|
Suaeda Vermiculata
''Suaeda vermiculata'' is a species of plant in the family Amaranthaceae (formerly classified under the Chenopodiaceae). It is a salt-tolerant plant (halophyte) that grows naturally in salt-affected areas. Description It is a shrub and can grow to 0.4–1 m height, with woody stems at its base, very branched. Distribution Its distribution includes Africa and the Middle East, including North Africa North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of t ..., the Arabian Peninsula, Yemen's Socotra, Iraq, Jordan and Palestine to the east of India as well as the Canary Islands in Cape Verde and from Senegal, Mauritania and Mali to Chad, Sudan, South Sudan, Kenya, Ethiopia and Somalia. Ecology They are found in coastal bushlands as well as inland saline sites, sand plains, stony places and des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
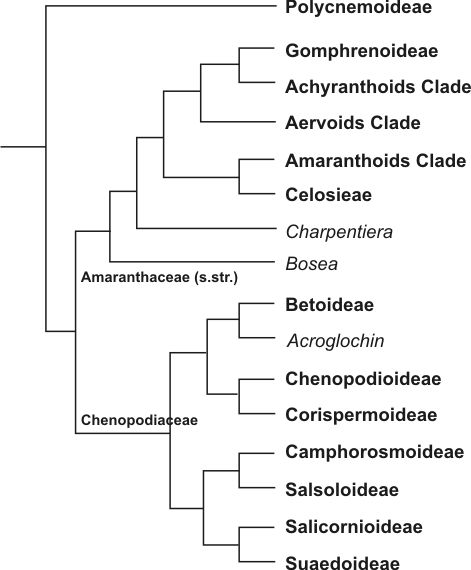
Amaranthaceae
Amaranthaceae ( ) is a family of flowering plants commonly known as the amaranth family, in reference to its type genus '' Amaranthus''. It includes the former goosefoot family Chenopodiaceae and contains about 165 genera and 2,040 species, making it the most species-rich lineage within its parent order, Caryophyllales. Description Most species in the Amaranthaceae are annual or perennial herbs or subshrubs; others are shrubs; very few species are vines or trees. Some species are succulent. Many species have stems with thickened nodes. The wood of the perennial stem has a typical "anomalous" secondary growth; only in subfamily Polycnemoideae is secondary growth normal. The leaves are simple and mostly alternate, sometimes opposite. They never possess stipules. They are flat or terete, and their shape is extremely variable, with entire or toothed margins. In some species, the leaves are reduced to minute scales. In most cases, neither basal nor terminal aggregations of leav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chenopodiaceae
Amaranthaceae ( ) is a family of flowering plants commonly known as the amaranth family, in reference to its type (biology), type genus ''Amaranthus''. It includes the former goosefoot family Chenopodiaceae and contains about 165 genera and 2,040 species, making it the most species-rich lineage within its parent order (biology), order, Caryophyllales. Description Most species in the Amaranthaceae are Annual plant, annual or perennial herbs or subshrubs; others are shrubs; very few species are vines or trees. Some species are succulent. Many species have stems with thickened nodes. The wood of the perennial stem has a typical "anomalous" secondary growth; only in subfamily Polycnemoideae is secondary growth normal. The Leaf, leaves are simple and mostly alternate, sometimes opposite. They never possess stipules. They are flat or terete, and their shape is extremely variable, with entire or toothed margins. In some species, the leaves are reduced to minute scales. In most cases, n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservatory And Botanical Garden Of The City Of Geneva
The Conservatory and Botanical Garden of the city of Geneva () is a museum and an institution of the City of Geneva. Establishment and location It was founded in 1817 in a former area of ''Bastions Park'' in 1817 by Augustin Pyramus de Candolle. The Botanical Gardens were transferred to the Console site (192 rue de Lausanne) in 1904, constructed by the Genevan architect Henri Juvet in 1902–1904 specifically to house the Delessert herbarium held at Bastions. The collection grew in 1911–1912 with the gift of the Emile Burant herbarium, then again in 1923–1924 with the posthumous donation of the de Candolle herbarium. In its present location, it occupies an area of adjacent to Lake Geneva and the park of the United Nations Office at Geneva and ranks as one of the five most important in the world. The gardens themselves were designed by . The Botanical Garden's greenhouses initially remained at the Bastions site for financial reasons. Then, in 1910–1911, the architect Henri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Africa
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of the Western Sahara in the west, to Egypt and Sudan's Red Sea coast in the east. The most common definition for the region's boundaries includes Algeria, Egypt, Libya, Morocco, Tunisia, and Western Sahara, the territory territorial dispute, disputed between Morocco and the list of states with limited recognition, partially recognized Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic. The United Nations’ definition includes all these countries as well as Sudan. The African Union defines the region similarly, only differing from the UN in excluding the Sudan and including Mauritania. The Sahel, south of the Sahara, Sahara Desert, can be considered as the southern boundary of North Africa. North Africa includes the Spanish cities of Ceuta and Melilla, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamarix Usneoides
''Tamarix usneoides'', locally known as wild tamarisk, is a twiggy shrub or small evergreen tree that grows in saline habitats, semi-deserts and karroid areas in southern Africa, ranging from Angola through Namibia to the Cape Provinces of South Africa. It has a short trunk, thin branches usually growing from ground level, tiny scale-like leaves and spikes of creamy-white flowers. Description ''Tamarix usneoides'' is a shrub or small tree, up to tall, with slender branches and an upright form. It usually branches from the base and often grows in clumps. The trunk is greyish-brown and rough, with longitudinal fissures. The roots are designed to harvest water from a large area; the taproot may descend to , and the adventitious roots spread out for on either side. The greyish-green leaves are minute and scale-like, overlapping each other and clasping the stem. The inflorescences can be loose or dense sprays of small flowers in the leaf axils or forming racemes at the tips of the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odyssea Paucinervis
''Odyssea paucinervis'' is a species of African plants in the grass family. The genus is named after the ancient Greek tale the "Odyssey", in allusion to the long journey the type species has taken through nine genera before settling in this one. The specific name means "few veined". Description This grass is a perennial plant with long, stout, rhizomes that penetrate deeply into the ground. The stems branch only at the base, have an L-shaped bend and are up to in length. They grow in matted tufts and are bluish-green. The ligules are formed from rings of hairs and the leaves are rolled, stiff and tough, and somewhat pungent. The inflorescence is narrowly elliptic or elliptic-oblong and up to long. It is composed of many spikelets, each with four to nine flowers. Distribution ''Odyssea paucinervis'' is native to Zaire, Somalia, Tanzania, Angola, Zambia, Zimbabwe, Botswana, Cape Province, Namibia, Limpopo and Mpumalanga Mpumalanga () is one of the nine provinces of Sout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suaeda
__NOTOC__ ''Suaeda'' is a genus of plants also known as seepweeds and sea-blites. Most species are confined to saline or alkaline soil habitats, such as coastal salt-flats and tidal wetlands. Many species have thick, succulent leaves, a characteristic seen in various plant genera that thrive in salty habitats (halophile plants). There are about 110 species in the genus ''Suaeda''. The most common species in northwestern Europe is ''S. maritima''. It grows along the coasts, especially in saltmarsh areas, and is known in Britain as "common sea-blite", but as "herbaceous seepweed" in the USA. It is also common along the east coast of North America from Virginia northward. One of its varieties is common in tropical Asia on the land-side edge of mangrove tidal swamps. Another variety of this polymorphic species is common in tidal zones all around Australia (''Suaeda maritima var. australis'' is also classed as ''S. australis''). On the coasts of the Mediterranean Sea a common ''Sua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halophytes
A halophyte is a salt-tolerant plant that grows in soil or waters of high salinity, coming into contact with saline water through its roots or by salt spray, such as in saline semi-deserts, mangrove swamps, marshes and sloughs, and seashores. The word derives from Ancient Greek ἅλας (halas) 'salt' and φυτόν (phyton) 'plant'. Halophytes have different anatomy, physiology and biochemistry than glycophytes.Physiology of halophytes, T. J. FLOWERS, Plant and Soil 89, 41–56 (1985) An example of a halophyte is the salt marsh grass ''Spartina alterniflora'' (smooth cordgrass). Relatively few plant species are halophytes—perhaps only 2% of all plant species. Information about many of the earth's halophytes can be found in thhalophytedatabase. The large majority of plant species are glycophytes, which are not salt-tolerant and are damaged fairly easily by high salinity. Classification Halophytes can be classified in many ways. According to Stocker (1933), it is mainly of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of The Arabian Peninsula
Flora (: floras or florae) is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring ( indigenous) native plants. The corresponding term for animals is ''fauna'', and for fungi, it is '' funga''. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora as in the terms ''gut flora'' or ''skin flora'' for purposes of specificity. Etymology The word "flora" comes from the Latin name of Flora, the goddess of plants, flowers, and fertility in Roman mythology. The technical term "flora" is then derived from a metonymy of this goddess at the end of the sixteenth century. It was first used in poetry to denote the natural vegetation of an area, but soon also assumed the meaning of a work cataloguing such vegetation. Moreover, "Flora" was used to refer to the flowers of an artificial garden in the seventeenth century. The distinction between vegetation (the general appearance of a community) and flora (the taxonomic composition of a community) wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |