|
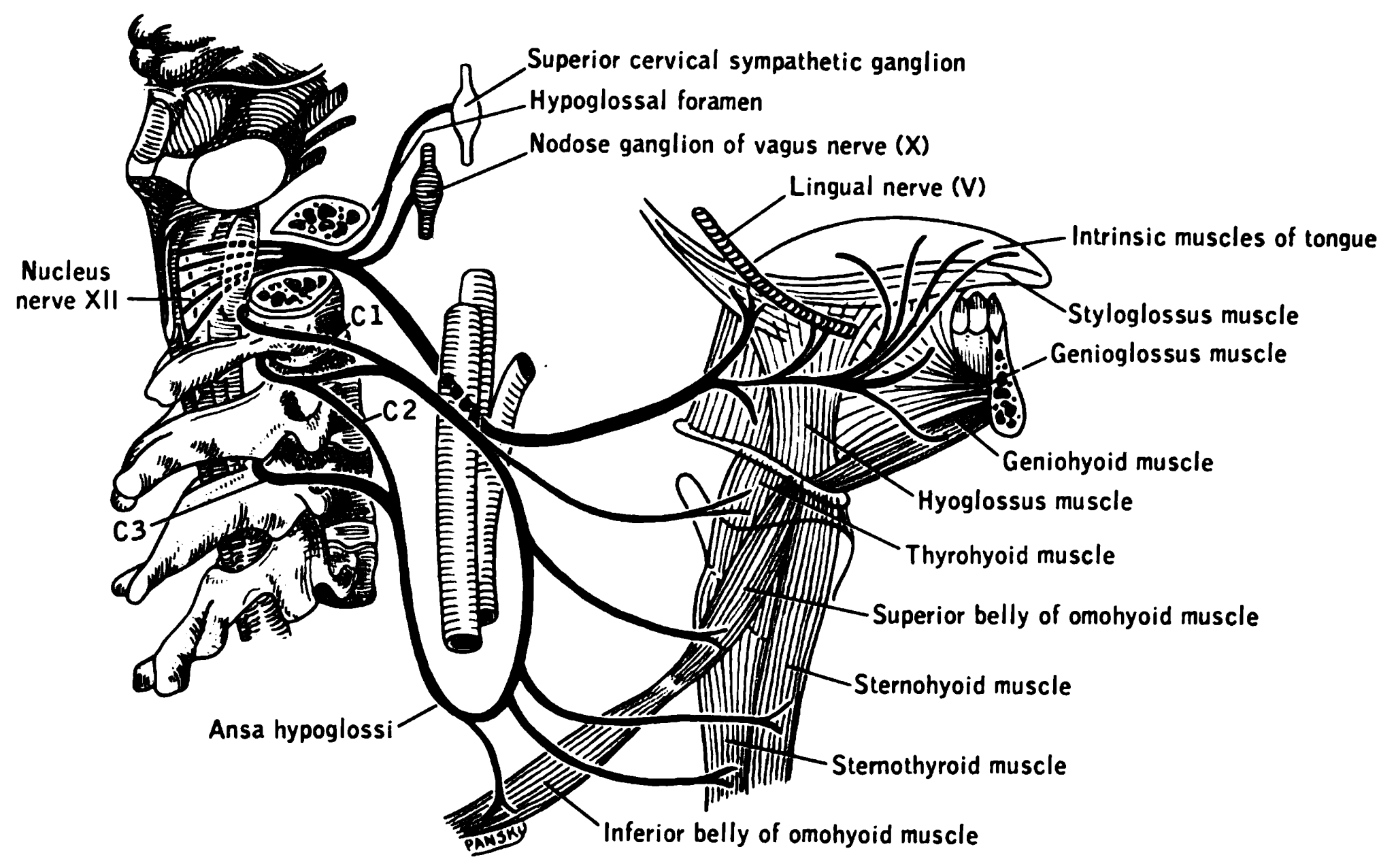
Styloglossus
The styloglossus muscle is a bilaterally paired muscle of the tongue. It originates at the styloid process of the temporal bone. It inserts onto the side of the tongue. It acts to elevate and retract the tongue. It is innervated by the hypoglossal nerve (cranial nerve XII). Anatomy The styloglossus muscle is the shortest and smallest of the three styloid muscles. Origin It arises from (the anterior and lateral surfaces of) the styloid process of the temporal bone near its apex, and from the stylomandibular ligament. Course and relations It passes anterioinferiorly from its origin to its insertion between the internal carotid artery and the external carotid artery, and between the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle The superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle is a quadrilateral muscle of the pharynx. It is the uppermost and thinnest of the three pharyngeal constrictors. The muscle is divided into four parts according to its four distincts origins: a pterygop ... an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tongue
The tongue is a Muscle, muscular organ (anatomy), organ in the mouth of a typical tetrapod. It manipulates food for chewing and swallowing as part of the digestive system, digestive process, and is the primary organ of taste. The tongue's upper surface (dorsum) is covered by taste buds housed in numerous lingual papillae. It is sensitive and kept moist by saliva and is richly supplied with nerves and blood vessels. The tongue also serves as a natural means of cleaning the teeth. A major function of the tongue is to enable speech in humans and animal communication, vocalization in other animals. The human tongue is divided into two parts, an oral cavity, oral part at the front and a pharynx, pharyngeal part at the back. The left and right sides are also separated along most of its length by a vertical section of connective tissue, fibrous tissue (the lingual septum) that results in a groove, the median sulcus, on the tongue's surface. There are two groups of glossal muscles. The f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Styloid Process (temporal)
The temporal styloid process is a slender bony process of the temporal bone extending downward and forward from the undersurface of the temporal bone just below the ear. The styloid process gives attachments to several muscles, and ligaments. Structure The styloid process is a slender and pointed bony process of the temporal bone projecting anteroinferiorly from the inferior surface of the temporal bone just below the ear. Its length normally ranges from just under 3 cm to just over 4 cm. It is usually nearly straight, but may be curved in some individuals. Its ''proximal'' (''tympanohyal'') ''part'' is ensheathed by the tympanic part of the temporal bone ''(vaginal process), whereas'' its ''distal (stylohyal)'' ''part'' gives attachment to several structures. Attachments The styloid process gives attachments to several muscles, and ligaments. It serves as an anchor point for several muscles associated with the tongue and larynx. * stylohyoid ligament * stylomandi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lingual Artery
The lingual artery arises from the external carotid artery between the superior thyroid artery and facial artery. It can be located easily in the tongue. Structure The lingual artery first branches off from the external carotid artery. It runs obliquely upward and medially to the greater horns of the hyoid bone. It then curves downward and forward, forming a loop which is crossed by the hypoglossal nerve. It then passes beneath the digastric muscle and stylohyoid muscle running horizontally forward, beneath the hyoglossus. This takes it through the sublingual space. Finally, ascending almost perpendicularly to the tongue, it turns forward on its lower surface as far as the tip of the tongue, now called the deep lingual artery ( profunda linguae). Branches The lingual artery gives 4 main branches: the deep lingual artery, the sublingual artery, the suprahyoid branch, and the dorsal lingual branch. Deep lingual artery The deep lingual artery (or ranine artery) is the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypoglossal Nerve
The hypoglossal nerve, also known as the twelfth cranial nerve, cranial nerve XII, or simply CN XII, is a cranial nerve that innervates all the extrinsic and intrinsic muscles of the tongue except for the palatoglossus, which is innervated by the vagus nerve. CN XII is a nerve with a sole motor function. The nerve arises from the hypoglossal nucleus in the medulla as a number of small rootlets, pass through the hypoglossal canal and down through the neck, and eventually passes up again over the tongue muscles it supplies into the tongue. The nerve is involved in controlling tongue movements required for speech and swallowing, including sticking out the tongue and moving it from side to side. Damage to the nerve or the neural pathways which control it can affect the ability of the tongue to move and its appearance, with the most common sources of damage being injury from trauma or surgery, and motor neuron disease. The first recorded description of the nerve was by Her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temporal Styloid Process
The temporal styloid process is a slender bony process of the temporal bone extending downward and forward from the undersurface of the temporal bone just below the ear. The styloid process gives attachments to several muscles, and ligaments. Structure The styloid process is a slender and pointed bony process of the temporal bone projecting anteroinferiorly from the inferior surface of the temporal bone just below the ear. Its length normally ranges from just under 3 cm to just over 4 cm. It is usually nearly straight, but may be curved in some individuals. Its ''proximal'' (''tympanohyal'') ''part'' is ensheathed by the tympanic part of the temporal bone ''(vaginal process), whereas'' its ''distal (stylohyal)'' ''part'' gives attachment to several structures. Attachments The styloid process gives attachments to several muscles, and ligaments. It serves as an anchor point for several muscles associated with the tongue and larynx. * stylohyoid ligament * stylomandi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stylomandibular Ligament
The stylomandibular ligament is the thickened posterior portion of the investing cervical fascia around the neck. It extends from near the apex of the styloid process of the temporal bone to the angle and posterior border of the angle of the mandible, between the masseter muscle and medial pterygoid muscle. The stylomandibular ligament limits mandibular movements, such as preventing excessive opening. Structure The stylomandibular ligament extends from near the apex of the styloid process of the temporal bone to the angle and posterior border of the angle of the mandible, between the masseter muscle and medial pterygoid muscle. From its deep surface, some fibers of the styloglossus muscle originate. Although classed among the ligaments of the temporomandibular joint, it can only be considered as accessory to it. Function The stylomandibular ligament, along with the sphenomandibular ligament, limits mandibular movements, such as preventing excessive opening. Clinical sig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Carotid Arteries
The internal carotid artery is an artery in the neck which supplies the anterior and middle cerebral circulation. In human anatomy, the internal and external carotid arise from the common carotid artery, where it bifurcates at cervical vertebrae C3 or C4. The internal carotid artery supplies the brain, including the eyes, while the external carotid nourishes other portions of the head, such as the face, scalp, skull, and meninges. Classification Terminologia Anatomica in 1998 subdivided the artery into four parts: "cervical", "petrous", "cavernous", and "cerebral". In clinical settings, however, usually the classification system of the internal carotid artery follows the 1996 recommendations by Bouthillier, describing seven anatomical segments of the internal carotid artery, each with a corresponding alphanumeric identifier: C1 cervical; C2 petrous; C3 lacerum; C4 cavernous; C5 clinoid; C6 ophthalmic; and C7 communicating. The Bouthillier nomenclature remains in widespread ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
External Carotid Arteries
The external carotid artery is the major artery of the head and upper neck. It arises from the common carotid artery. It terminates by splitting into the superficial temporal and maxillary artery within the parotid gland. Structure Origin The external carotid artery arises from the common carotid artery just inferior to the upper border of the thyroid cartilage. At its origin, this artery is closer to the skin and more medial than the internal carotid, and is situated within the carotid triangle. Course and fate It curves to pass anterosuperiorly before inclining posterior-ward to reach the space posterior the neck of the mandible, where it divides into the superficial temporal and maxillary artery within the parotid gland. It rapidly diminishes in size as it travels up the neck, owing to the number and large size of its branches. Relations At the origin, external carotid artery is more medial than internal carotid artery. When external carotid artery ascends the neck, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Pharyngeal Constrictor Muscle
The superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle is a quadrilateral muscle of the pharynx. It is the uppermost and thinnest of the three pharyngeal constrictors. The muscle is divided into four parts according to its four distincts origins: a pterygopharyngeal, buccopharyngeal, mylopharyngeal, and a glossopharyngeal part. The muscle inserts onto the pharyngeal raphe, and pharyngeal spine. It is innervated by pharyngeal branch of the vagus nerve via the pharyngeal plexus. It acts to convey a bolus down towards the esophagus, facilitating swallowing. Anatomy The superior constrictor muscle is a quadrilateral, sheet-like muscle. It is thinner than the middle and inferior constrictor muscles. Origin The sites of origin of the muscles collectively are the pterygoid hamulus (and occasionally the adjoining posterior margin of the medial pterygoid plate) anteriorly, (the posterior margin of) the pterygomandibular raphe, the posterior extremity of the mylohyoid line of mandible, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Pharyngeal Constrictor Muscle
The middle pharyngeal constrictor is a fan-shaped muscle located in the neck. It is one of three pharyngeal constrictor muscles. It is smaller than the inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle. The middle pharyngeal constrictor originates from the greater cornu and lesser cornu of the hyoid bone, and the stylohyoid ligament. It inserts onto the pharyngeal raphe. It is innervated by a branch of the vagus nerve through the pharyngeal plexus. It acts to propel a bolus downwards along the pharynx towards the esophagus, facilitating swallowing. Structure The middle pharyngeal constrictor is a sheet-like, fan-shaped muscle. The muscle's fibers diverge from their origin: the more inferior fibres descend deep to the inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle; the middle portion of fibres pass transversely; the more superior fibers ascend and overlap the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle. Origin Two parts of the middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle are distinguished according to i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longitudinalis Inferior
The inferior longitudinal muscle of tongue is an intrinsic muscle of the tongue. It is situated on the under surface of the tongue between the genioglossus and hyoglossus. It is innervated by the hypoglossal nerve (cranial nerve XII). Its contraction shortens and thickens the tongue. Structure The inferior longitudinal muscle of the tongue is an intrinsic muscle of the tongue. It is thin and oval in cross-section. It is situated between the paramedian septum, and the lateral septum. It extends from the root to the apex of the tongue. Posteriorly, some of its fibers attach onto the body of the hyoid bone. Anteriorly, its fibres blend with those of the styloglossus, hyoglossus, and genioglossus The genioglossus is one of the paired extrinsic muscles of the tongue. It is a fan-shaped muscle that comprises the bulk of the body of the tongue. It arises from the mental spine of the mandible; it inserts onto the hyoid bone, and the bottom o ... to form the ventral area of the tip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyoglossus
The hyoglossus is a thin and quadrilateral extrinsic muscle of the tongue. It originates from the hyoid bone; it inserts onto the side of the tongue. It is innervated by the hypoglossal nerve (cranial nerve XII). It acts to depress and retract the tongue. Structure It forms a part of the floor of submandibular triangle. Origin from the side of the body and from the whole length of the greater cornu of the hyoid bone. The fibers arising from the body of the hyoid bone overlap those from the greater cornu. Insertion Its fibres pass almost vertically upward to enter the side of the tongue, inserting between the styloglossus and the inferior longitudinal muscle of the tongue. Relations Structures that are medial/deep to the hyoglossus are the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX), the stylohyoid ligament and the lingual artery and lingual vein. The lingual vein passes medial to the hyoglossus. The lingual artery passes deep to the hyoglossus. Laterally, in between the hyo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |