|
Strzegom
Strzegom (german: Striegau) is a town in Świdnica County, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, in south-western Poland. It is the seat of the Gmina Strzegom administrative district ( gmina). It lies approximately north-west of Świdnica, and west of the regional capital Wrocław. As of 2019, the town had a population of 16,106. History Middle Ages Traces of settlement on the site during the Roman Empire period have been found. In the Middle Ages it was a fortified settlement under the rule of a castellan, founded in the 10th century, as part of Piast Poland, first mentioned in a deed issued by Pope Hadrian IV in 1155, confirming the boundaries of the Wrocław diocese. Its name is of Polish origin and comes either from the words ''strzec'' ("guard"), ''strzyc głowy'' ("cut hair") or ''trzy góry'' ("three mountains"). As a result of the fragmentation of Poland into smaller duchies, Strzegom became part of the Duchy of Silesia in the 12th century. The Piast Castle was built at tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gmina Strzegom
__NOTOC__ Gmina Strzegom is an urban-rural gmina (administrative district) in Świdnica County, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, in south-western Poland. Its seat is the town of Strzegom (German: ''Striegau''), which lies approximately north-west of Świdnica, and west of the regional capital Wrocław. The gmina covers an area of , and as of 2019 its total population is 25,775. Neighbouring gminas Gmina Strzegom is bordered by the town of Świebodzice ''(''German: ''Freiburg)'' the gminas of Dobromierz (German: ''Hohenfriedeberg''), Jaworzyna Śląska, Mściwojów, Udanin and Żarów. Villages Apart from the town of Strzegom ''(Stiegau),'' the gmina contains the villages of * Bartoszówek ''(Barzdorf)'' * Goczałków ''(Gutschdorf)'' * Goczałków Górny ''(Kohlhöhe)'' * Godzieszówek''(Günthersdorf)'' * Granica ''(Halbendorf)'' * Graniczna ''(Streit)'' * Grochotów ''(Hoymsberg)'' * Jaroszów''(Järischau)'' * Kostrza ''(Häslicht)'' * Międzyrzecze ''(Haidau)'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
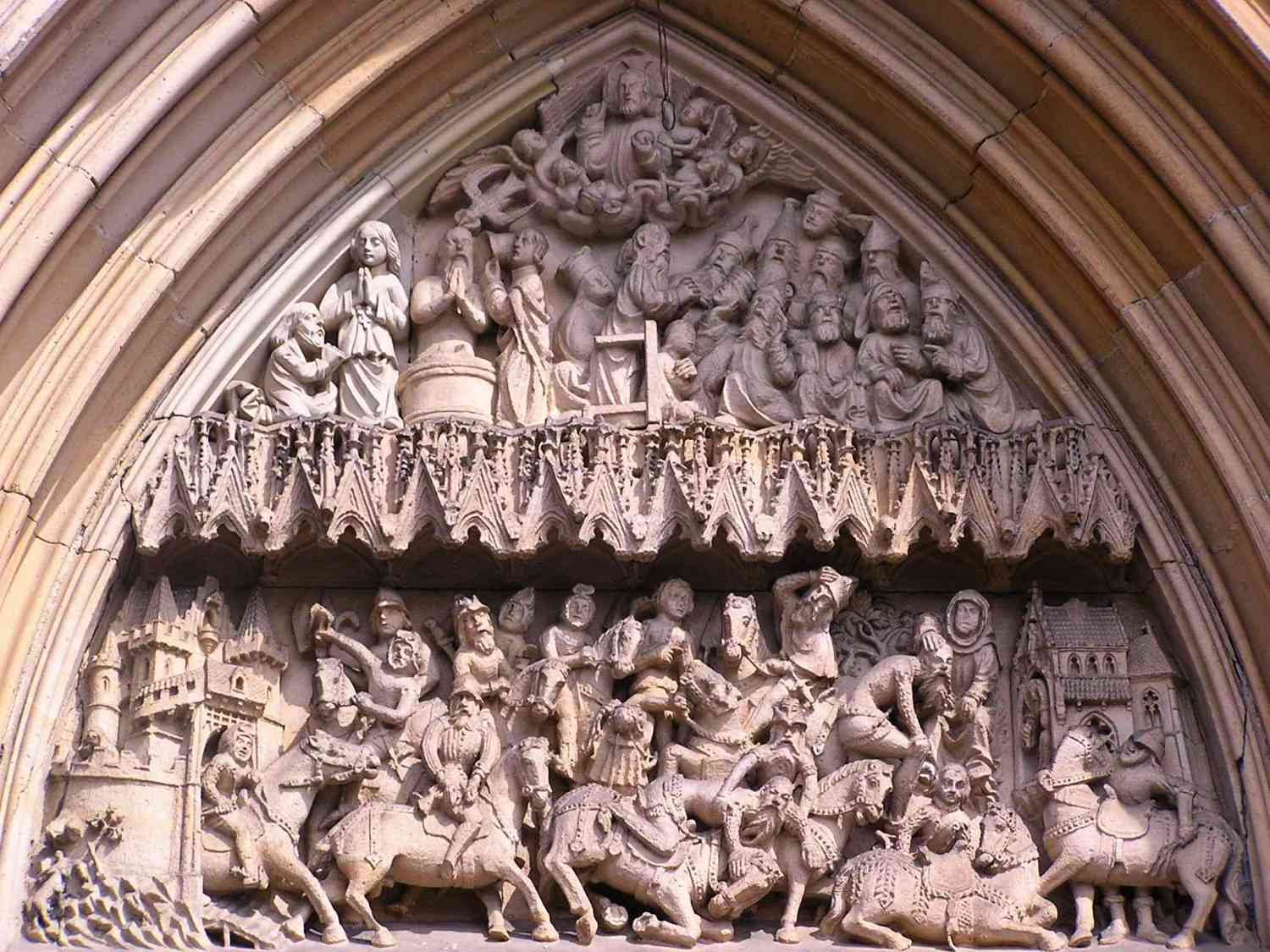
Saints Peter And Paul Basilica, Strzegom
Saints Peter and Paul Church in Strzegom, Poland (til 1945: Striegau, Germany), is a historic brick, Gothic minor basilica, located in Strzegom as part of the Diocese of Świdnica. Formerly, the basilica belonged to the Sovereign Military Order of Malta. Since 2002, the church serves as a minor basilica. It is the most prized heritage site of the town and is one of the largest churches in Lower Silesia (with a length of the nave at 76 metres, height of 26 m and a main building width of 26 m). An example of Lower Silesian Gothic architecture. the church is enriched with artisanal handicraft , mainly from the fourteenth and fifteenth-century. On September 22, 2012 the minor basilica was registered on the List of Historic Monuments of Poland. References {{coord, 50.5733, N, 16.2057, E, source:wikidata, display=title Świdnica County Basilica churches in Poland Strzegom Strzegom (german: Striegau) is a town in Świdnica County, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, in south-west ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Świdnica County
__NOTOC__ Świdnica County ( pl, powiat świdnicki) is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Lower Silesian Voivodeship, south-western Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. The county covers an area of . Its administrative seat is Świdnica, and it also contains the towns of Świebodzice, Strzegom, Jaworzyna Śląska and Żarów. As of 2019 the total population of the county is 157,178. The most populated towns are Świdnica with 57,041 inhabitants, Świebodzice with 22,793 inhabitants, and Strzegom with 16,106 inhabitants. Neighbouring counties Świdnica County is bordered by Środa Śląska County to the north, Wrocław County to the north-east, Dzierżoniów County to the south, Wałbrzych County to the south-west and Jawor County __NOTOC__ Jawor County ( pl, powiat jaworski) is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Lower Silesian Vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Silesian Voivodeship
Lower Silesian Voivodeship, or Lower Silesia Province, in southwestern Poland, is one of the 16 voivodeships (provinces) into which Poland is divided. The voivodeship was created on 1 January 1999 out of the former Wrocław, Legnica, Wałbrzych and Jelenia Góra Voivodeships, following the Polish local government reforms adopted in 1998. It covers an area of , and has a total population of 2,899,986. It is one of the richest provinces in Poland as it has valuable natural resources such as copper, silver, gold, brown coal and rock materials (inter alia granite, basalt, gabbro, diabase, amphibolite, porphyry, gneiss, serpentinite, sandstone, greywacke, limestone, dolomite, bentonite, kaolinite, clay, aggregate), which are exploited by the biggest enterprises. Its well developed and varied industries attract both domestic and foreign investors. Its capital and largest city is Wrocław, situated on the Oder River. It is one of Poland's largest and most dynamic ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
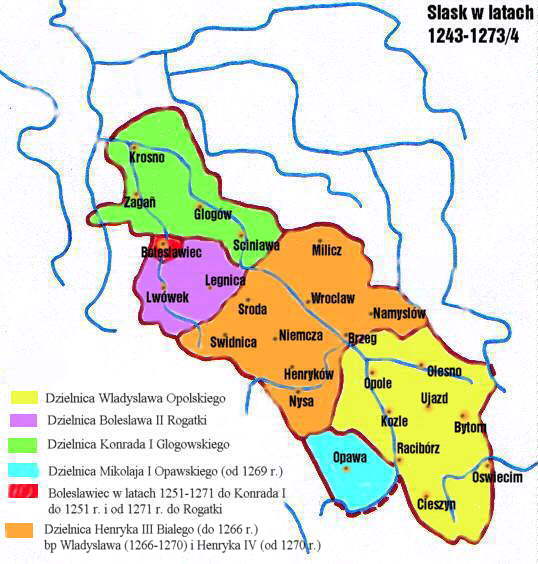
Henryk IV Probus
Henryk IV Probus (Latin for ''the Righteous'') ( pl, Henryk IV Probus or ''Prawy''; german: Heinrich IV. der Gerechte) ( – 23 June 1290) was a member of the Silesian branch of the royal Polish Piast dynasty. He was Duke of Silesia at Wrocław from 1266, and from also 1288 High Duke of the Polish Seniorate Province of Kraków until his death in 1290. Life Henry IV was the only son of Duke Henry III the White of Silesia-Wrocław by his first wife Judith, daughter of Duke Konrad I of Masovia. Under the tutelage of Władysław of Salzburg and King Ottokar II of Bohemia A minor upon the early death of his father in 1266, Henry IV was placed under the guardianship of his paternal uncle, Archbishop Władysław of Salzburg. The Archbishop decided that the constant travels between Wrocław and Salzburg were inappropriate for a child, and, in 1267, sent Henry to Prague to be raised at the court of King Ottokar II of Bohemia. Ottokar after Władysław's death in 1270 also took ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry II The Pious
Henry II the Pious ( pl, Henryk II Pobożny; 1196 – 9 April 1241) was Duke of Silesia and High Duke of Poland as well as Duke of South-Greater Poland from 1238 until his death. Between 1238 and 1239 he also served as regent of Sandomierz and Opole– Racibórz. He was the son of Henry the Bearded and a member of the Silesian Piast dynasty. In October 2015, the Roman Catholic Diocese of Legnica opened up his cause for beatification, obtaining him the title of Servant of God. Early life Henry the Pious was the second son of High Duke Henry the Bearded of Poland and Hedwig of Andechs. His elder brother, Bolesław, died in 1206. In 1213, his younger brother Konrad the Curly died during a hunt, leaving the young Henry as the sole heir of Lower Silesia. Around 1218 his father arranged his marriage to Anne, daughter of King Ottokar I of Bohemia. This union with the royal Přemyslid dynasty allowed Henry the Pious to participate actively in international politics. Henry t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anne Of Bohemia (1204–1265)
Anne of Bohemia ( cs, Anna Lehnická, pl, Anna Przemyślidka; c. 1203/1204 – 26 June 1265), a member of the Přemyslid dynasty, was Duchess of Silesia and High Duchess of Poland from 1238 to 1241, by her marriage to the Piast ruler Henry II the Pious. She was celebrated by the community of Franciscan nuns at St Clara of Prague Abbey in Wrocław as their founder and patron. Life Anna was probably born in Prague, Bohemia, the daughter of King Ottokar I of Bohemia and his second wife, Constance of Hungary. Her maternal grandparents were Béla III of Hungary and his first wife, Agnes of Antioch. Her paternal grandparents were King Vladislaus II of Bohemia and Judith of Thuringia. She was a sister of the Franciscan nun Agnes of Bohemia (1211–1282). Around the age of twelve (in 1216) she was married to the Piast prince Henry II the Pious, member of the Silesian branch of the Piast dynasty, the son and heir of Duke Henry the Bearded. During internal political struggles, the Si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Catholic Archdiocese Of Wrocław
The Archdiocese of Wrocław ( pl, Archidiecezja wrocławska; german: Erzbistum Breslau; cs, Arcidiecéze vratislavská; la, Archidioecesis Vratislaviensis) is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or archdiocese of the Catholic Church centered in the city of Wrocław in Poland. From its founding as a bishopric in 1000 until 1821, it was under the Archbishopric of Gniezno in Greater Poland. From 1821 to 1930 it was subjected directly to the Apostolic See. Between 1821 and 1972 it was officially known as (Arch)Diocese of Breslau. History Medieval era (within Poland) Christianity was first introduced into Silesia by missionaries from Moravia and Bohemia. After the conversion of Duke Mieszko I of Poland and the conquest of Silesia, the work of bringing the people to the new faith went on more rapidly. Up to about the year 1000 Silesia had no bishop of its own, but was united with neighbouring dioceses. The upper part of the Oder River formed the boundary of the Kingdom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Mongol Invasion Of Poland
The Mongol Invasion of Poland from late 1240 to 1241 culminated in the Battle of Legnica, where the Mongols defeated an alliance which included forces from fragmented Poland and their allies, led by Henry II the Pious, the Duke of Silesia. The first invasion's intention was to secure the flank of the main Mongolian army attacking the Kingdom of Hungary. The Mongols neutralized any potential help to King Béla IV being provided by the Poles or any military orders. Background The Mongols invaded Europe with three armies. One of the three armies was tasked with distracting Poland, before joining the main Mongol force invading Hungary. The Mongol general in charge, Subutai, did not want the Polish forces to be able to threaten his flank during the primary invasion of Hungary. Thus, the Mongol goal was to use a small detachment to prevent the Poles from assisting Hungary until the Hungarians were defeated. That army, under Baidar, Kadan and Orda Khan, began scouting operat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knights Hospitaller
The Order of Knights of the Hospital of Saint John of Jerusalem ( la, Ordo Fratrum Hospitalis Sancti Ioannis Hierosolymitani), commonly known as the Knights Hospitaller (), was a medieval and early modern Catholic military order. It was headquartered in the Kingdom of Jerusalem until 1291, on the island of Rhodes from 1310 until 1522, in Malta from 1530 until 1798 and at Saint Petersburg from 1799 until 1801. Today several organizations continue the Hospitaller tradition, specifically the mutually recognized orders of St. John, which are the Sovereign Military Order of Malta, the Most Venerable Order of the Hospital of Saint John, the Bailiwick of Brandenburg of the Chivalric Order of Saint John, the Order of Saint John in the Netherlands, and the Order of Saint John in Sweden. The Hospitallers arose in the early 12th century, during the time of the Cluniac movement (a Benedictine Reform movement). Early in the 11th century, merchants from Amalfi founded a hospital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jus Patronatus
The right of patronage (in Latin ''jus patronatus'' or ''ius patronatus'') in Roman Catholic canon law is a set of rights and obligations of someone, known as the patron in connection with a gift of land (benefice). It is a grant made by the church out of gratitude towards a benefactor. Its counterpart in English law and in the Church of England is called an advowson. The right of patronage is designated in papal letters as ''"ius spirituali annexum"'' and is therefore subject to ecclesiastical legislation and jurisdiction as well as civil laws relating to the ownership of property. Background In the Eastern Catholic Churches, the founder of a church was permitted to nominate an administrator for the temporal goods and indicate to the bishop a cleric suitable for appointment. In the Latin Church, the Synod of Orange in 441 granted a right of "presentation" to a bishop who had built a church in another diocese and the Synod of Toledo in 655 gave a layman this privilege for ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |