|
Sugammadex Encaps Rocuronium
Sugammadex, sold under the brand name Bridion, is a medication for the reversal of neuromuscular blockade induced by rocuronium and vecuronium in general anaesthesia. It is the first selective relaxant binding agent (SRBA). It is marketed by Merck. The most common side effects include cough, airway problems due to the anaesthesia wearing off, reduced blood pressure and other complications such as changes in heart rate. Text was copied from this source which is copyright European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged. Sugammadex is available as a generic medication. Medical uses Sugammadex is indicated for the reversal of neuromuscular blockade induced by rocuronium or vecuronium. Pharmacology Pharmacodynamics Sugammadex is a modified γ-cyclodextrin, with a lipophilic core and a hydrophilic periphery. This gamma cyclodextrin has been modified from its natural state by placing eight carboxyl thio ether groups at the sixth carbon posi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intravenous
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrients for those who cannot, or will not—due to reduced mental states or otherwise—consume food or water per os, by mouth. It may also be used to administer pharmaceutical drug, medications or other medical therapy such as blood transfusion, blood products or electrolytes to correct electrolyte imbalances. Attempts at providing intravenous therapy have been recorded as early as the 1400s, but the practice did not become widespread until the 1900s after the development of techniques for safe, effective use. The intravenous route is the fastest way to deliver medications and fluid replacement throughout the body as they are introduced directly into the circulatory system and thus quickly distributed. For this reason, the intravenous route ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
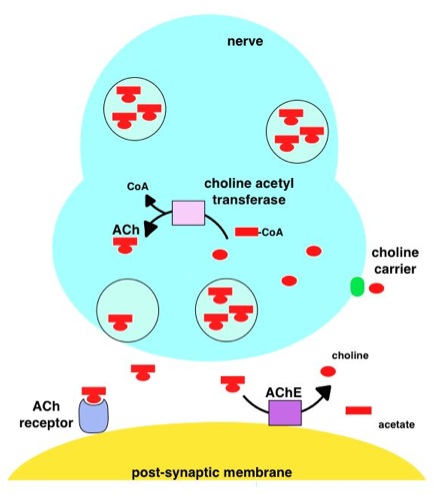
Acetylcholinesterase
Acetylcholinesterase (HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee, HGNC symbol ACHE; EC 3.1.1.7; systematic name acetylcholine acetylhydrolase), also known as AChE, AChase or acetylhydrolase, is the primary cholinesterase in the body. It is an enzyme that catalysis, catalyzes the breakdown of acetylcholine and some other choline esters that function as neurotransmitters: : acetylcholine + H2O = choline + acetate It is found at mainly neuromuscular junctions and in chemical synapses of the cholinergic type, where its activity serves to terminate cholinergic neurotransmission, synaptic transmission. It belongs to the carboxylesterase family of enzymes. It is the primary target of inhibition by organophosphorus compounds such as nerve agents and pesticides. Enzyme structure and mechanism AChE is a hydrolase that hydrolyzes choline esters. It has a very high catalytic activity—each molecule of AChE degrades about 5,000 molecules of acetylcholine (ACh) per second, approaching the limit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Journal Of Anaesthesia
The ''British Journal of Anaesthesia'' is a monthly peer-reviewed medical journal published by Elsevier on behalf of the Royal College of Anaesthetists (and its Faculty of Pain Medicine), the College of Anaesthesiologists of Ireland, and the Hong Kong College of Anaesthesiologists, for all of which it serves as their official journal. The journal covers all aspects of anaesthesia, perioperative medicine, intensive care medicine, and pain management. The editor-in-chief is Hugh C. Hemmings (Weill Cornell Medical College). The journal was established in 1923, one year after the first anaesthetic journal (''Anesthesia & Analgesia'') was published by the International Anaesthesia Research Society. The first editor-in-chief was H.M. Cohen, who edited the journal from 1923 to 1928. Recent editors-in-chief include Ravi Mahajan (University of Nottingham), Charles Reilly (University of Sheffield), and Jennifer Hunter (University of Liverpool). ''BJA Education'' ''BJA Education'' is a si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cochrane Review
Cochrane is a British international charitable organisation formed to synthesize medical research findings to facilitate evidence-based choices about health interventions involving health professionals, patients and policy makers. It includes 53 review groups that are based at research institutions worldwide. Cochrane has over volunteer experts from around the world. The group conducts systematic reviews of healthcare interventions and diagnostic tests and publishes them in the Cochrane Library. While Cochrane reviews typically focus on randomized controlled trials, some reviews, particularly in areas such as public and occupational health, also incorporate other study designs. These may include non-randomised observational studies as well as controlled before–after (CBA) studies and interrupted time-series studies. According to the Library, articles are available via one-click access, though some may require registration or a subscription. History Cochrane, previ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
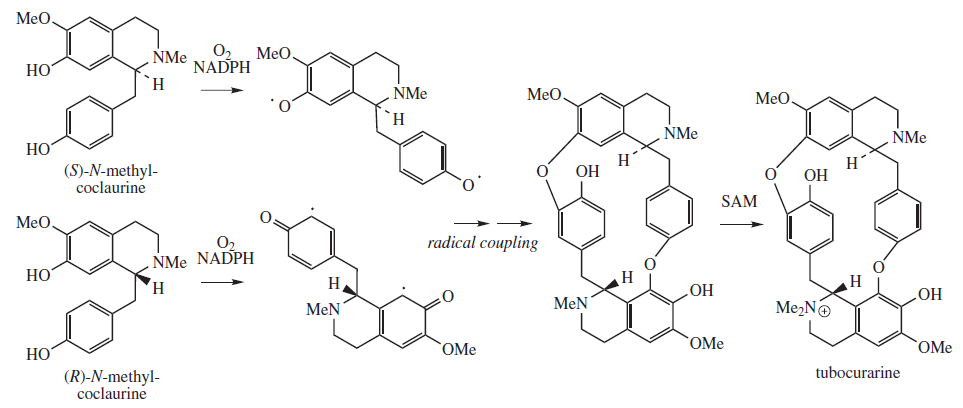
Tubocurarine
Tubocurarine (also known as ''d''-tubocurarine or DTC) is a toxic benzylisoquinoline alkaloid historically known for its use as an arrow poison. In the mid-1900s, it was used in conjunction with an anesthetic to provide skeletal muscle relaxation during surgery or mechanical ventilation. Safer alternatives, such as cisatracurium and rocuronium, have largely replaced it as an adjunct for clinical anesthesia and it is now rarely used. The specific form used was tubocurarine chloride, its hydrated hydrochloride salt. History Tubocurarine is a naturally occurring mono-quaternary alkaloid obtained from the bark of the Menispermaceous South American plant '' Chondrodendron tomentosum'', a climbing vine known to the European world since the Spanish conquest of South America. Curare had been used as a source of arrow poison by South American natives to hunt animals, and they were able to eat the animals' contaminated flesh subsequently without any adverse effects because tubocur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pancuronium
Pancuronium (trademarked as Pavulon) is an aminosteroid muscle relaxant with various medical uses. It is used in euthanasia and is used in some states as the second of three drugs administered during lethal injections in the United States. Mechanism of action Pancuronium is a typical non-depolarizing curare-mimetic muscle relaxant. It competitively inhibits the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor at the neuromuscular junction by blocking the binding of acetylcholine. It has slight vagolytic activity, causing an increase in heart rate, but no ganglioplegic (i.e., blocking ganglions) activity. It is a very potent muscle relaxant drug, with an ED95 (i.e., the dose that causes 95% depression of muscle twitch response) of only 60 μg/kg body weight. Onset of action is relatively slow compared to other similar drugs, in part due to its low dose: an intubating dose takes 3–6 minutes for full effect. Clinical effects (muscle activity lower than 25% of physiological) last for ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
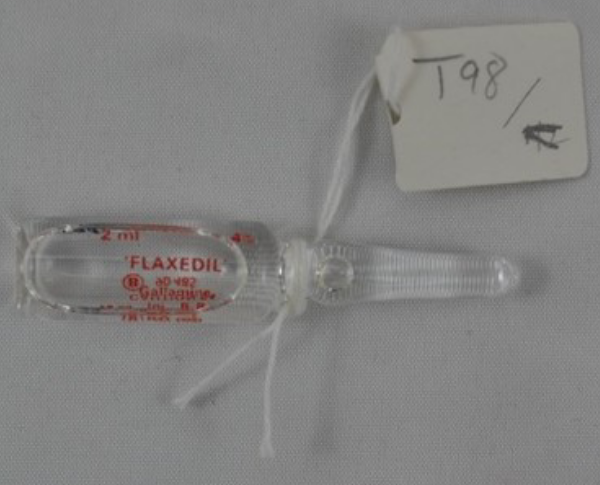
Gallamine
Gallamine triethiodide (Flaxedil) is a non-depolarising muscle relaxant. It acts by combining with the cholinergic receptor sites in muscle and competitively blocking the transmitter action of acetylcholine. Gallamine is a non-depolarising type of blocker as it binds to the acetylcholine receptor but does not have the biological activity of acetyl choline. Gallamine triethiodide has a parasympatholytic effect on the cardiac vagus nerve, which causes tachycardia and occasionally hypertension. Very high doses cause histamine release. Presence of iodine makes it radio opaque, and its ampule in a bag at airport's x-ray scanner raise the false suspicion of a bullet in the bag. Gallamine triethiodide was commonly used to prevent muscle contractions during surgical procedures, but is now superseded by new neuromuscular blocking drugs with less side effects. It was developed by Daniel Bovet in 1947. The drug is no longer marketed in the United States, according to the FDA Orang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudocholinesterase Deficiency
Pseudocholinesterase deficiency is an autosomal recessive inherited blood plasma enzyme abnormality in which the body's production of butyrylcholinesterase (BCHE; pseudocholinesterase aka PCE) is impaired. People who have this abnormality may be sensitive to certain anesthetic drugs, including the muscle relaxants succinylcholine and mivacurium as well as other ester local anesthetics. Signs and symptoms The effects are varied depending on the particular drug given. When anesthetists administer standard doses of these anesthetic drugs to a person with pseudocholinesterase deficiency, the patient experiences prolonged paralysis of the respiratory muscles, requiring an extended period of time during which the patient must be mechanically ventilated. Eventually the muscle-paralyzing effects of these drugs will wear off despite the deficiency of the pseudocholinesterase enzyme. If the patient is maintained on a mechanical respirator until normal breathing function returns, there i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malignant Hyperthermia
Malignant hyperthermia (MH) is a type of severe reaction that occurs in response to particular medications used during general anesthesia, among those who are susceptible. Symptoms include muscle rigidity, fever, and a fast heart rate. Complications can include muscle breakdown and high blood potassium. Most people who are susceptible to MH are generally unaffected when not exposed to triggering agents. Exposure to triggering agents (certain volatile anesthetic agents or succinylcholine) can lead to the development of MH in those who are susceptible. Susceptibility can occur due to at least six genetic mutations, with the most common one being of the '' RYR1'' gene. These genetic variations are often inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. The condition may also occur as a new mutation or be associated with a number of inherited muscle diseases, such as central core disease. In susceptible individuals, the medications induce the release of stored calcium ions within ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Succinylcholine
Suxamethonium chloride (brand names Scoline and Sucostrin, among others), also known as suxamethonium or succinylcholine, or simply sux in medical abbreviation, is a medication used to cause short-term paralysis as part of general anesthesia. This is done to help with tracheal intubation or electroconvulsive therapy. It is administered by injection, either intravenous, into a vein or intramuscular, into a muscle. When used in a vein, onset of action is generally within one minute and effects last for up to 10 minutes. Common side effects include low blood pressure, increased saliva production, muscle pain, and rash. Serious side effects include malignant hyperthermia, hyperkalemia and allergic reactions. It is not recommended in people who are at risk of high blood potassium or a history of myopathy. Use during pregnancy appears to be safe for the baby. Suxamethonium is in the neuromuscular-blocking drugs, neuromuscular blocker family of medications and is of the depolarizing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |