|
Suba Language
Kisuba, also known as Olusuba, is a Bantu language spoken by the Suba people (Kenya), Suba people of Kenya. The language features an extensive noun-classification system using prefixes that address gender and number. Suba clans are located on the eastern shore and islands of Lake Victoria in Kenya and Tanzania. They have formed alliances with neighboring clans, such as the Luo dialect, Luo people, via intermarriages, and as a result a majority of Suba people are bilingual in Dholuo language, Dholuo. The Suba religion has an ancient polytheistic history that includes writings of diverse, ancestral spirits. A recent revival of the Suba language and its culture has influenced the increasing number of native speakers each year. History Suba is an African language spoken by the Sub-Saharan people on the eastern shores of Lake Victoria. Trade dependence was established in the mid-19th century between the Suba people (Kenya), Suba people and the Luo, a larger neighboring clan. After a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenya
Kenya, officially the Republic of Kenya, is a country located in East Africa. With an estimated population of more than 52.4 million as of mid-2024, Kenya is the 27th-most-populous country in the world and the 7th most populous in Africa. Kenya's capital and largest city is Nairobi. Its second-largest and oldest city is Mombasa, a major port city located on Mombasa Island. Other major cities within the country include Kisumu, Nakuru & Eldoret. Going clockwise, Kenya is bordered by South Sudan to the northwest (though much of that border includes the disputed Ilemi Triangle), Ethiopia to the north, Somalia to the east, the Indian Ocean to the southeast, Tanzania to the southwest, and Lake Victoria and Uganda to the west. Kenya's geography, climate and population vary widely. In western, rift valley counties, the landscape includes cold, snow-capped mountaintops (such as Batian, Nelion and Point Lenana on Mount Kenya) with vast surrounding forests, wildlife and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dholuo Language
The Dholuo dialect () or ''Nilotic Kavirondo'', is a dialect of the Luo group of Nilotic languages, spoken by about 4.2 million Luo people of Kenya and Tanzania, who occupy parts of the eastern shore of Nam Lolwe (Lake Victoria) and areas to the south. It is used for broadcasts on Ramogi TV and KBC ( Kenya Broadcasting Corporation, formerly the ''Voice of Kenya''). Dholuo is mutually intelligible with Alur, Acholi, Adhola and Lango of Uganda. Dholuo and the aforementioned Uganda languages are all linguistically related to Dholuo of South Sudan and Anuak of Ethiopia due to common ethnic origins of the larger Luo peoples who speak Luo languages. It is estimated that Dholuo has 93% lexical similarity with Dhopadhola (Adhola), 90% with Leb Alur (Alur), 83% with Leb Achol (Acholi) and 81% with Leb Lango. However, these are often counted as separate languages despite common ethnic origins due to linguistic shift occasioned by geographical movement. Literacy (''Of the Luo f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Languages Of Kenya
Kenya is a Multilingualism, multilingual country. The two official languages of Kenya, Swahili language, Swahili and English language, English, are widely spoken as lingua francas; however, including second-language speakers, Swahili is more widely spoken than English. Swahili is a Bantu language native to East Africa and English is inherited from British Kenya, British colonial rule. Overview According to ''Ethnologue'', there are a total of 68 languages spoken in Kenya. This variety is a reflection of the country's diverse population that includes most major ethnoracial and linguistic groups found in Africa (see Languages of Africa). Languages spoken locally belong to three broad language families: Niger-Congo languages, Niger-Congo (Bantu languages, Bantu branch), Nilo-Saharan languages, Nilo-Saharan (Nilotic languages, Nilotic branch) and Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic (Cushitic languages, Cushitic). They are spoken by the country's Bantu peoples, Bantu, Nilotic and Cus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Exclusion
Social exclusion or social marginalisation is the social disadvantage and relegation to the fringe of society. It is a term that has been used widely in Europe and was first used in France in the late 20th century. In the EU context, the European Commission defines it as ''"a situation whereby a person is prevented (or excluded) from contributing to and benefiting from economic and social progress"''. It is used across disciplines including education, sociology, psychology, healthcare, politics and economics. Social exclusion is the process in which individuals are blocked from (or denied full access to) various rights, opportunities and resources that are normally available to members of a different group, and which are fundamental to social integration and observance of human rights within that particular group (e.g. due process). Alienation or disenfranchisement resulting from social exclusion can be connected to a person's social class, race, skin color, religious aff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numeral System
A numeral system is a writing system for expressing numbers; that is, a mathematical notation for representing numbers of a given set, using digits or other symbols in a consistent manner. The same sequence of symbols may represent different numbers in different numeral systems. For example, "11" represents the number ''eleven'' in the decimal or base-10 numeral system (today, the most common system globally), the number ''three'' in the binary or base-2 numeral system (used in modern computers), and the number ''two'' in the unary numeral system (used in tallying scores). The number the numeral represents is called its ''value''. Additionally, not all number systems can represent the same set of numbers; for example, Roman, Greek, and Egyptian numerals don't have a representation of the number zero. Ideally, a numeral system will: *Represent a useful set of numbers (e.g. all integers, or rational numbers) *Give every number represented a unique representation (or a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Script
The Latin script, also known as the Roman script, is a writing system based on the letters of the classical Latin alphabet, derived from a form of the Greek alphabet which was in use in the ancient Greek city of Cumae in Magna Graecia. The Greek alphabet was altered by the Etruscan civilization, Etruscans, and subsequently their alphabet was altered by the Ancient Romans. Several Latin-script alphabets exist, which differ in graphemes, collation and phonetic values from the classical Latin alphabet. The Latin script is the basis of the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA), and the 26 most widespread letters are the letters contained in the ISO basic Latin alphabet, which are the same letters as the English alphabet. Latin script is the basis for the largest number of alphabets of any writing system and is the List of writing systems by adoption, most widely adopted writing system in the world. Latin script is used as the standard method of writing the languages of Western and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Writing System
A writing system comprises a set of symbols, called a ''script'', as well as the rules by which the script represents a particular language. The earliest writing appeared during the late 4th millennium BC. Throughout history, each independently invented writing system gradually emerged from a system of proto-writing, where a small number of ideographs were used in a manner incapable of fully encoding language, and thus lacking the ability to express a broad range of ideas. Writing systems are generally classified according to how its symbols, called ''graphemes'', relate to units of language. Phonetic writing systemswhich include alphabets and syllabariesuse graphemes that correspond to sounds in the corresponding spoken language. Alphabets use graphemes called ''letter (alphabet), letters'' that generally correspond to spoken phonemes. They are typically divided into three sub-types: ''Pure alphabets'' use letters to represent both consonant and vowel sounds, ''abjads'' gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
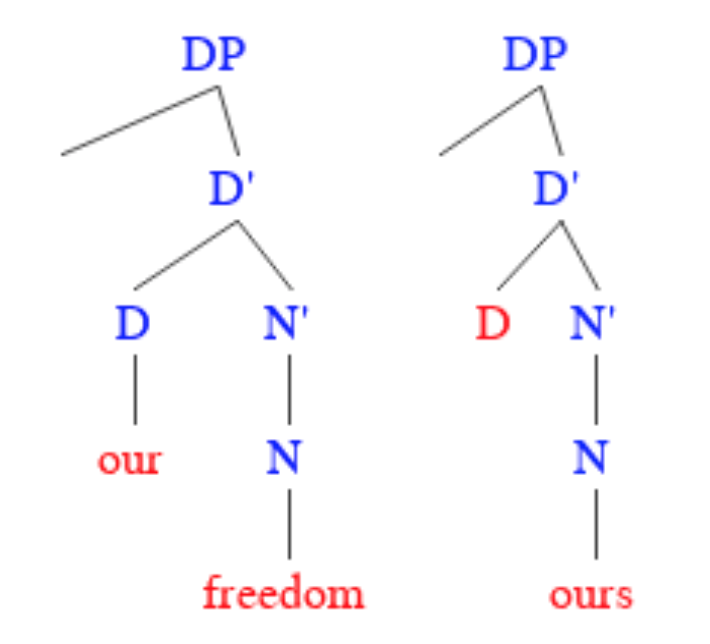
Pronoun
In linguistics and grammar, a pronoun (Interlinear gloss, glossed ) is a word or a group of words that one may substitute for a noun or noun phrase. Pronouns have traditionally been regarded as one of the part of speech, parts of speech, but some modern theorists would not consider them to form a single class, in view of the variety of functions they perform cross-linguistically. An example of a pronoun is "you", which can be either singular or plural. Sub-types include personal pronoun, personal and possessive pronouns, reflexive pronoun, reflexive and reciprocal pronoun, reciprocal pronouns, demonstrative pronouns, relative pronoun, relative and interrogative pronouns, and indefinite pronouns. The use of pronouns often involves anaphora (linguistics), anaphora, where the meaning of the pronoun is dependent on an antecedent (grammar), antecedent. For example, in the sentence ''That poor man looks as if he needs a new coat'', the meaning of the pronoun ''he'' is dependent on its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
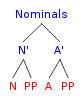
Nominal (linguistics)
In linguistics, the term ''nominal'' refers to a category used to group together nouns and adjectives based on shared properties. The motivation for nominal grouping is that in many languages nouns and adjectives share a number of Morphology (linguistics), morphological and Syntax, syntactic properties. The systems used in such languages to show agreement can be classified broadly as gender systems, noun class systems or Grammatical case, case marking, classifier systems, and mixed systems. Typically an affix related to the noun appears attached to the other Part of speech, parts of speech within a sentence to create agreement. Such morphological agreement usually occurs in parts within the noun phrase, such as determiners and adjectives. Languages with overt nominal agreement vary in how and to what extent agreement is required. History The history of research on ''nominals'' dates back to European studies on Latin and Bantu in which agreement between ''nouns'' and ''adjectives ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grave Accent
The grave accent () ( or ) is a diacritical mark used to varying degrees in French, Dutch, Portuguese, Italian, Catalan and many other Western European languages as well as for a few unusual uses in English. It is also used in other languages using the Latin alphabet, such as Mohawk and Yoruba, and with non-Latin writing systems such as the Greek and Cyrillic alphabets and the Bopomofo or Zhuyin Fuhao semi-syllabary. It has no single meaning, but can indicate pitch, stress, or other features. For the most commonly encountered uses of the accent in the Latin and Greek alphabets, precomposed characters are available. For less-used and compound diacritics, a combining character facility is available. A free-standing version of the symbol (), commonly called a backtick, also exists and has acquired other uses. Uses Pitch The grave accent first appeared in the polytonic orthography of Ancient Greek to mark a lower pitch than the high pitch of the acute accent. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Accent
The acute accent (), , is a diacritic used in many modern written languages with alphabets based on the Latin alphabet, Latin, Cyrillic script, Cyrillic, and Greek alphabet, Greek scripts. For the most commonly encountered uses of the accent in the Latin and Greek alphabets, precomposed characters are available. Uses History An early precursor of the acute accent was the Apex (diacritic), apex, used in Latin language, Latin inscriptions to mark vowel length, long vowels. The acute accent was first used in French in 1530 by Geoffroy Tory, the royal printer. Pitch Ancient Greek The acute accent was first used in the Greek diacritics, polytonic orthography of Ancient Greek, where it indicated a syllable with a high pitch accent, pitch. In Modern Greek, a stress (linguistics), stress accent has replaced the pitch accent, and the acute marks the stressed syllable of a word. The Greek name of the accented syllable was and is (''oxeîa'', Modern Greek ''oxía'') "sharp" or "h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |