|
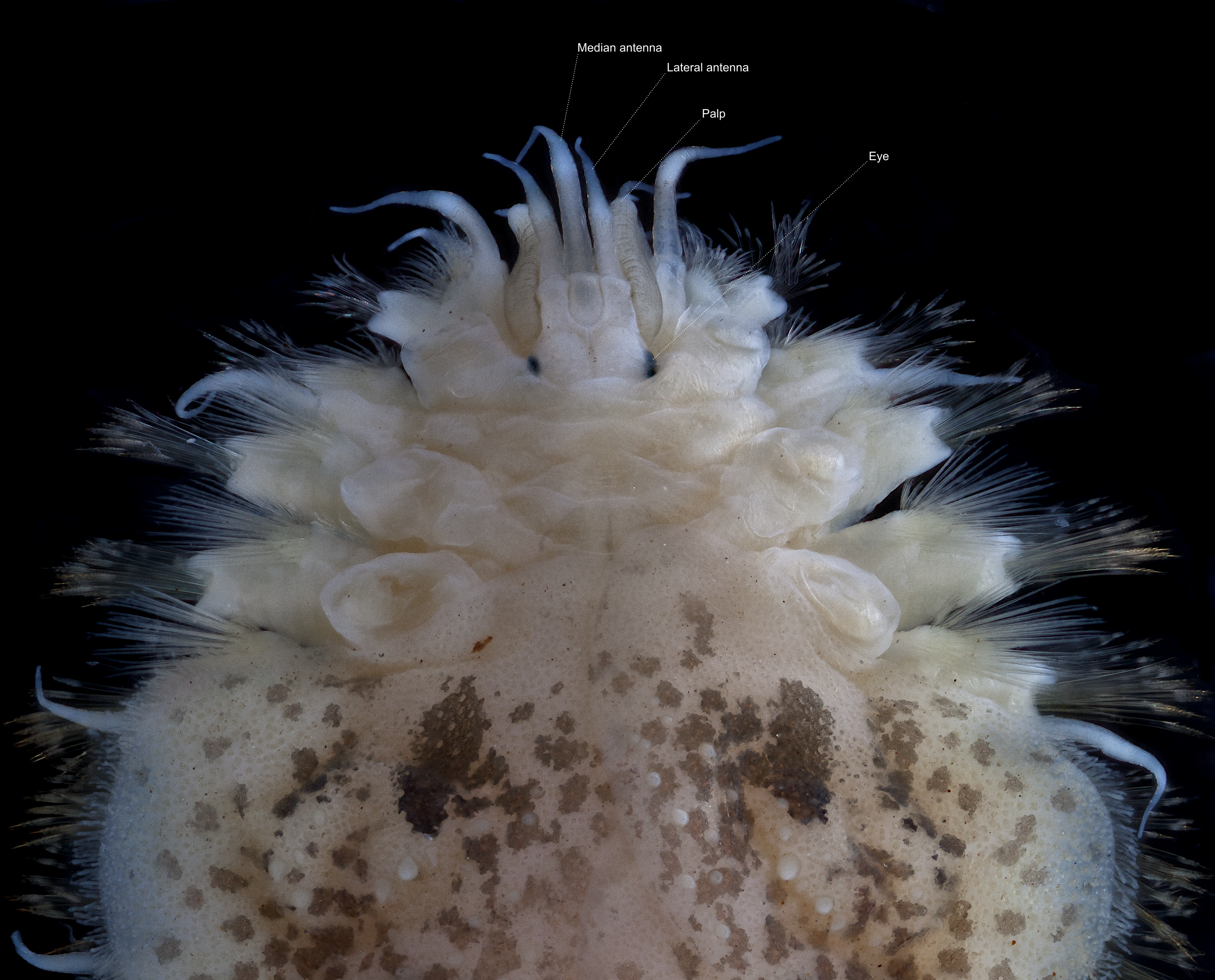
Subadyte Pellucida
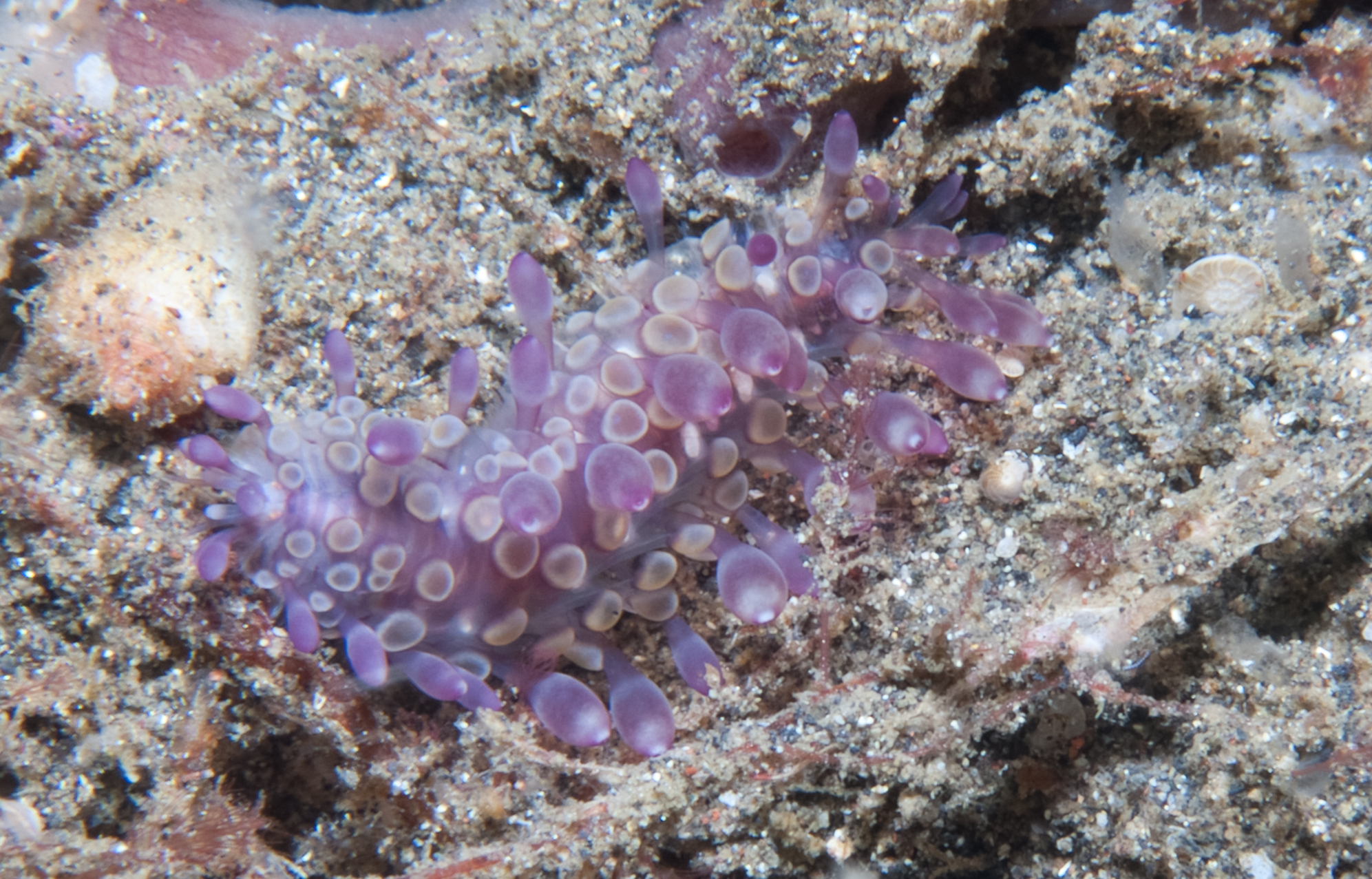
''Subadyte pellucida'' is a scale worm widely reported from the Indian, Pacific and North Atlantic Oceans from the intertidal zone to depths of about 800 m.Ehlers, E. H. (1864). Die Borstenwürmer (Annelida Chaetopoda) nach systematischen und anatomischen Untersuchungen dargestellt. , available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/1985759Johnston, G. (1865). A catalogue of the British non-parasitical worms in the collection of the British Museum. ook 1-365. British Museum. London. ee also separate entry for Baird supplement, available online at http://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/bibliography/12291Pettibone, Marian H. (1993). Scaled polychaetes (Polynoidae) associated with ophiuroids and other invertebrates and review of species referred to Malmgrenia McIntosh and replaced by Malmgreniella Hartman, with descriptions of new taxa. Smithsonian Contributions to Zoology. 538: 1-92., available online at http://hdl.handle.net/10088/5682 Description ''Subadyte pellucida'' i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polynoidae
Polynoidae is a family of marine Polychaete worms known as "scale worms" due to the scale-like elytra on the dorsal surface. Almost 900 species are currently recognised belonging to 9 subfamilies and 167 genera. They are active hunters, but generally dwell in protected environments such as under stones. The group is widely distributed from shallow intertidal waters to hadal trenches. They are the most diverse group of polychaetes in terms of genus number and second most diverse in terms of species number which is almost 8% of all segmented worm species. Description Most Polynoidae species are short and flattened, but can reach as much as 20 cm in length and 10 cm width in '' Eulagisca gigantea'' and '' Eulagisca uschakovi''. Individuals are usually covered almost entirely by elytra, which can be shed and regenerated in many species. The elytra of some species are faintly bioluminescent, and leave glowing traces around the mouthparts of their predators, making those pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by the Southern Ocean or Antarctica, depending on the definition in use. Along its core, the Indian Ocean has some large marginal or regional seas such as the Arabian Sea, Laccadive Sea, Bay of Bengal, and Andaman Sea. Etymology The Indian Ocean has been known by its present name since at least 1515 when the Latin form ''Oceanus Orientalis Indicus'' ("Indian Eastern Ocean") is attested, named after India, which projects into it. It was earlier known as the ''Eastern Ocean'', a term that was still in use during the mid-18th century (see map), as opposed to the ''Western Ocean'' ( Atlantic) before the Pacific was surmised. Conversely, Chinese explorers in the Indian Ocean during the 15th century called it the Western Oceans. In Anci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continents of Asia and Oceania in the west and the Americas in the east. At in area (as defined with a southern Antarctic border), this largest division of the World Ocean—and, in turn, the hydrosphere—covers about 46% of Earth's water surface and about 32% of its total surface area, larger than Earth's entire land area combined .Pacific Ocean . '' Britannica Concise.'' 2008: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. The centers of both the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe and Asia from the "New World" of the Americas in the European perception of the World. The Atlantic Ocean occupies an elongated, S-shaped basin extending longitudinally between Europe and Africa to the east, and North and South America to the west. As one component of the interconnected World Ocean, it is connected in the north to the Arctic Ocean, to the Pacific Ocean in the southwest, the Indian Ocean in the southeast, and the Southern Ocean in the south (other definitions describe the Atlantic as extending southward to Antarctica). The Atlantic Ocean is divided in two parts, by the Equatorial Counter Current, with the North(ern) Atlantic Ocean and the South(ern) Atlantic Ocean split at about 8°N. Scientific explorations of the At ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intertidal Zone
The intertidal zone, also known as the foreshore, is the area above water level at low tide and underwater at high tide (in other words, the area within the tidal range). This area can include several types of habitats with various species of life, such as seastars, sea urchins, and many species of coral with regional differences in biodiversity. Sometimes it is referred to as the '' littoral zone'' or '' seashore'', although those can be defined as a wider region. The well-known area also includes steep rocky cliffs, sandy beaches, bogs or wetlands (e.g., vast mudflats). The area can be a narrow strip, as in Pacific islands that have only a narrow tidal range, or can include many meters of shoreline where shallow beach slopes interact with high tidal excursion. The peritidal zone is similar but somewhat wider, extending from above the highest tide level to below the lowest. Organisms in the intertidal zone are adapted to an environment of harsh extremes, living in w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elytron (Annelida)
In annelids, elytra (; from Greek ἔλυτρον "sheath, cover"; singular: elytron ) are shield-like scales that are attached dorsally, one pair on each of a number of alternating segments and entirely or partly cover the dorsum. Elytra are modified dorsal cirri, and their number, size, location, and ornamentation are important taxonomic characters. The basal part of the elytra is known as the elytrophore; if (as is often the case) elytra are lost their presence is indicated by the elytrophore which is still present and visible. Annelids possessing elytra are also known as "scale worms". Possession of elytra is characteristic of the annelid suborder Aphroditiformia. Gallery File:Eunoe leiotentaculata lower res.jpg, A ''Eunoe leiotentaculata'' specimen showing its 15 pairs of elytra. File:Euphione sp. dorsal.jpg, ''Euphione ''Euphione'' is a genus of polychaetes belonging to the family Polynoidae. The species of this genus are found in Australia, Malesia Malesia is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostomium
The prostomium (From Ancient Greek, meaning "before the mouth"; plural: prostomia; sometimes also called the "acron") is the cephalized first body segment in an annelid worm's body at the anterior end. It is in front of (but does not include) the mouth, being usually a small shelf- or lip-like extension over the dorsal side of the mouth. The prostomium together with the peristomium, which includes the mouth and pharynx, make up the annelid head. Description The prostomium is part of the head and holds at least part of the brain and often bears sensory structures such as the eyes, antennae and palps. It may function like a kind of overlip when the animal is feeding. The prostomium bears many important taxonomic characters and its shape and composition are important for annelid systematics. In addition to the eyes, antennae and palps, the prostomium can possess appendages such as tentacles or cirri. Moreover, some polychaete Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class of gener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaeta
A chaeta or cheta (from Greek χαίτη “crest, mane, flowing hair"; plural: chaetae) is a chitinous bristle or seta found in annelid worms, (although the term is also frequently used to describe similar structures in other invertebrates such as arthropods). Polychaete annelids, ('polychaeta' literally meaning "many bristles") are named for their chaetae. In Polychaeta, chaetae are found as bundles on the parapodia, paired appendages on the side of the body. The chaetae are epidermal extracellular structures, and clearly visible in most polychaetes. They are probably the best studied structures in these animals. Use in taxonomy and identification The ultrastructure of chaetae is fundamentally similar for all taxa but there is vast diversity in chaetal morphology. Moreover, chaetae bear precise characters for determination of species and taxonomic assessment. The shape, absolute and relative size, number, position, ornamentation and type are important taxonomic characters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commensal
Commensalism is a long-term biological interaction ( symbiosis) in which members of one species gain benefits while those of the other species neither benefit nor are harmed. This is in contrast with mutualism, in which both organisms benefit from each other; amensalism, where one is harmed while the other is unaffected; parasitism, where one is harmed and the other benefits, and parasitoidism, which is similar to parasitism but the parasitoid has a free-living state and instead of just harming its host, it eventually ends up killing it. The commensal (the species that benefits from the association) may obtain nutrients, shelter, support, or locomotion from the host species, which is substantially unaffected. The commensal relation is often between a larger host and a smaller commensal; the host organism is unmodified, whereas the commensal species may show great structural adaptation consistent with its habits, as in the remoras that ride attached to sharks and other fish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophiuroidea
Brittle stars, serpent stars, or ophiuroids (; ; referring to the serpent-like arms of the brittle star) are echinoderms in the class Ophiuroidea, closely related to starfish. They crawl across the sea floor using their flexible arms for locomotion. The ophiuroids generally have five long, slender, whip-like arms which may reach up to in length on the largest specimens. The Ophiuroidea contain two large clades, Ophiurida (brittle stars) and Euryalida (basket stars). Over 2,000 species of brittle stars live today. More than 1,200 of these species are found in deep waters, greater than 200 m deep. Range The ophiuroids diverged in the Early Ordovician, about 500 million years ago. Ophiuroids can be found today in all of the major marine provinces, from the poles to the tropics. Basket stars are usually confined to the deeper parts of this range; Ophiuroids are known even from abyssal (>6,000 m) depths. However, brittle stars are also common members of reef communities, where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Stars
Starfish or sea stars are star-shaped echinoderms belonging to the class Asteroidea (). Common usage frequently finds these names being also applied to ophiuroids, which are correctly referred to as brittle stars or basket stars. Starfish are also known as asteroids due to being in the class Asteroidea. About 1,900 species of starfish live on the seabed in all the world's oceans, from warm, tropical zones to frigid, polar regions. They are found from the intertidal zone down to abyssal depths, at below the surface. Starfish are marine invertebrates. They typically have a central disc and usually five arms, though some species have a larger number of arms. The aboral or upper surface may be smooth, granular or spiny, and is covered with overlapping plates. Many species are brightly coloured in various shades of red or orange, while others are blue, grey or brown. Starfish have tube feet operated by a hydraulic system and a mouth at the centre of the oral or lower surfa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)