|
Subacute Thyroiditis
Subacute thyroiditis refers to a temporal classification of the different forms of thyroiditis based on onset of symptoms. The temporal classification of thyroiditis includes presentation of symptoms in an acute, subacute, or chronic manner. There are also other classification systems for thyroiditis based on factors such as clinical symptoms and underlying etiology. Broadly, there are three categories of thyroiditis that can present in a subacute fashion, including subacute granulomatous thyroiditis, subacute lymphocytic thyroiditis, and drug-induced thyroiditis. In all three categories, there is inflammation of the thyroid gland causing damage to the thyroid follicular cells which produce and secrete thyroid hormone. This often results in three phases of thyroid dysfunction beginning with initial thyrotoxicosis followed by hypothyroidism before resolution back to normal thyroid function. In the thyrotoxic stage, individuals usually complain of fever, myalgia, and may have a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subacute Granulomatous Thyroiditis
De Quervain's thyroiditis, also known as subacute granulomatous thyroiditis or giant cell thyroiditis, is a self-limiting inflammatory illness of the thyroid gland. De Quervain thyroiditis is characterized by fever, flu-like symptoms, a painful goiter, and neck pain. The disease has a natural history of four phases: thyroid pain, thyrotoxicosis, euthyroid phase, hypothyroid phase, and recovery euthyroid phase. De Quervain's thyroiditis has been linked to various diseases, including mumps, adenovirus, and enterovirus. It may have a hereditary component, with two-thirds of patients having positive histocompatibility antigen (HLA) B35 results. Atypical cases have HLA B15/62 positivity, and it is more common in summer or fall months in people who test positive for HLA B67. De Quervain thyroiditis is diagnosed through clinical and test results, with laboratory features including elevated C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Thyroid function testing often shows dec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
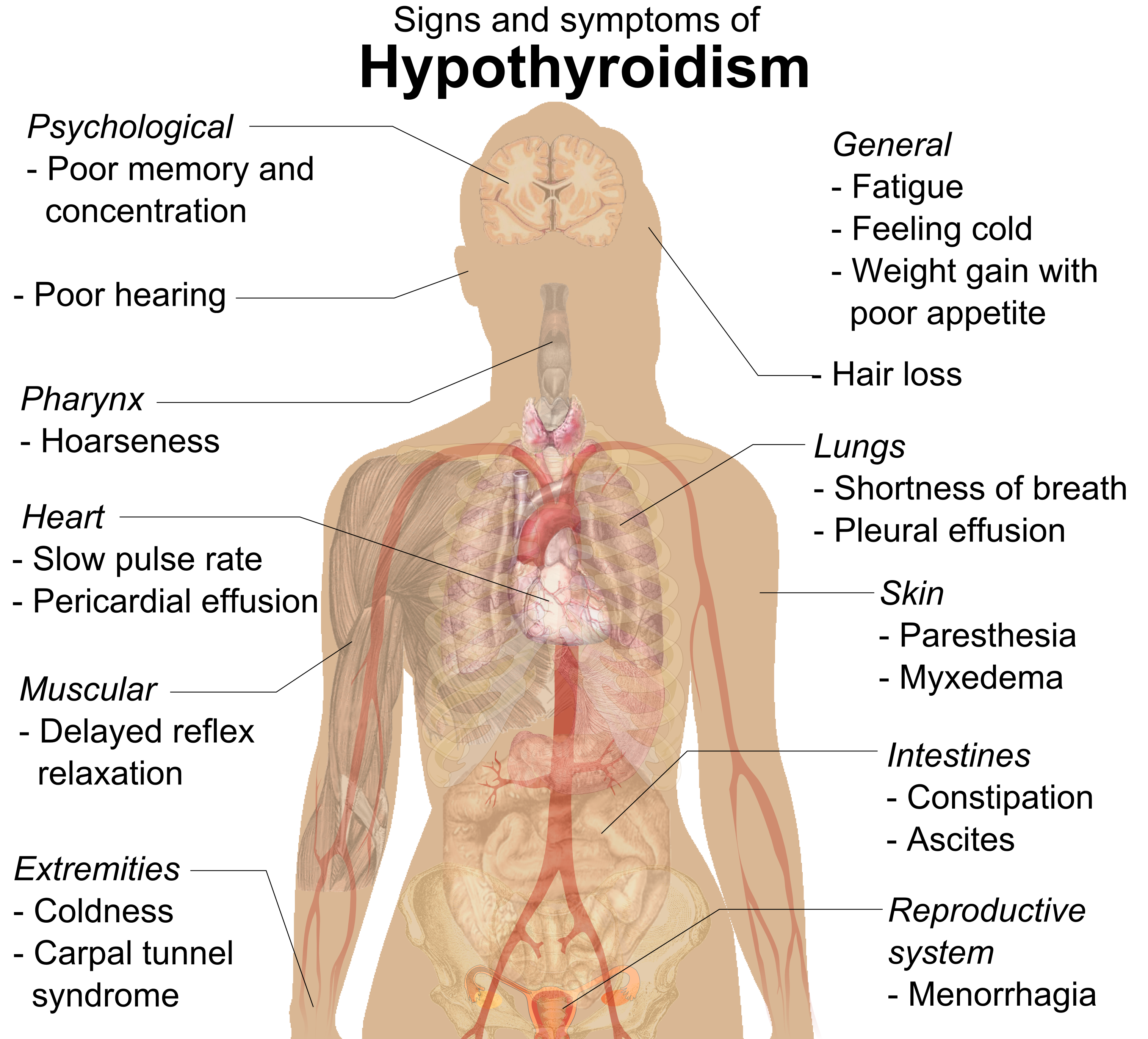
Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
Hashimoto's thyroiditis, also known as chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis, Hashimoto's disease and autoimmune thyroiditis, is an autoimmune disease in which the thyroid gland is gradually destroyed. Early on, symptoms may not be noticed. Over time, the thyroid may enlarge, forming a painless goiter. Most people eventually develop hypothyroidism with accompanying weight gain, fatigue, constipation, hair loss, and general pains. After many years the thyroid typically shrinks in size. Potential complications include thyroid lymphoma. Further complications of hypothyroidism can include high cholesterol, heart disease, heart failure, high blood pressure, myxedema, and potential problems in pregnancy. Hashimoto's thyroiditis is thought to be due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Risk factors include a family history of the condition and having another autoimmune disease. Diagnosis is confirmed with blood tests for TSH, thyroxine ( T4), antithyroid autoant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antithyroid Agent
An antithyroid agent is a hormone inhibitor acting upon thyroid hormones. The main antithyroid drugs are carbimazole (in the UK), methimazole (in the US), and propylthiouracil (PTU). A less common antithyroid agent is potassium perchlorate. Classification based on mechanisms of action The mechanisms of action of antithyroid drugs are not completely understood. Based on their mechanisms of action, the drugs are classified into following six classes. Thyroid hormone synthesis inhbitors These drugs probably inhibit the enzyme thyroid peroxidase ( thyroperoxidase), decreasing iodide oxidation, iodination of tyrosyl residues in thyroglobulin, and coupling of iodotyrosyl and iodothyronyl residues. It is thought that they inhibit the thyroperoxidase-catalyzed oxidation reactions by acting as substrates for the postulated peroxidase-iodine complex, thus competitively inhibiting the interaction with the amino acid tyrosine. The most common drugs in this class are thioamides, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Blocker
Beta blockers, also spelled β-blockers, are a class of medications that are predominantly used to manage abnormal heart rhythms ( arrhythmia), and to protect the heart from a second heart attack after a first heart attack ( secondary prevention). They are also widely used to treat high blood pressure, although they are no longer the first choice for initial treatment of most people. Beta blockers are competitive antagonists that block the receptor sites for the endogenous catecholamines epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline) on adrenergic beta receptors, of the sympathetic nervous system, which mediates the fight-or-flight response. Beta-adrenergic receptors are found on cells of the heart muscles, smooth muscles, airways, arteries, kidneys, and other tissues that are part of the sympathetic nervous system and lead to stress responses, especially when they are stimulated by epinephrine (adrenaline). Beta blockers interfere with the binding to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drug
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a Indication (medicine), therapeutic drug class which Analgesic, reduces pain, Anti-inflammatory, decreases inflammation, Antipyretic, decreases fever, and Antithrombotic, prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose and duration of use, but largely include an increased risk of Stomach ulcers, gastrointestinal ulcers and bleeds, heart attack, and kidney disease. The term ''non-steroidal'', common from around 1960, distinguishes these drugs from corticosteroids, another class of anti-inflammatory drugs, which during the 1950s had acquired a bad reputation due to overuse and side-effect problems after their introduction in 1948. NSAIDs work by inhibiting the activity of cyclooxygenase enzymes (the COX-1 and COX-2 isozyme, isoenzymes). In cells, these enzymes are involved in the synthesis of key biological mediators, namely prostaglandins, which are involved in inflammation, and thromboxanes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fine-needle Aspiration
Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) is a diagnostic procedure used to investigate lumps or masses. In this technique, a thin (23–25 gauge (0.52 to 0.64 mm outer diameter)), hollow needle is inserted into the mass for sampling of cells that, after being stained, are examined under a microscope (biopsy). The sampling and biopsy considered together are called fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) or fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) (the latter to emphasize that any aspiration biopsy involves cytopathology, not histopathology). Fine-needle aspiration biopsies are very safe for minor surgical procedures. Often, a major surgical (excisional or open) biopsy can be avoided by performing a needle aspiration biopsy instead, eliminating the need for hospitalization. In 1981, the first fine-needle aspiration biopsy in the United States was done at Maimonides Medical Center. The modern procedure is widely used to diagnose cancer and inflammatory conditions. Fine needle aspiration is g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radioactive Iodine Uptake Test
The radioactive iodine uptake test is a type of scan used in the diagnosis of thyroid problems, particularly hyperthyroidism. It is entirely different from radioactive iodine therapy (RAI therapy), which uses much higher doses to destroy cancerous cells. The RAIU test is also used as a follow-up to RAI therapy to verify that no thyroid cells survived, which could still be cancerous. ThyCa: Thyroid Cancer Survivors' Association, Inc., Radioactive Iodine (RAI). The patient swallows Isotopes of iodine#Notable radioisotopes, a radioisotope of iodine in the form of capsule or fluid, and the absorption (uptake) of this radioactive tracer, radiotracer by the thyroid is studied after 4–6 hours and after 24 hours with the aid of a scintillation counter. The dose is typically 0.15–0.37 Megabecquerel, MBq (4–10 Microcurie, μCi) of Iodine-131, 131I iodide, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflammatory Markers
Acute-phase proteins (APPs) are a class of proteins whose concentrations in blood plasma either increase (positive acute-phase proteins) or decrease (negative acute-phase proteins) in response to inflammation. This response is called the ''acute-phase reaction'' (also called ''acute-phase response''). The acute-phase reaction characteristically involves fever, acceleration of peripheral leukocytes, circulating neutrophils and their precursors. The terms ''acute-phase protein'' and ''acute-phase reactant'' (APR) are often used synonymously, although some APRs are (strictly speaking) polypeptides rather than proteins. In response to injury, local inflammatory cells (neutrophil granulocytes and macrophages) secrete a number of cytokines into the bloodstream, most notable of which are the interleukins IL1, and IL6, and TNF-α. The liver responds by producing many acute-phase reactants. At the same time, the production of a number of other proteins is reduced; these proteins are, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroid Function Tests
Thyroid function tests (TFTs) is a collective term for blood tests used to check the function of the thyroid. TFTs may be requested if a patient is thought to suffer from hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) or hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid), or to monitor the effectiveness of either thyroid-suppression or hormone replacement therapy. It is also requested routinely in conditions linked to thyroid disease, such as atrial fibrillation and anxiety disorder. A TFT panel typically includes thyroid hormones such as thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH, thyrotropin) and thyroxine (T4), and triiodothyronine (T3) depending on local laboratory policy. Thyroid-stimulating hormone Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH, thyrotropin) is generally increased in hypothyroidism and decreased in hyperthyroidism,Military Obstetrics & Gynecology > Thyroid Function TestsIn turn citing: Operational Medicine 2001, Health Care in Military Settings, NAVMED P-5139, May 1, 2001, Bureau of Medicine and Surge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dysphagia
Dysphagia is difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under " symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, in some contexts it is classified as a condition in its own right. It may be a sensation that suggests difficulty in the passage of solids or liquids from the mouth to the stomach, a lack of pharyngeal sensation or various other inadequacies of the swallowing mechanism. Dysphagia is distinguished from other symptoms including odynophagia, which is defined as painful swallowing, and globus, which is the sensation of a lump in the throat. A person can have dysphagia without odynophagia (dysfunction without pain), odynophagia without dysphagia (pain without dysfunction) or both together. A psychogenic dysphagia is known as phagophobia. Classification Dysphagia is classified into the following major types: # Oropharyngeal dysphagia # Esophageal and obstructive dysphagia # Neuromuscular symptom complexes # Functional dysphagia is defined in some patients as having no organic c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes (T1D), formerly known as juvenile diabetes, is an autoimmune disease that occurs when the body's immune system destroys pancreatic cells (beta cells). In healthy persons, beta cells produce insulin. Insulin is a hormone required by the body to store and convert blood sugar into energy. T1D results in high blood sugar levels in the body prior to treatment. Common symptoms include frequent urination, increased thirst, increased hunger, weight loss, and other complications. Additional symptoms may include blurry vision, tiredness, and slow wound healing (owing to impaired blood flow). While some cases take longer, symptoms usually appear within weeks or a few months. The cause of type 1 diabetes is not completely understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. The underlying mechanism involves an autoimmune destruction of the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. Diabetes is diagnosed by testing the leve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postpartum Thyroiditis
Postpartum thyroiditis is a type of thyroiditis, inflammation of the thyroid, occurring in the first 12 months after pregnancy and typically involves hyperthyroidism followed by hypothyroidism which is most often temporary. Postpartum thyroiditis is believed to result from the modifications to the immune system necessary in pregnancy, and histologically is the same as subacute lymphocytic thyroiditis also called silent thyroiditis or painless thyroiditis, a form of subacute thyroiditis. The process is normally self-limiting, but when thyroid antibodies are found there is a high chance of this proceeding to permanent hypothyroidism. Signs and symptoms The initial phase of hyperthyroid symptoms occurs transiently about two to six months postpartum. Typical symptoms include irritability, nervousness, palpitations, and heat intolerance. Hormonal disturbances during this phase tend to occur with lower intensity compared with the hypothyroid phase. As a result, the hyperthyroid phas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |