|
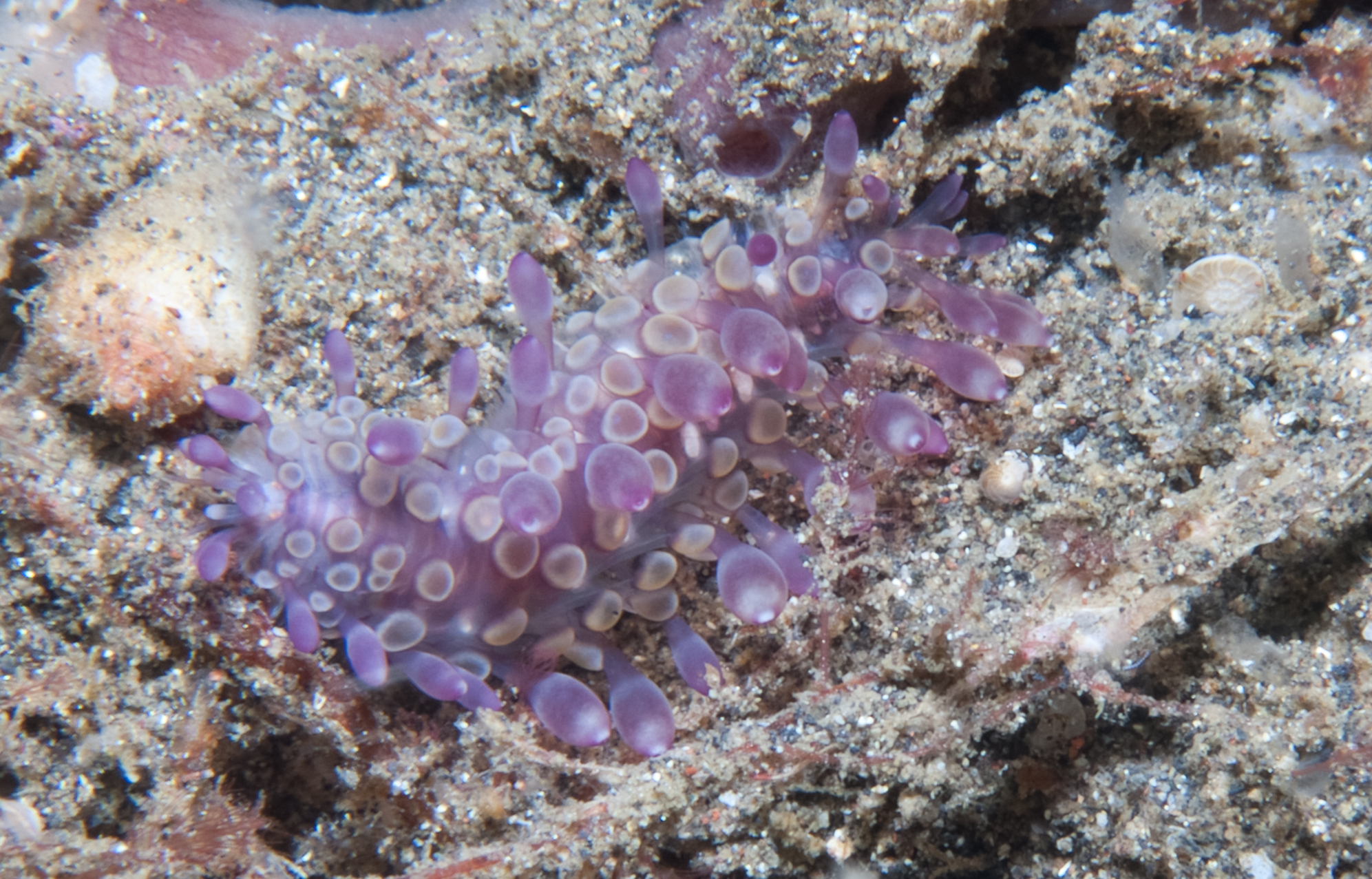
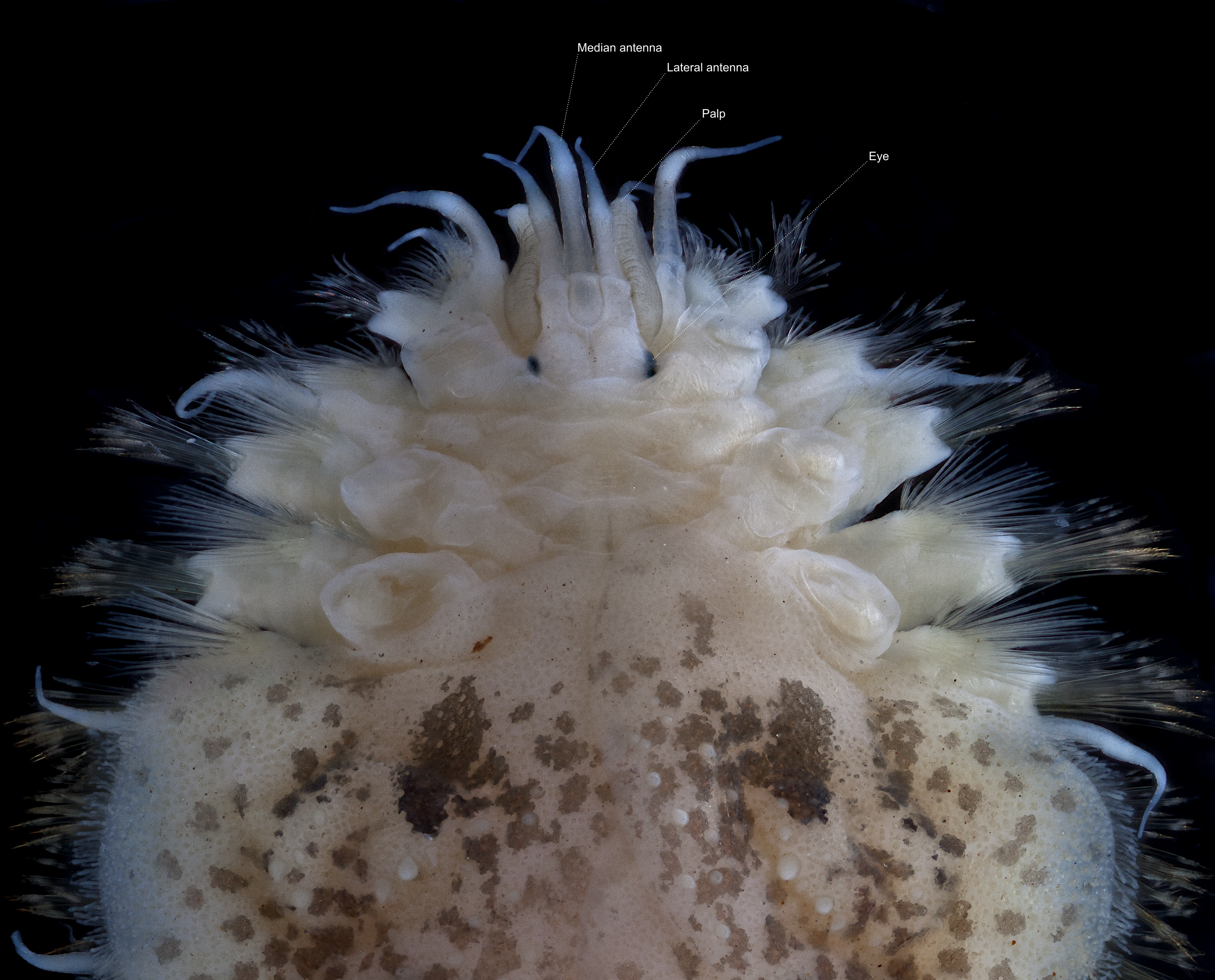
Subadyte Chesterfieldensis
''Subadyte chesterfieldensis'' is a scale worm known from the Coral Sea from a depths of about 55 m.Hanley, J. R.; Burke, M. (1991). Polychaeta Polynoidae: Scaleworms of the Chesterfield Islands and Fairway Reefs, Coral Sea. in: Crosnier, A. Résultats des Campagnes MUSORSTOM 8. Mémoires du Muséum national d'Histoire naturelle. Série A, Zoologie. 151: 9-82. Description ''Subadyte chesterfieldensis'' is a short-bodied worm with about 35 segments and 15 pairs of elytra, with no colour patterning. The prostomium The prostomium (From Ancient Greek, meaning "before the mouth"; plural: prostomia; sometimes also called the "acron") is the cephalized first body segment in an annelid worm's body at the anterior end. It is in front of (but does not include) th ... bears a pair acute anterior projections along the anterior margin, and the lateral antennae are positioned ventrally on it, directly beneath median antenna ceratophore. The notochaetae are about as thick as the neurochae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polynoidae
Polynoidae is a family of marine Polychaete worms known as "scale worms" due to the scale-like elytra on the dorsal surface. Almost 900 species are currently recognised belonging to 9 subfamilies and 167 genera. They are active hunters, but generally dwell in protected environments such as under stones. The group is widely distributed from shallow intertidal waters to hadal trenches. They are the most diverse group of polychaetes in terms of genus number and second most diverse in terms of species number which is almost 8% of all segmented worm species. Description Most Polynoidae species are short and flattened, but can reach as much as 20 cm in length and 10 cm width in '' Eulagisca gigantea'' and '' Eulagisca uschakovi''. Individuals are usually covered almost entirely by elytra, which can be shed and regenerated in many species. The elytra of some species are faintly bioluminescent, and leave glowing traces around the mouthparts of their predators, making those pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coral Sea
The Coral Sea () is a marginal sea of the South Pacific off the northeast coast of Australia, and classified as an interim Australian bioregion. The Coral Sea extends down the Australian northeast coast. Most of it is protected by the French Natural Park of the Coral Sea (french: Parc Naturel de la Mer de Corail) and the Australian Coral Sea Marine Park. The sea was the location for the Battle of the Coral Sea, a major confrontation during World War II between the navies of the Empire of Japan, and the United States and Australia. The sea contains numerous islands and reefs, as well as the world's largest reef system, the Great Barrier Reef (GBR), which was declared a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1981. All previous oil exploration projects were terminated at the GBR in 1975, and fishing is restricted in many areas. The reefs and islands of the Coral Sea are particularly rich in birds and aquatic life and are a popular tourist destination, both domestically and inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elytron (Annelida)
In annelids, elytra (; from Greek ἔλυτρον "sheath, cover"; singular: elytron ) are shield-like scales that are attached dorsally, one pair on each of a number of alternating segments and entirely or partly cover the dorsum. Elytra are modified dorsal cirri, and their number, size, location, and ornamentation are important taxonomic characters. The basal part of the elytra is known as the elytrophore; if (as is often the case) elytra are lost their presence is indicated by the elytrophore which is still present and visible. Annelids possessing elytra are also known as "scale worms". Possession of elytra is characteristic of the annelid suborder Aphroditiformia. Gallery File:Eunoe leiotentaculata lower res.jpg, A ''Eunoe leiotentaculata'' specimen showing its 15 pairs of elytra. File:Euphione sp. dorsal.jpg, ''Euphione ''Euphione'' is a genus of polychaetes belonging to the family Polynoidae. The species of this genus are found in Australia, Malesia Malesia is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostomium
The prostomium (From Ancient Greek, meaning "before the mouth"; plural: prostomia; sometimes also called the "acron") is the cephalized first body segment in an annelid worm's body at the anterior end. It is in front of (but does not include) the mouth, being usually a small shelf- or lip-like extension over the dorsal side of the mouth. The prostomium together with the peristomium, which includes the mouth and pharynx, make up the annelid head. Description The prostomium is part of the head and holds at least part of the brain and often bears sensory structures such as the eyes, antennae and palps. It may function like a kind of overlip when the animal is feeding. The prostomium bears many important taxonomic characters and its shape and composition are important for annelid systematics. In addition to the eyes, antennae and palps, the prostomium can possess appendages such as tentacles or cirri. Moreover, some polychaete Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class of gener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaeta
A chaeta or cheta (from Greek χαίτη “crest, mane, flowing hair"; plural: chaetae) is a chitinous bristle or seta found in annelid worms, (although the term is also frequently used to describe similar structures in other invertebrates such as arthropods). Polychaete annelids, ('polychaeta' literally meaning "many bristles") are named for their chaetae. In Polychaeta, chaetae are found as bundles on the parapodia, paired appendages on the side of the body. The chaetae are epidermal extracellular structures, and clearly visible in most polychaetes. They are probably the best studied structures in these animals. Use in taxonomy and identification The ultrastructure of chaetae is fundamentally similar for all taxa but there is vast diversity in chaetal morphology. Moreover, chaetae bear precise characters for determination of species and taxonomic assessment. The shape, absolute and relative size, number, position, ornamentation and type are important taxonomic characters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |