|
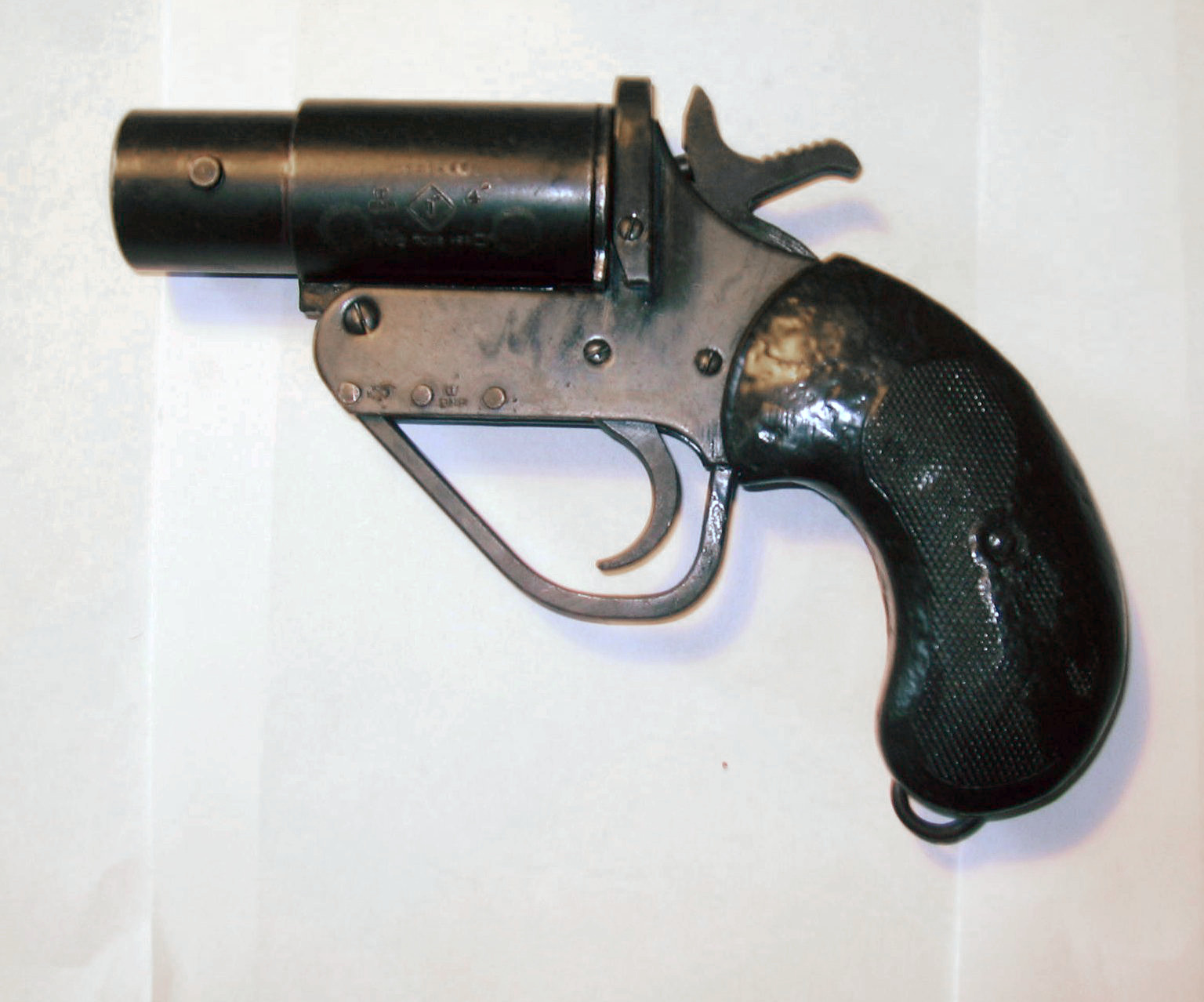
Sturmpistole
The ''Sturmpistole'' ("assault-pistol") was an attempt by Germany during World War II to create a multi-purpose weapon which could be used by any infantryman. It consisted of a modified flare gun (''Leuchtpistole'') which could fire a variety of grenades, including a shaped charge Panzerwurfkörper 42 which could penetrate of rolled homogeneous armor. The idea was not pursued wholeheartedly, and took second stage to the then current anti-tank rifles and later weapon developments, such as the ''Panzerfaust'' recoilless and ''Panzerschreck'' rocket. Service use The ''Sturmpistole'' was a multi-purpose weapon for signaling, illumination, target marking, or concealment with a smoke grenade. Later during World War II, explosive rounds were developed to give German troops a small and lightweight grenade launcher for engaging targets from close range which could not be engaged satisfactorily by infantry weapons or artillery without endangering friendly troops. Conversions of both th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leuchtpistole 42
The Leuchtpistole 42 or flare gun in English was introduced into German service in 1943 and served throughout World War II. Design The Leuchtpistole 42 was a single shot, break action, smoothbore, flare gun that was a successor to the earlier Leuchtpistole 34. The Leuchtpistole 42 which was made from stamped mild steel components, was galvanized to stop corrosion and used bakelite for the pistol grips. The focus of the Leuchtpistole 42 was to reduce the consumption of light alloys, reduce reliance on machined components, reduce production time, and reduce production costs. Despite being made from mild steel and stamped components it was considered rugged and its rough appearance didn't hinder its functionality. However, the Leuchtpistole 42 was nearly heavier than its predecessor. Variants * Sturmpistole – The Sturmpistole was a conversion of either Leuchtpistole 34's or Leuchtpistole 42's that added a padded buttstock and sights for firing both lethal and non-lethal round ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leuchtpistole 34
The Leuchtpistole 34 or flare gun in English was introduced into German service before World War II and served throughout World War II. Design The Leuchtpistole 34 was a single shot, break action, smoothbore, flare gun designed and produced by Walther that was a successor to the earlier Leuchtpistole 26. The Leuchtpistole 26 was of steel construction, was blued to stop corrosion, and had dyed oak pistol grips. While the Leuchtpistole 34's frame was machined from duralumin, the barrel was machined from steel, was blued to stop corrosion, and had bakelite pistol grips. Due to the use of light alloys, the Leuchtpistole 34 was lighter than its predecessor and the trigger guard was enlarged so the user could fire the gun in cold weather while wearing gloves. Successors * Kampfpistole – The Kampfpistole was a rifled variant of the Leuchtpistole 34 which could fire both lethal and non-lethal rounds. * Leuchtpistole 42 – The Leuchtpistole 34 was succeeded by the Leuchtpistole 4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wurfkörper 361
The Wurfkörper 361 was a grenade that was developed by Germany and used by the Wehrmacht during World War II. The Wurfkörper 361 was designed to be fired from a ''Leuchtpistole'' or flare gun in English. Design The Wurfkörper 361 was a grenade that could be fired from the Leuchtpistole 34, Leuchtpistole 42, or Sturmpistole giving German troops a small and lightweight grenade launcher for engaging targets from close range which could not be engaged satisfactorily by infantry weapons or artillery without endangering friendly troops. The Wurfkörper 361 grenade was formed by screwing a bakelite or wooden stem into an Model 39 grenade, Eierhandgranate 39 which allowed it to be fired from a Leuchtpistole. Inside the base of the stem, there was a flash cap inside an alloy flash tube which connected to a time fuze in the base of the grenade. The Leuchtpistole was a break action gun and a brass or aluminum Cartridge (firearms), shell casing containing propellant was pushed into the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multi-Star Signal Cartridge
The Multi-Star Signal Cartridge was a non-lethal signal flare that was developed by Germany and used by the Wehrmacht during World War II. The Multi-Star Signal Cartridge was designed to be fired from a ''Leuchtpistole'' or flare gun in English. Design The Multi-Star Signal Cartridge was a signal flare that could be fired from the Leuchtpistole 34, Leuchtpistole 42, or Sturmpistole. The Leuchtpistole and Sturmpistole were single-shot break action smoothbore guns and the cartridge was breech loaded. The cartridge consisted of an inner light alloy projectile which contained a total of three red stars and three green stars inside of a light alloy cartridge case with propellant charge. The exterior of the cartridge was engraved with numbers and the projectile could be twisted to create six different number combinations. Each number combination corresponded to a combination of red and green stars. By twisting the projectile a series of ignition holes were either opened or closed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panzerwurfkörper 42
The Panzerwurfkörper 42 was a High-explosive anti-tank warhead, HEAT grenade that was developed by Germany and used by the Wehrmacht during World War II. The Panzerwurfkörper 42 was designed to be fired from a ''Leuchtpistole'' (or flare gun, ''flare gun'' in English). Design The Panzerwurfkörper 42 was an anti-tank grenade that could be fired from the Leuchtpistole 34, Leuchtpistole 42, or Sturmpistole giving German troops a small and lightweight anti-tank weapon for engaging enemy armor from close range which could not be engaged satisfactorily by infantry weapons or artillery without endangering friendly troops. The Panzerwurfkörper 42's layout was similar to the Wurfkorper 361 its primary components were a nose cap, internal steel cone, steel upper body, steel stem, rifled driving band, explosive filling, and a Artillery fuze#Graze fuzes, graze fuze. The Leuchtpistole was a break action gun and a Rifling, rifled brass or aluminum Cartridge (firearms), shell casing contai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flare Gun
A flare gun, also known as a Very pistol or signal pistol, is a large-bore handgun that discharges flares, blanks and smoke. The flare gun is typically used to produce a distress signal. Types The most common type of flare gun is a Very (sometimes spelled Verey), which was named after Edward Wilson Very (1847–1910), an American naval officer who developed and popularized a single-shot breech-loading snub-nosed pistol that fired flares (Very lights). They have a single action trigger mechanism, hammer action, and a center fire pin. Modern varieties are frequently made out of durable plastic of a bright colour that makes them more conspicuous and easier to retrieve in an emergency and assists in distinguishing them from conventional firearms. The Very pistol, typical of the type used in the Second World War, are of one inch bore (26.5mm), now known as "Calibre 4" for signal pistols. These are still available and more recent longer-barrel models can also fire parachute f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wurfgranate Patrone 326
The Wurfgranate Patrone 326 was a small grenade that was developed by Germany and used by the Wehrmacht during World War II. The Wurfgranate Patrone 326 was designed to be fired from a ''Leuchtpistole'' or flare gun in English. Design The Wurfgranate Patrone 326 could be fired from the Leuchtpistole 34, Leuchtpistole 42, or Sturmpistole giving German troops a small and lightweight grenade launcher for engaging targets from close range which could not be engaged satisfactorily by infantry weapons or artillery without endangering friendly troops. It was not recommended for use beyond due to inaccuracy or less than due to the risk from shell fragments. The Wurfgranate Patrone 326 consisted of a rounded metallic nose cap with a firing pin inside of a creep spring that screwed into a cylindrical metallic body. Inside the body was an inner case which held the detonator, TNT bursting charge, and safety rod. The base of the grenade had four tail fins for stabilization and the tail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
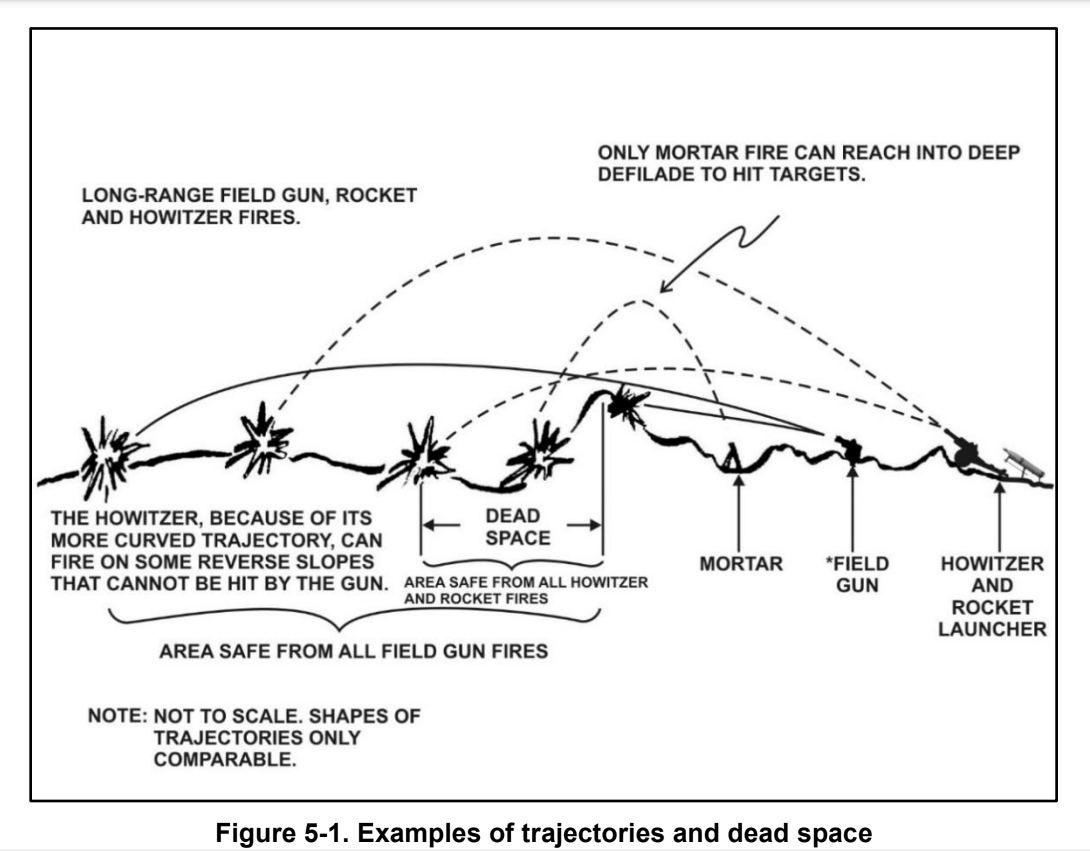
Indirect Fire
Indirect fire is aiming and firing a projectile without relying on a direct line of sight between the gun and its target, as in the case of direct fire. Aiming is performed by calculating azimuth and inclination, and may include correcting aim by observing the fall of shot and calculating new angles. Description Indirect fire is most commonly used by field artillery and mortars (although field artillery was originally and until after World War I a direct fire weapon, hence the bullet-shields fitted to the carriages of guns such as the famous M1897 75 mm). It is also used with missiles, howitzers, rocket artillery, multiple rocket launchers, cruise missiles, ballistic missiles, naval guns against shore targets, sometimes with machine guns, and has been used with tank and anti-tank guns and by anti-aircraft guns against surface targets. There are two dimensions in aiming a weapon: * In the horizontal plane (azimuth); and * In the vertical plane (elevation), which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bakelite
Bakelite ( ), formally , is a thermosetting polymer, thermosetting phenol formaldehyde resin, formed from a condensation reaction of phenol with formaldehyde. The first plastic made from synthetic components, it was developed by Belgian chemist Leo Baekeland in Yonkers, New York, in 1907, and patented on December 7, 1909. Bakelite was one of the first plastic-like materials to be introduced into the modern world and was popular because it could be Molding (process), molded and then hardened into any shape. Because of its electrical nonconductor, nonconductivity and heat-resistant properties, it became a great commercial success. It was used in electrical insulators, radio and telephone casings, and such diverse products as kitchenware, jewelry, pipe stems, children's toys, and firearms. The retro appeal of old Bakelite products has made them collectible. The creation of a synthetic plastic was revolutionary for the chemical industry, which at the time made most of its income f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Fire
Direct fire or line-of-sight fire refers to firing of a ranged weapon whose projectile is launched directly at a target within the line-of-sight of the user. The firing weapon must have a sighting device and an unobstructed view to the target, which means no obstacles or friendly units can be between it and the target. A weapon engaged in direct fire conversely exposes itself to direct return fire from the target.p.49, Bailey This is in contrast to indirect fire, which refers to firing a projectile on a curved ballistic trajectory or delivering self-accelerated munitions capable of long range and various degrees of homing abilities to alter the flight path. Indirect fire does not need a direct line-of-sight to the target because the shots are normally directed by a forward observer. As such, indirect-fire weapons can shoot over obstacles or friendly units and the weapons can be concealed from counter-battery fire. Description Examples of direct-fire weapons include most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shrapnel Shell
Shrapnel shells were anti-personnel artillery munitions that carried many individual bullets close to a target area and then ejected them to allow them to continue along the shell's trajectory and strike targets individually. They relied almost entirely on the shell's velocity for their lethality. The munition has been obsolete since the end of World War I for anti-personnel use; high-explosive shells superseded it for that role. The functioning and principles behind shrapnel shells are fundamentally different from high-explosive shell fragmentation. Shrapnel is named after Lieutenant-General Henry Shrapnel, a Royal Artillery officer, whose experiments, initially conducted on his own time and at his own expense, culminated in the design and development of a new type of artillery shell. Usage of the term "shrapnel" has changed over time to also refer to fragmentation of the casing of shells and bombs, which is its most common modern usage and strays from the original meaning. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |