Chenopodiaceae on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Amaranthaceae ( ) is a family of
 In the
In the
''
List of allergic plants in family Chenopodiaceae at pollenlibrary.com
/ref>
a
Genera of ''Amaranthaceae''
at Germplasm Resources Information Network (USDA) * *
Amaranthaceae
at Tropicos
i
IUCN link: Amaranthaceae threatened species
* Stanley L. Welsh, Clifford W. Crompton & Steven E. Clemants (2003)
Chenopodiaceae
in Flora of North America * Kenneth R. Robertson & Steven E. Clemants (2003)
Amaranthaceae
in Flora of North America * Gelin Zhu, Sergei L. Mosyakin & Steven E. Clemants (2003)
Chenopodiaceae
in Flora of China * Bojian Bao, Thomas Borsch & Steven E. Clemants (2003)
Amaranthaceae
in Flora of China {{Authority control Caryophyllales families
flowering plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (). The term angiosperm is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek words (; 'container, vessel') and (; 'seed'), meaning that the seeds are enclosed with ...
s commonly known as the amaranth family, in reference to its type
Type may refer to:
Science and technology Computing
* Typing, producing text via a keyboard, typewriter, etc.
* Data type, collection of values used for computations.
* File type
* TYPE (DOS command), a command to display contents of a file.
* ...
genus '' Amaranthus''. It includes the former goosefoot family Chenopodiaceae and contains about 165 genera and 2,040 species, making it the most species-rich lineage within its parent order
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* A socio-political or established or existing order, e.g. World order, Ancien Regime, Pax Britannica
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
...
, Caryophyllales
Caryophyllales ( ) is a diverse and heterogeneous order of flowering plants with well-known members including cacti, carnations, beets, quinoa, spinach, amaranths, pigfaces and ice plants, oraches and saltbushes, goosefoots, sundews, Venu ...
.
Description
Most species in the Amaranthaceae are annual orperennial
In horticulture, the term perennial ('' per-'' + '' -ennial'', "through the year") is used to differentiate a plant from shorter-lived annuals and biennials. It has thus been defined as a plant that lives more than 2 years. The term is also ...
herb
Herbs are a widely distributed and widespread group of plants, excluding vegetables, with savory or aromatic properties that are used for flavoring and garnishing food, for medicinal purposes, or for fragrances. Culinary use typically distingu ...
s or subshrub
A subshrub (Latin ''suffrutex'') or undershrub is either a small shrub (e.g. prostrate shrubs) or a perennial that is largely herbaceous but slightly woody at the base (e.g. garden pink and florist's chrysanthemum). The term is often interch ...
s; others are shrub
A shrub or bush is a small to medium-sized perennial woody plant. Unlike herbaceous plants, shrubs have persistent woody stems above the ground. Shrubs can be either deciduous or evergreen. They are distinguished from trees by their multiple ...
s; very few species are vine
A vine is any plant with a growth habit of trailing or scandent (that is, climbing) stems, lianas, or runners. The word ''vine'' can also refer to such stems or runners themselves, for instance, when used in wicker work.Jackson; Benjamin; Da ...
s or tree
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, e.g., including only woody plants with secondary growth, only ...
s. Some species are succulent
In botany, succulent plants, also known as succulents, are plants with parts that are thickened, fleshy, and engorged, usually to retain water in arid climates or soil conditions. The word ''succulent'' comes from the Latin word ''sucus'', meani ...
. Many species have stems with thickened nodes. The wood of the perennial stem has a typical "anomalous" secondary growth
In botany, secondary growth is the growth that results from cell division in the cambia or lateral meristems and that causes the stems and roots to thicken, while primary growth is growth that occurs as a result of cell division at the tips ...
; only in subfamily Polycnemoideae is secondary growth normal.
The leaves
A leaf (: leaves) is a principal appendage of the stem of a vascular plant, usually borne laterally above ground and specialized for photosynthesis. Leaves are collectively called foliage, as in "autumn foliage", while the leaves, stem, ...
are simple and mostly alternate, sometimes opposite. They never possess stipule
In botany, a stipule is an outgrowth typically borne on both sides (sometimes on just one side) of the base of a leafstalk (the petiole (botany), petiole). They are primarily found among dicots and rare among monocots. Stipules are considered part ...
s. They are flat or terete, and their shape is extremely variable, with entire or toothed margins. In some species, the leaves are reduced to minute scales. In most cases, neither basal nor terminal aggregations of leaves occur.
The flower
Flowers, also known as blooms and blossoms, are the reproductive structures of flowering plants ( angiosperms). Typically, they are structured in four circular levels, called whorls, around the end of a stalk. These whorls include: calyx, m ...
s are solitary or aggregated in cymes
In botany, an inflorescence is a group or cluster of flowers arranged on a plant's stem that is composed of a main branch or a system of branches. An inflorescence is categorized on the basis of the arrangement of flowers on a main axis ( ped ...
, spikes
The SPIKES protocol is a method used in clinical medicine to break bad news to patients and families. As receiving bad news can cause distress and anxiety, clinicians need to deliver the news carefully. Using the SPIKES method for introducing and ...
, or panicle
In botany, a panicle is a much-branched inflorescence. (softcover ). Some authors distinguish it from a compound spike inflorescence, by requiring that the flowers (and fruit) be pedicellate (having a single stem per flower). The branches of a p ...
s and typically perfect (bisexual) and actinomorphic
Floral symmetry describes whether, and how, a flower, in particular its perianth, can be divided into two or more identical or mirror-image parts.
Uncommonly, flowers may have no axis of symmetry at all, typically because their parts are spirall ...
. Some species have unisexual flowers. Bract
In botany, a bract is a modified or specialized leaf, associated with a reproductive structure such as a flower, inflorescence axis or cone scale.
Bracts are usually different from foliage leaves in size, color, shape or texture. They also lo ...
s and bracteoles are either herbaceous or scarious. Flowers are regular with an herbaceous or scarious perianth of (one to) mostly five (rarely to eight) tepal
A tepal is one of the outer parts of a flower (collectively the perianth). The term is used when these parts cannot easily be classified as either sepals or petals. This may be because the parts of the perianth are undifferentiated (i.e. of very ...
s, often joined. One to five stamen
The stamen (: stamina or stamens) is a part consisting of the male reproductive organs of a flower. Collectively, the stamens form the androecium., p. 10
Morphology and terminology
A stamen typically consists of a stalk called the filament ...
s are opposite to tepals or alternating, inserting from a hypogynous disc, which may have appendages (pseudo staminodes) in some species. The anther
The stamen (: stamina or stamens) is a part consisting of the male reproductive organs of a flower. Collectively, the stamens form the androecium., p. 10
Morphology and terminology
A stamen typically consists of a stalk called the filament ...
s have two or four pollen sacs (locule
A locule (: locules) or loculus (; : loculi) is a small cavity or compartment within an organ or part of an organism (animal, plant, or fungus).
In angiosperms (flowering plants), the term ''locule'' usually refers to a chamber within an ovary ...
s). In tribe Caroxyloneae, anthers have vesicular appendages. The pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by most types of flowers of seed plants for the purpose of sexual reproduction. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced Gametophyte#Heterospory, microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm ...
grains are spherical with many pores (pantoporate), with pore numbers from a few to 250 (in '' Froelichia''). One to three (rarely six) carpel
Gynoecium (; ; : gynoecia) is most commonly used as a collective term for the parts of a flower that produce ovules and ultimately develop into the fruit and seeds. The gynoecium is the innermost whorl of a flower; it consists of (one or more ...
s are fused to a superior ovary
The ovary () is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova; when released, an ovum travels through the fallopian tube/ oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries are end ...
with one (rarely two) basal ovule. Idioblasts are found in the tissues.
The diaspore
Diaspore ()also called diasporite, empholite, kayserite, or tanatariteis an aluminium hydroxide oxide mineral, α-AlO(OH), crystallizing in the orthorhombic system and isomorphous with goethite. It occurs sometimes as flattened crystals, but ...
s are seed
In botany, a seed is a plant structure containing an embryo and stored nutrients in a protective coat called a ''testa''. More generally, the term "seed" means anything that can be Sowing, sown, which may include seed and husk or tuber. Seeds ...
s or fruit
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants (angiosperms) that is formed from the ovary after flowering.
Fruits are the means by which angiosperms disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in particular have long propaga ...
s ( utricles), more often the perianth persists and is modified in fruit for means of dispersal. Sometimes even bracts and bracteoles may belong to the diaspore. More rarely the fruit is a circumscissile capsule or a berry
A berry is a small, pulpy, and often edible fruit. Typically, berries are juicy, rounded, brightly colored, sweet, sour or tart, and do not have a stone or pit although many pips or seeds may be present. Common examples of berries in the cul ...
. The horizontal or vertical seed often has a thickened or woody seed coat. The green or white embryo is either spirally (and without perisperm
In seed plants, the ovule is the structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells. It consists of three parts: the ''integument'', forming its outer layer, the ''nucellus'' (or remnant of the megasporangium), and the fema ...
) or annular (rarely straight).
Chromosome number
The basicchromosome
A chromosome is a package of DNA containing part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome-forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells, the most import ...
number is (rarely 6) mostly 8–9 (rarely 17).
Phytochemistry
Widespread in the Amaranthaceae is the occurrence of betalain pigments. The former Chenopodiaceae often containisoflavonoid
Isoflavonoids are a class of flavonoid phenolic compounds, many of which are biologically active. Isoflavonoids and their derivatives are sometimes referred to as phytoestrogens, as many isoflavonoid compounds have biological effects via the estr ...
s.
In phytochemical research, several methylenedioxyflavonols, saponins
Saponins (Latin ''sapon'', 'soap' + ''-in'', 'one of') are bitter-tasting, usually toxic plant-derived secondary metabolites. They are Organic compound, organic chemicals that become foamy when agitated in water and have high Molar mass, molecul ...
, triterpenoids, ecdysteroids, and specific root-located carbohydrates
A carbohydrate () is a biomolecule composed of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms. The typical hydrogen-to-oxygen atomic ratio is 2:1, analogous to that of water, and is represented by the empirical formula (where ''m'' and ''n'' ma ...
have been found in these plants.
Photosynthesis pathway
Although most of the family use the more common photosynthesis pathway, around 800 species are plants; this makes the Amaranthaceae the largest group with thisphotosynthesis
Photosynthesis ( ) is a system of biological processes by which photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into the chemical energy necessary to fuel their metabo ...
pathway among the eudicot
The eudicots or eudicotyledons are flowering plants that have two seed leaves (cotyledons) upon germination. The term derives from ''dicotyledon'' (etymologically, ''eu'' = true; ''di'' = two; ''cotyledon'' = seed leaf). Historically, authors h ...
s (which collectively includes about 1,600 species). Within the family, several types of photosynthesis occur, and about 17 different types of leaf anatomy are realized. Therefore, this photosynthesis pathway seems to have developed about 15 times independently during the evolution of the family. About two-thirds of the species belong to the former Chenopodiaceae. The first occurrence of photosynthesis dates from the early Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and mea ...
, about 24 million years ago, but in some groups, this pathway evolved much later, about 6 (or less) million years ago.
The multiple origin of photosynthesis in the Amaranthaceae is regarded as an evolutionary response to inexorably decreasing atmospheric levels, coupled with a more recent permanent shortage in water supply as well as high temperatures. Species that use water more efficiently had a selective advantage and were able to spread out into arid habitats.
Taxonomy
 In the
In the APG IV system
The APG IV system of flowering plant classification is the fourth version of a modern, mostly molecular-based, system of plant taxonomy for flowering plants (angiosperms) being developed by the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group (APG). It was publish ...
of 2016, as in the previous Angiosperm Phylogeny Group
The Angiosperm Phylogeny Group (APG) is an informal international group of systematic botanists who collaborate to establish a consensus on the taxonomy of flowering plants (angiosperms) that reflects new knowledge about plant relationships disc ...
classifications, the family is placed in the order Caryophyllales
Caryophyllales ( ) is a diverse and heterogeneous order of flowering plants with well-known members including cacti, carnations, beets, quinoa, spinach, amaranths, pigfaces and ice plants, oraches and saltbushes, goosefoots, sundews, Venu ...
and includes the plants formerly treated as the family Chenopodiaceae. The monophyly of this broadly defined Amaranthaceae has been strongly supported by both morphological and phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical dat ...
analyses.
The family Amaranthaceae was first published in 1789 by Antoine Laurent de Jussieu
Antoine Laurent de Jussieu (; 12 April 1748 – 17 September 1836) was a French botanist, notable as the first to publish a natural classification of flowering plants; much of his system remains in use today. His classification was based on an e ...
in ''Genera Plantarum'', p. 87–88. The first publication of family Chenopodiaceae was in 1799 by Étienne Pierre Ventenat in ''Tableau du Regne Vegetal'', 2, p. 253. The older name has priority and is now the valid scientific name of the extended Amaranthaceae (''s.l.'' = ''sensu lato'').
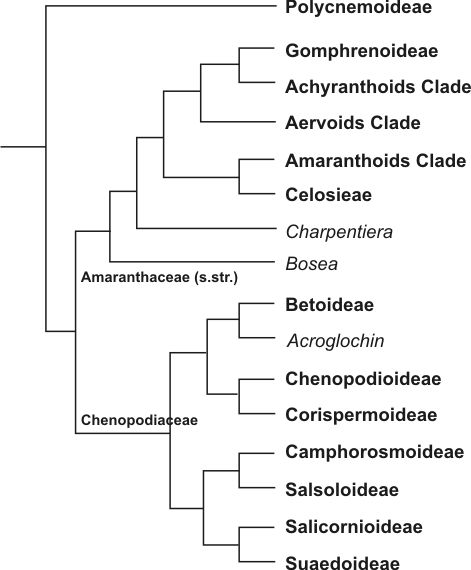
Some publications still continued to use the family name Chenopodiaceae. Phylogenetic research revealed the important impact of the subfamily Polycnemoideae on the classification (see cladogram): if Polycnemoideae are considered a part of Chenopodiaceae, then Amaranthaceae (''s.str.'' = ''sensu stricto'') have to be included, too, and the name of the extended family is Amaranthaceae. If Polycnemoideae would be separated as its own family, Chenopodiaceae and Amaranthaceae (''s.str.'') would form two distinct monophyletic
In biological cladistics for the classification of organisms, monophyly is the condition of a taxonomic grouping being a clade – that is, a grouping of organisms which meets these criteria:
# the grouping contains its own most recent co ...
groups and could be treated as two separate families.
Amaranthaceae (''s.l.'') includes the former families Achyranthaceae , Atriplicaceae , Betaceae , Blitaceae , Celosiaceae , Chenopodiaceae ''nom. cons.'', Corispermaceae , Deeringiaceae , Dysphaniaceae ''nom. cons.'', Gomphrenaceae , Polycnemaceae , Salicorniaceae , Salsolaceae , and Spinaciaceae .
The systematics of Amaranthaceae are the subject of intensive recent research. Molecular genetic studies revealed the traditional classification, based on morphological and anatomical characters, often did not reflect the phylogenetic relationships.
The former Amaranthaceae (in their narrow circumscription) are classified into two subfamilies, Amaranthoideae and Gomphrenoideae, and contain about 65 genera and 900 species in tropical Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
and North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
. The Amaranthoideae and some genera of Gomphrenoideae were found to be polyphyletic
A polyphyletic group is an assemblage that includes organisms with mixed evolutionary origin but does not include their most recent common ancestor. The term is often applied to groups that share similar features known as Homoplasy, homoplasies ...
, so taxonomic changes are needed.
Current studies classified the species of former Chenopodiaceae to eight distinct subfamilies (the research is not yet completed): Polycnemoideae, which are regarded as a basal lineage, Betoideae, Camphorosmoideae, Chenopodioideae
The Chenopodioideae are a subfamily of the flowering plant family Amaranthaceae in the APG III system, which is largely based on molecular phylogeny, but were included – together with other subfamilies – in the family Chenopodiaceae, or goose ...
, Corispermoideae, Salicornioideae, Salsoloideae, and Suaedoideae. In this preliminary classification, the Amaranthaceae ''s.l.'' are divided into 10 subfamilies with approximately 180 genera and 2,500 species.
Genera
183 genera are accepted.Amaranthaceae Juss.''
Plants of the World Online
Plants of the World Online (POWO) is an online taxonomic database published by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew.
History
Following the Convention on Biological Diversity, the Royal Botanic Gardens in Kew launched Plants of the World Online i ...
''. Retrieved 3 April 2024. A short synoptic list of genera is given here. For further and more detailed information, see the subfamily pages.
Distribution and habitat
Amaranthaceae is a widespread and cosmopolitan family from the tropics to cool temperate regions. The Amaranthaceae (''sensu stricto'') are predominantly tropical, whereas the former Chenopodiaceae have their centers of diversity in dry temperate and warm temperate areas. Many of the species arehalophyte
A halophyte is a salt-tolerant plant that grows in soil or waters of high salinity, coming into contact with saline water through its roots or by salt spray, such as in saline semi-deserts, mangrove swamps, marshes and sloughs, and seashores. ...
s, tolerating salty soils, or grow in dry steppes or semi-deserts.
Uses
Some species, such asspinach
Spinach (''Spinacia oleracea'') is a leafy green flowering plant native to Central Asia, Central and Western Asia. It is of the order Caryophyllales, family Amaranthaceae, subfamily Chenopodioideae. Its leaves are a common vegetable consumed eit ...
(''Spinacia oleracea
Spinach (''Spinacia oleracea'') is a leafy green flowering plant native to Central Asia, Central and Western Asia. It is of the order Caryophyllales, family Amaranthaceae, subfamily Chenopodioideae. Its leaves are a common vegetable consumed eit ...
'') or forms of beet
The beetroot (British English) or beet (North American English) is the taproot portion of a '' Beta vulgaris'' subsp. ''vulgaris'' plant in the Conditiva Group. The plant is a root vegetable also known as the table beet, garden beet, dinner ...
(''Beta vulgaris
''Beta vulgaris'' (beet) is a species of flowering plant in the subfamily Betoideae of the family Amaranthaceae. Economically, it is the most important crop of the large order Caryophyllales. It has several cultivar groups: the sugar beet, of gre ...
'') (beetroot
The beetroot (British English) or beet (North American English) is the taproot portion of a ''Beta vulgaris'' subsp. ''vulgaris'' plant in the Conditiva Group. The plant is a root vegetable also known as the table beet, garden beet, dinner bee ...
, chard
Chard (; '' Beta vulgaris'' subsp. ''vulgaris'', Cicla Group and Flavescens Group) is a green leafy vegetable. In the cultivars of the Flavescens Group, or Swiss chard, the leaf stalks are large and often prepared separately from the leaf b ...
), are used as vegetable
Vegetables are edible parts of plants that are consumed by humans or other animals as food. This original meaning is still commonly used, and is applied to plants collectively to refer to all edible plant matter, including edible flower, flo ...
s. Forms of ''Beta vulgaris'' include fodder beet (''Mangelwurzel
Mangelwurzel or mangold wurzel (from German ''Mangel/Mangold'', "chard" and ''Wurzel'', "root"), also called mangold,Wright, Clifford A. (2001) ''Mediterranean Vegetables: a cook's ABC of vegetables and their preparation in Spain, France, Italy, ...
'') and sugar beet
A sugar beet is a plant whose root contains a high concentration of sucrose and that is grown commercially for sugar production. In plant breeding, it is known as the Altissima cultivar group of the common beet (''Beta vulgaris''). Together with ...
. The seeds of '' Amaranthus'', lamb's quarters (''Chenopodium berlandieri''), quinoa
Quinoa (''Chenopodium quinoa''; , from Quechuan languages, Quechua ' or ') is a flowering plant in the Amaranthaceae, amaranth family. It is a herbaceous annual plant grown as a crop primarily for its edible seeds; the seeds are high in prote ...
(''Chenopodium quinoa'') and kañiwa
''Chenopodium pallidicaule'', known as cañihua, canihua or cañahua (from Quechua 'qañiwa, qañawa or qañawi') and also kañiwa or kaniwa, is a species of goosefoot, similar in character and uses to the closely related quinoa (''Chenopodium ...
(''Chenopodium pallidicaule'') are edible and are used as pseudocereals
A pseudocereal or pseudograin is one of any non-grasses that are used in much the same way as cereals (true cereals are grasses). Pseudocereals can be further distinguished from other non-cereal staple crops (such as potatoes) by their being proc ...
.
'' Dysphania ambrosioides'' (epazote) and ''Dysphania anthelmintica'' are used as medicinal herbs. Several amaranth species are also used indirectly as a source of soda ash
Sodium carbonate (also known as washing soda, soda ash, sal soda, and soda crystals) is the inorganic compound with the formula and its various hydrates. All forms are white, odourless, water-soluble salts that yield alkaline solutions in water ...
, such as members of the genus ''Salicornia
''Salicornia'' is a genus of succulent, halophytic (salt tolerant) flowering plants in the family Amaranthaceae that grow in salt marshes, on beaches, and among mangroves. ''Salicornia'' species are native to North America, Europe, central Asia, ...
'' (see glasswort).
A number of species are popular garden ornamental plant
Ornamental plants or ''garden plants'' are plants that are primarily grown for their beauty but also for qualities such as scent or how they shape physical space. Many flowering plants and garden varieties tend to be specially bred cultivars th ...
s, especially species from the genera ''Alternanthera
''Alternanthera'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Amaranthaceae. It is a widespread genus with most species occurring in the tropics, tropical Americas,Sánchez-Del Pino, I., et al. (2012)Molecular phylogenetics of ''Alternanthera'' ...
'', '' Amaranthus'', ''Celosia
''Celosia'' ( ) is a small genus of edible and ornamental plants in the amaranth family, Amaranthaceae. Its species are commonly known as woolflowers, or, if the flower heads are crested by fasciation, cockscombs. The plants are well known in E ...
'', and ''Iresine
''Iresine'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Amaranthaceae. It contains 20 to 25 species, all of which are native to the American tropics. The generic name is derived from the Greek word εριος (''erios''), meaning "wooly", refer ...
''. Other species are considered weed
A weed is a plant considered undesirable in a particular situation, growing where it conflicts with human preferences, needs, or goals.Harlan, J. R., & deWet, J. M. (1965). Some thoughts about weeds. ''Economic botany'', ''19''(1), 16-24. Pla ...
s, e.g., redroot pigweed (''Amaranthus retroflexus
''Amaranthus retroflexus'' is a species of flowering plant in the family Amaranthaceae with several common names, including red-root amaranth, redroot pigweed, red-rooted pigweed, common amaranth, pigweed amaranth, and common tumbleweed.
Outside ...
'') and alligatorweed (''Alternanthera philoxeroides
''Alternanthera philoxeroides'', commonly referred to as alligator weed, is a native species to the temperate regions of South America, which includes Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay and Uruguay. Argentina alone hosts around 27 species that fall with ...
''), and several are problematic invasive species
An invasive species is an introduced species that harms its new environment. Invasive species adversely affect habitats and bioregions, causing ecological, environmental, and/or economic damage. The term can also be used for native spec ...
, particularly in North America, including '' Salsola tragus'' and '' Bassia scoparia''. Many species are known to cause pollen allergies./ref>
References
External links
* *a
Genera of ''Amaranthaceae''
at Germplasm Resources Information Network (USDA) * *
Amaranthaceae
at Tropicos
i
IUCN link: Amaranthaceae threatened species
* Stanley L. Welsh, Clifford W. Crompton & Steven E. Clemants (2003)
Chenopodiaceae
in Flora of North America * Kenneth R. Robertson & Steven E. Clemants (2003)
Amaranthaceae
in Flora of North America * Gelin Zhu, Sergei L. Mosyakin & Steven E. Clemants (2003)
Chenopodiaceae
in Flora of China * Bojian Bao, Thomas Borsch & Steven E. Clemants (2003)
Amaranthaceae
in Flora of China {{Authority control Caryophyllales families