|
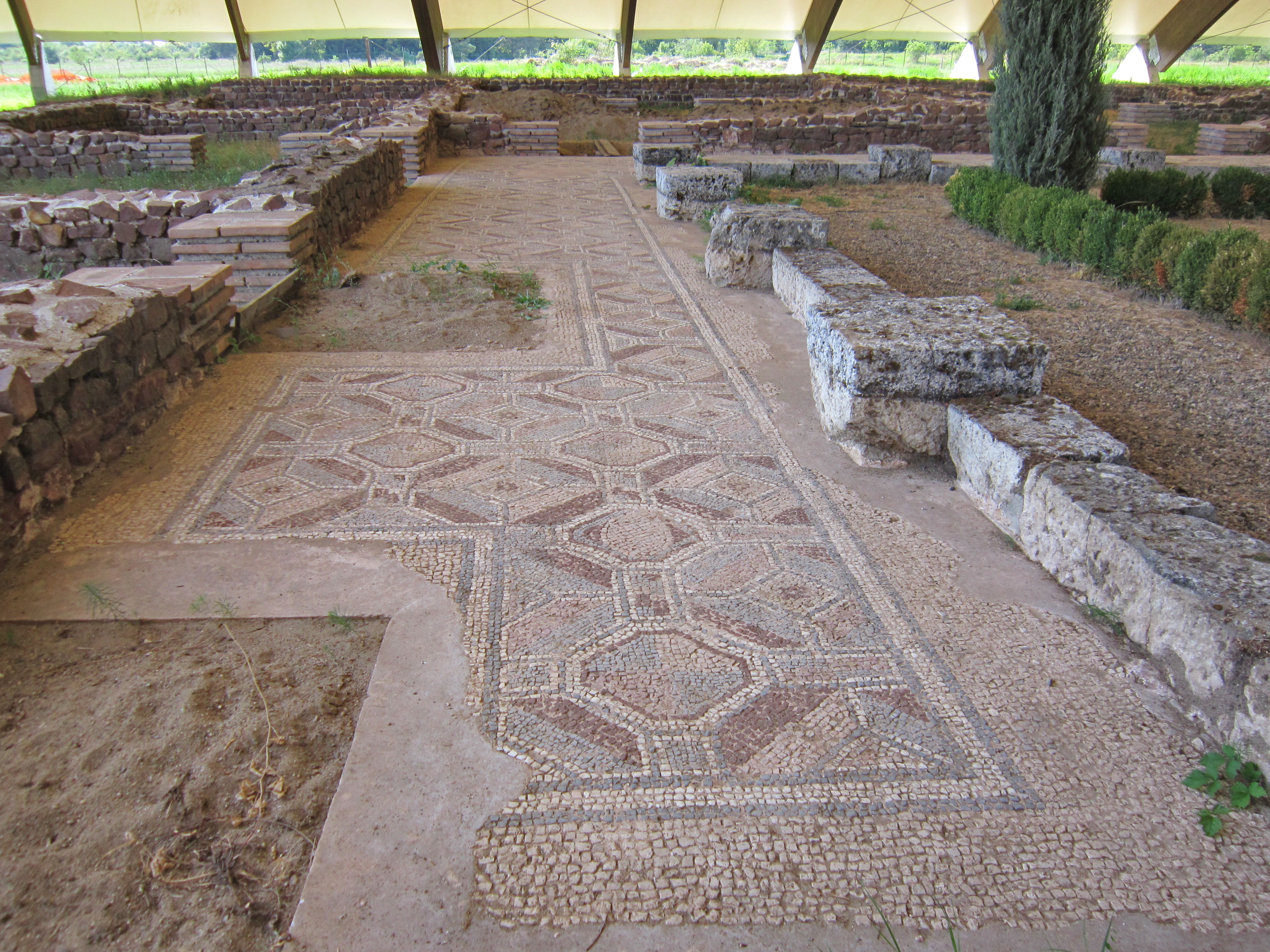
Sucidava City Plan
Sucidava (Sykibid, Skedevà after Procopius,Olga Karagiorgou Σucidava after Vasile Pârvan, where Σ is pronounced "sh"Pârvan - știri din Dacia Malvensis http://www.cimec.ro/Arheologie/ParvanArticole/ParvanStiriNouaDinDaciaMalvensis.pdf)) is a Dacian and Daco-Roman historical site, situated in Corabia, Romania, on the north bank of the Danube. The first Christian Basilica established in Romania can be found there and the foot of a Roman bridge over the Danube built by Constantine the Great to link Sucidava with Oescus (today in Bulgaria, in Moesia), in order to start the reconquest of Dacia. There is also a secret underground fountain which flows under the walls of the town to a water spring situated outside. From an archaeological point of view, the coins found at Sucidava show an uninterrupted series from Aurelian (270-275) to Theodosius II (408-450). The archaeological evidence show that in AD 443 or 447 the city was sacked by the Huns, and was restored under Justin I 518 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabula Peutingeriana
' (Latin for "The Peutinger Map"), also referred to as Peutinger's Tabula or Peutinger Table, is an illustrated ' (ancient Roman road map) showing the layout of the '' cursus publicus'', the road network of the Roman Empire. The map is a 13th-century parchment copy of a possible Roman original. It covers Europe (without the Iberian Peninsula and the British Isles), North Africa, and parts of Asia, including the Middle East, Persia, and India. According to one hypothesis, the existing map is based on a document of the 4th or 5th century that contained a copy of the world map originally prepared by Agrippa during the reign of the emperor Augustus (27 BC – AD 14). However, Emily Albu has suggested that the existing map could instead be based on an original from the Carolingian period. The map was likely stolen by the renowned humanist Conrad Celtes, who bequeathed it to his friend, the economist and archaeologist Konrad Peutinger, who gave it to Emperor Maximilian I, as part of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantine I
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to convert to Christianity. Born in Naissus, Dacia Mediterranea (now Niš, Serbia), he was the son of Flavius Constantius, a Roman army officer of Illyrian origin who had been one of the four rulers of the Tetrarchy. His mother, Helena, was a Greek Christian of low birth. Later canonized as a saint, she is traditionally attributed with the conversion of her son. Constantine served with distinction under the Roman emperors Diocletian and Galerius. He began his career by campaigning in the eastern provinces (against the Persians) before being recalled in the west (in AD 305) to fight alongside his father in Britain. After his father's death in 306, Constantine became emperor. He was acclaimed by his army at Eboracum ( York, England), and eventually emerged victorious in the civil wars against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Museum Of Romanian History
The National History Museum of Romania ( ro, Muzeul Național de Istorie a României) is a museum located on the Calea Victoriei in Bucharest, Romania, which contains Romanian historical artifacts from prehistoric times up to modern times. The museum is located inside the former Postal Services Palace, which also houses a philatelic museum. With a surface of over 8,000 square meters, the museum has approx. 60 valuable exhibition rooms. The permanent displays include a plaster cast of the entirety of Trajan's Column, the Romanian Crown Jewels, and the Pietroasele treasure. The building was authorized, in 1892, and the architect, Alexandru Săvulescu was sent with the postal inspector, Ernest Sturza, to tour various postal facilities of Europe for the design. The final sketches were influenced primarily by the postal facility in Geneva. Built in an eclectic style, it is rectangular with a large porch on a high basement and three upper floors. The stone façade features a portico su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Notitia Dignitatum
The ''Notitia Dignitatum'' (Latin for "The List of Offices") is a document of the late Roman Empire that details the administrative organization of the Western and the Eastern Roman Empire. It is unique as one of very few surviving documents of Roman government, and describes several thousand offices from the imperial court to provincial governments, diplomatic missions, and army units. It is usually considered to be accurate for the Western Roman Empire in the AD 420s and for the Eastern or Byzantine Empire in the AD 390s. However, the text itself is not dated (nor is its author named), and omissions complicate ascertaining its date from its content. Copies of the manuscript There are several extant 15th- and 16th-century copies of the document, plus a colour-illuminated iteration of 1542. All the known, extant copies are derived, either directly or indirectly, from ''Codex Spirensis'', a codex known to have existed in the library of the Chapter of Speyer Cathedral in 1542, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of North Carolina Press
The University of North Carolina Press (or UNC Press), founded in 1922, is a university press that is part of the University of North Carolina. It was the first university press founded in the Southern United States. It is a member of the Association of University Presses (AUPresses) and publishes both scholarly and general-interest books and journals. According to its website, UNC Press advances "the University of North Carolina's triple mission of teaching, research, and public service by publishing first-rate books and journals for students, scholars, and general readers." It receives support from the state of North Carolina and the contributions of individual and institutional donors who created its endowment. Its headquarters are located in Chapel Hill. History In 1922, on the campus of the nation's oldest state university, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, thirteen educators and civic leaders met to charter a publishing house. Their creation, the University ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul MacKendrick
Paul Lachlan MacKendrick (February 11, 1914 in Taunton, Massachusetts – February 10, 1998 in Madison, Wisconsin) was an American classicist, author, and teacher. Biography MacKendrick was born in Taunton, Massachusetts, but most of his productive years had been lived in Madison, Wisconsin. MacKendrick was educated at Harvard University (1934 B.A., summa cum laude; 1937 M.A.; 1938 Ph.D.) and Balliol College, Oxford, after which he taught at Phillips Academy for some years. Future United States President George H. W. Bush was a student of MacKendrick's while he taught at Phillips Academy. He joined the U.S. Naval Reserve and served from 1941–45. He taught at Harvard in 1946 and then moved to University of Wisconsin–Madison as Assistant Professor of Classics where he taught for six years. MacKendrick was named a Professor of Classics in 1952 and in 1975, the Lily Ross Taylor Professor of Classics. In all, he taught at the University of Wisconsin from 1946 to 1984. In 1952, he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Castra
Castra ( Latin, singular castrum) were military forts of various sizes used by the Roman army throughout the Empire in various places of Europe, Asia and Africa. The largest castra were permanent legionary fortresses. Locations The disposition of the castra reflects the most important zones of the empire from a military point of view. Many castra were disposed along frontiers particularly in Northern and Central Europe. Another focal point was the Eastern border, where the Roman Empire confronted one of its long-term enemies, the Persian Empire. Other castra were located in strategically important zones, as in Egypt, from which most of the wealth of the empire came. Finally, other castra were located in zones in which the Romans experienced local unrest, such as Northern Spain and Judea. Provinces where the Roman power was unchallenged, such as Italy, Gaul, Africa and Greece, were provided with few or no castra. In the long history of the Roman Empire, the character of the mil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Justinian I
Justinian I (; la, Iustinianus, ; grc-gre, Ἰουστινιανός ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was the Byzantine emperor from 527 to 565. His reign is marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovatio imperii'', or "restoration of the Empire". This ambition was expressed by the partial recovery of the territories of the defunct Western Roman Empire. His general, Belisarius, swiftly conquered the Vandal Kingdom in North Africa. Subsequently, Belisarius, Narses, and other generals conquered the Ostrogothic kingdom, restoring Dalmatia, Sicily, Italian peninsula, Italy, and Rome to the empire after more than half a century of rule by the Ostrogoths. The Liberius (praetorian prefect), praetorian prefect Liberius reclaimed the south of the Iberian peninsula, establishing the province of Spania. These campaigns re-established Roman control over the western Mediterranean, increasing the Empire's annual revenue by over a million Solidus (coin) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Justin I
Justin I ( la, Iustinus; grc-gre, Ἰουστῖνος, ''Ioustînos''; 450 – 1 August 527) was the Eastern Roman emperor from 518 to 527. Born to a peasant family, he rose through the ranks of the army to become commander of the imperial guard, and when Emperor Anastasius died he out-maneouvered his rivals and was elected as his successor, in spite of being almost 70 years old. His reign is significant for the founding of the Justinian dynasty that included his eminent nephew Justinian I and three succeeding emperors. His consort was Empress Euphemia. He was noted for his strongly orthodox Christian views. This facilitated the ending of the Acacian schism between the churches of Rome and Constantinople, resulting in good relations between Justin and the papacy. Throughout his reign he stressed the religious nature of his office and passed edicts against various Christian groups seen at the time as non-Orthodox. In foreign affairs he used religion as an instrument of sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part of Scythia at the time; the Huns' arrival is associated with the migration westward of an Iranian people, the Alans. By 370 AD, the Huns had arrived on the Volga, and by 430, they had established a vast, if short-lived, dominion in Europe, conquering the Goths and many other Germanic peoples living outside of Roman borders and causing many others to flee into Roman territory. The Huns, especially under their King Attila, made frequent and devastating raids into the Eastern Roman Empire. In 451, they invaded the Western Roman province of Gaul, where they fought a combined army of Romans and Visigoths at the Battle of the Catalaunian Fields, and in 452, they invaded Italy. After the death of Attila in 453, the Huns ceased to be a major t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodosius II
Theodosius II ( grc-gre, Θεοδόσιος, Theodosios; 10 April 401 – 28 July 450) was Roman emperor for most of his life, proclaimed ''augustus'' as an infant in 402 and ruling as the eastern Empire's sole emperor after the death of his father Arcadius in 408. His reign was marked by the promulgation of the Theodosian law code and the construction of the Theodosian Walls of Constantinople. He also presided over the outbreak of two great Christological controversies, Nestorianism and Eutychianism. Early life Theodosius was born on 10 April 401 as the only son of Emperor Arcadius and his wife Aelia Eudoxia.'' PLRE'' 2, p. 1100 On 10 January 402, at the age of 9 months, he was proclaimed co-a''ugustus'' by his father, thus becoming the youngest to bear the imperial title up to that point. On 1 May 408, his father died and the seven-year-old boy became emperor of the Eastern half of the Roman Empire. Reign Early reign The government was at first administered b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aurelian
Aurelian ( la, Lucius Domitius Aurelianus; 9 September 214 October 275) was a Roman emperor, who reigned during the Crisis of the Third Century, from 270 to 275. As emperor, he won an unprecedented series of military victories which reunited the Roman Empire after it had nearly disintegrated under the pressure of barbarian invasions and internal revolts. Born in humble circumstances, near the Danube River, he entered the Roman military in 235, and climbed up the ranks. He went on to lead the cavalry of the emperor Gallienus, until Gallienus' assassination in 268. Following that, Claudius Gothicus became emperor until his own death in 270. Claudius' brother Quintillus ruled the empire for three months, before Aurelian became emperor. During his reign, he defeated the Alamanni after a devastating war. He also defeated the Goths, Vandals, Juthungi, Sarmatians, and Carpi. Aurelian restored the Empire's eastern provinces after his conquest of the Palmyrene Empire in 273. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |