Gordon Moore, the co-founder of Fairchild Semiconductor and Intel and former CEO of the latter, who in 1965 noted that the number of components per integrated circuit had been exponential growth, doubling every year, and projected this rate of growth would continue for at least another decade. In 1975, looking forward to the next decade, he revised the forecast to doubling every two years, a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 41%. Moore's empirical evidence did not directly imply that the historical trend would continue, nevertheless, his prediction has held si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parallel Computing
Parallel computing is a type of computing, computation in which many calculations or Process (computing), processes are carried out simultaneously. Large problems can often be divided into smaller ones, which can then be solved at the same time. There are several different forms of parallel computing: Bit-level parallelism, bit-level, Instruction-level parallelism, instruction-level, Data parallelism, data, and task parallelism. Parallelism has long been employed in high-performance computing, but has gained broader interest due to the physical constraints preventing frequency scaling.S.V. Adve ''et al.'' (November 2008)"Parallel Computing Research at Illinois: The UPCRC Agenda" (PDF). Parallel@Illinois, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. "The main techniques for these performance benefits—increased clock frequency and smarter but increasingly complex architectures—are now hitting the so-called power wall. The computer industry has accepted that future performance inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computing Cluster
A computer cluster is a set of computers that work together so that they can be viewed as a single system. Unlike grid computers, computer clusters have each node set to perform the same task, controlled and scheduled by software. The newest manifestation of cluster computing is cloud computing. The components of a cluster are usually connected to each other through fast local area networks, with each node (computer used as a server) running its own instance of an operating system. In most circumstances, all of the nodes use the same hardware and the same operating system, although in some setups (e.g. using Open Source Cluster Application Resources (OSCAR)), different operating systems can be used on each computer, or different hardware. Clusters are usually deployed to improve performance and availability over that of a single computer, while typically being much more cost-effective than single computers of comparable speed or availability. Computer clusters emerged as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the capability of computer, computational systems to perform tasks typically associated with human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. It is a field of research in computer science that develops and studies methods and software that enable machines to machine perception, perceive their environment and use machine learning, learning and intelligence to take actions that maximize their chances of achieving defined goals. High-profile applications of AI include advanced web search engines (e.g., Google Search); recommendation systems (used by YouTube, Amazon (company), Amazon, and Netflix); virtual assistants (e.g., Google Assistant, Siri, and Amazon Alexa, Alexa); autonomous vehicles (e.g., Waymo); Generative artificial intelligence, generative and Computational creativity, creative tools (e.g., ChatGPT and AI art); and Superintelligence, superhuman play and analysis in strategy games (e.g., ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michigan Technological University
Michigan Technological University (Michigan Tech, MTU, or simply Tech) is a public research university in Houghton, Michigan, United States. It was founded in 1885 as the Michigan Mining School, the first post-secondary institution in the Upper Peninsula of Michigan. The university comprises five colleges and schools: the College of Engineering, the College of Computing, the College of Sciences and Arts, the College of Business, and the College of Forest Resources and Environmental Science. They offer more than 140 degree programs to nearly 7,000 graduate and undergraduate students. Its main campus sits on on a bluff overlooking Portage Lake. The campus consists of 36 buildings, the first of which was built in 1908. Michigan Tech's athletic teams are nicknamed the Huskies and compete primarily in the NCAA Division II Great Lakes Intercollegiate Athletic Conference (GLIAC). The men's hockey team competes in Division I as a member of the Central Collegiate Hockey Associ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |