|
Sudan Black B
Solvent Black 3 is an azo dye. It is a non-fluorescent, relatively thermostable lysochrome (fat-soluble dye) diazo dye used for Staining (biology), staining of neutral triglycerides and lipids on frozen sections and some lipoproteins on paraffin sections. It has the appearance of a dark brown to black powder with maximum absorption at 596–605 nm and melting point 120–124 °C. It stains blue-black. Applications Solvent Black 3 is used for a wide variety of commercial applications. In the laboratory, Solvent Black 3 is used for Sudan staining. Similar dyes include Oil Red O, Sudan III, and Sudan IV. It can be used to stain some other materials than the other Sudan dyes, as it is not so specific to lipids. It is used in fingerprint enhancement. It is useful for detecting fats that are contaminated with oil and grease. In differentiating Hematological malignancy, haematological disorders, it will stain Acute Myeloid Leukaemia, myeloblasts but not Acute Lymphoblastic Leuke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sudan Stain
Sudan stains and Sudan dyes are synthetic organic compounds that are used as dyes for various plastics (plastic colorants) and are also used to stain sudanophilic biological samples, usually lipids. Sudan II, Sudan III, Sudan IV, Oil Red O, and Sudan Black B are important members of this class of compounds (see images below). Staining Sudan dyes have high affinity to fats, therefore they are used to demonstrate triglycerides, lipids, and lipoproteins. Alcoholic solutions of Sudan dyes are usually used, however pyridine solutions can be used in some situations as well. Sudan stain test is often used to determine the level of fecal fat to diagnose steatorrhea. A small sample is dissolved in water or saline, glacial acetic acid is added to hydrolyze the insoluble salts of fatty acids, a few drops of alcoholic solution of Sudan III are added, the sample is spread on a microscopic slide, and heated twice to boil. Normally a stool sample should show only a few drops of red-orange stained ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
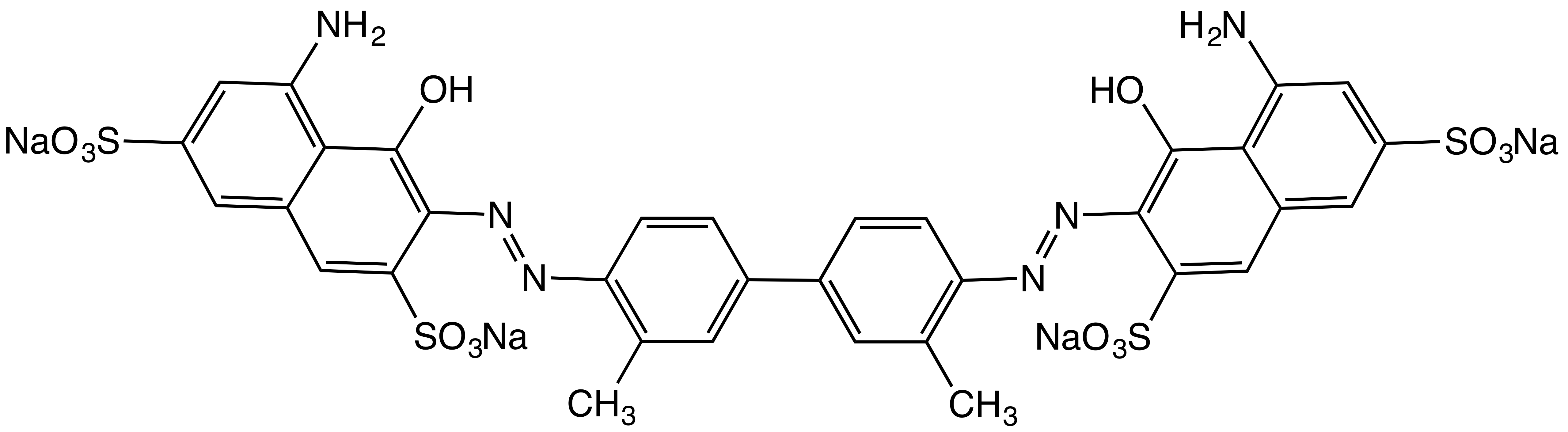
Azo Dye
Azo dyes are organic compounds bearing the functional group R−N=N−R′, in which R and R′ are usually aryl and substituted aryl groups. They are a commercially important family of azo compounds, i.e. compounds containing the C−N=N−C linkage. Azo dyes are synthetic dyes and do not occur naturally. Most azo dyes contain only one azo group but there are some that contain two or three azo groups, called "diazo dyes" and "triazo dyes" respectively. Azo dyes comprise 60–70% of all dyes used in food and textile industries. Azo dyes are widely used to treat textiles, leather articles, and some foods. Chemically related derivatives of azo dyes include azo pigments, which are insoluble in water and other solvents. Classes Many kinds of azo dyes are known, and several classification systems exist. Some classes include disperse dyes, metal-complex dyes, reactive dyes, and substantive dyes. Also called direct dyes, substantive dyes are employed for cellulose-based textil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sudan IV
Sudan IV (C24H20N4O) is a lysochrome (fat-soluble dye) diazo dye used for the staining of lipids, triglycerides and lipoproteins on frozen paraffin sections. It has the appearance of reddish brown crystals with melting point 199 °C and maximum absorption at 520(357) nm. Sudan IV is one of the dyes used for Sudan staining. Similar dyes include Oil Red O, Sudan III, and Sudan Black B. Staining is an important biochemical technique, offering the ability to visually qualify the presence of the fatty compound of interest without isolating it. For staining purposes, Sudan IV can be made up in propylene glycol. Alternatively, authors have reported using the dye saturated in isopropyl alcohol, 95% ethanol, or 0.05% by weight in acetone:ethanol:water (50:35:15). The idea is to use a moderately apolar solvent to solubilize the dye allowing it to partition into the highly apolar fat without the solvent solubilizing the fat to be stained. Sudan I, Sudan III, and Sudan IV have been cla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naphthalenes
Naphthalene is an organic compound with formula . It is the simplest polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, and is a white crystalline solid with a characteristic odor that is detectable at concentrations as low as 0.08 ppm by mass. As an aromatic hydrocarbon, naphthalene's structure consists of a fused pair of benzene rings. It is the main ingredient of traditional mothballs. History In the early 1820s, two separate reports described a white solid with a pungent odor derived from the distillation of coal tar. In 1821, John Kidd cited these two disclosures and then described many of this substance's properties and the means of its production. He proposed the name ''naphthaline'', as it had been derived from a kind of naphtha (a broad term encompassing any volatile, flammable liquid hydrocarbon mixture, including coal tar). Naphthalene's chemical formula was determined by Michael Faraday in 1826. The structure of two fused benzene rings was proposed by Emil Erlenmeyer in 1866, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staining Dyes
Staining is a technique used to enhance contrast in samples, generally at the microscopic level. Stains and dyes are frequently used in histology (microscopic study of biological tissues), in cytology (microscopic study of cells), and in the medical fields of histopathology, hematology, and cytopathology that focus on the study and diagnoses of diseases at the microscopic level. Stains may be used to define biological tissues (highlighting, for example, muscle fibers or connective tissue), cell populations (classifying different blood cells), or organelles within individual cells. In biochemistry, it involves adding a class-specific (DNA, proteins, lipids, carbohydrates) dye to a substrate to qualify or quantify the presence of a specific compound. Staining and fluorescent tagging can serve similar purposes. Biological staining is also used to mark cells in flow cytometry, and to flag proteins or nucleic acids in gel electrophoresis. Light microscopes are used for viewing s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azo Dyes
Azo dyes are organic compounds bearing the functional group R−N=N−R′, in which R and R′ are usually aryl and substituted aryl groups. They are a commercially important family of azo compounds, i.e. compounds containing the C−N=N−C linkage. Azo dyes are synthetic dyes and do not occur naturally. Most azo dyes contain only one azo group but there are some that contain two or three azo groups, called "diazo dyes" and "triazo dyes" respectively. Azo dyes comprise 60–70% of all dyes used in food industry, food and textile industry, textile industries. Azo dyes are widely used to treat textile, textiles, leather, leather articles, and some foods. Chemically related derivatives of azo dyes include #Azo pigments, azo pigments, which are insoluble in water and other solvents. Classes Many kinds of azo dyes are known, and several classification systems exist. Some classes include disperse dyes, metal-complex dyes, reactive dyes, and substantive dyes. Also called direct d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is a cancer of the Lymphocyte, lymphoid line of blood cells characterized by the development of large numbers of lymphoblast, immature lymphocytes. Symptoms may include feeling tired, pale skin color, fever, easy bleeding or bruising, lymphadenopathy, enlarged lymph nodes, or bone pain. As an acute leukemia, ALL progresses rapidly and is typically fatal within weeks or months if left untreated. In most cases, the cause is unknown. Genetic risk factors may include Down syndrome, Li–Fraumeni syndrome, or neurofibromatosis type 1. Environmental risk factors may include significant radiation exposure or prior chemotherapy. Evidence regarding electromagnetic fields or pesticides is unclear. Some hypothesize that an abnormal immune response to a common infection may be a trigger. The underlying mechanism involves multiple genetic mutations that results in rapid cell division. The excessive immature lymphocytes in the bone marrow interfere with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Myeloid Leukaemia
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a cancer of the myeloid line of blood cells, characterized by the rapid growth of abnormal cells that build up in the bone marrow and blood and interfere with normal blood cell production. Symptoms may include feeling tired, shortness of breath, easy bruising and bleeding, and increased risk of infection. Occasionally, spread may occur to the brain, skin, or gums. As an acute leukemia, AML progresses rapidly, and is typically fatal within weeks or months if left untreated. Risk factors include getting older, being male, smoking, previous chemotherapy or radiation therapy, myelodysplastic syndrome, and exposure to the chemical benzene. The underlying mechanism involves replacement of normal bone marrow with leukemia cells, which results in a drop in red blood cells, platelets, and normal white blood cells. Diagnosis is generally based on bone marrow aspiration and specific blood tests. AML has several subtypes for which treatments and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hematological Malignancy
Tumors of the hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues (American English) or tumours of the haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues (British English) are tumors that affect the blood, bone marrow, lymph, and lymphatic system. Because these tissues are all intimately connected through both the circulatory system and the immune system, a disease affecting one will often affect the others as well, making aplasia, myeloproliferation and lymphoproliferation (and thus the leukemias, myelomas, and the lymphomas) closely related and often overlapping problems. While uncommon in solid tumors, chromosomal translocations are a common cause of these diseases. This commonly leads to a different approach in diagnosis and treatment of hematological malignancies. Hematological malignancies are malignant neoplasms ("cancer"), and they are generally treated by specialists in hematology and/or oncology. In some centers "hematology/oncology" is a single subspecialty of internal medicine while in others the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sudan III
Sudan III is a lysochrome (fat-soluble dye) diazo dye. It is structurally related to azobenzene. Uses It is used to color nonpolar substances such as oils, fats, waxes, greases, various hydrocarbon products, and acrylic emulsions. Its main use is as a fuel dye in the United States mandated by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) to distinguish low-taxed heating oil from automotive diesel fuel, and by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to mark fuels with higher sulfur content; it is a replacement for Solvent Red 26 with better solubility in hydrocarbons. The IRS requires "a concentration spectrally equivalent to at least 3.9 pounds of... Solvent Red 26 per thousand barrels of fuel" (); the concentrations required by EPA are roughly 5 times lower. It should be stored at room temperature. Biological staining Sudan III is a dye used for Sudan staining. Similar dyes include Oil Red O, Sudan IV, and Sudan Black B. They are used for staining of triglycerides in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lysochrome
A lysochrome is a soluble dye used for histochemical staining of lipids, which include triglycerides, fatty acids, and lipoproteins. Lysochromes such as Sudan IV dissolve in the lipid and show up as colored regions. The dye does not stick to any other substrates, so a quantification or qualification of lipid presence can be obtained. The name was coined by John Baker (biologist) John Randal Baker FRS (23 October 1900 – 8 June 1984) was an English biologist, zoologist, and microscopist, and a professor at the University of Oxford, where he was Emeritus Reader in Cytology. He received his D.Phil. at the University of ... in his book "Principles of Biological Microtechnique", published in 1958, from the Greek words lysis (solution) and chroma (colour).Baker, J.R. 1958. Principles of Biological Microtechnique. London: Methuen, p.297-298. References {{Reflist Biochemistry methods Lipids Histochemistry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oil Red O
Oil Red O (Solvent Red 27, Sudan Red 5B, C.I. 26125, C26H24N4O) is a lysochrome (fat-soluble dye) diazo dye used for staining of neutral triglycerides and lipids on frozen sections and some lipoproteins on paraffin sections. It has the appearance of a red powder with an absorbance maximum at 518 nanometers. Uses Oil Red O is one of the dyes used for Sudan staining. Similar dyes include Sudan III, Sudan IV, and Sudan Black B. The staining has to be performed on fresh samples, as alcohol fixation removes most lipids. Oil Red O largely replaced Sudan III and Sudan IV, as it provides much deeper red color and the stains are therefore much easier to see. Oil Red O can be used to mark lipid-containing vacuoles, particularly in cases of acute lymphoblastic leukemia or Burkitt's lymphoma. It can also be used to stain liver sections for histological analysis, quantify cell lipid content, and to stain the aorta to examine lesions from atherosclerosis. In pyrotechnics, Oil Red O is use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |