|
Strychnos Pungens
''Strychnos pungens'' (English: spine-leaved monkey-orange, Afrikaans: Stekelblaarklapper) is a tree which belongs to the Loganiaceae. Usually about 5m tall, occurring in mixed woodland or in rocky places. Branches are short and rigid. Leaves are smooth, stiff, opposite, elliptic and with a sharp, spine-like tip. Occurring in South Africa on the Witwatersrand, Magaliesberg and further north to northern Namibia, northern Botswana and Zimbabwe. The fruit is large (120mm diameter), round and with a smooth hard shell, bluish-green in colour and turning yellow when ripe. The pulp of ripe fruit is rich in citric acid and is edible, but the seeds are mildly poisonous. The tree is a close relative of '' Strychnos nux-vomica'', the source of strychnine Strychnine (, , US chiefly ) is a highly toxic, colorless, bitter, crystalline alkaloid used as a pesticide, particularly for killing small vertebrates such as birds and rodents. Strychnine, when inhaled, swallowed, or absorbed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soler
Soler may refer to: * Soler Township, Roseau County, Minnesota * Soler (band), Hong Kong based rock band * Soler (grape), French wine grape, also known as Peloursin People with the surname Soler * Alay Soler (born 1979), Cuban baseball player for the New York Mets * Alexandra Soler (born 1983), French artistic gymnast * Álvaro Soler (born 1991), Spanish singer-songwriter * Amalia Domingo Soler (1835–1909), Spanish writer * Andrés Soler (1898–1969), Mexican actor * Angelino Soler (born 1939), Spanish professional road bicycle racer * Antonio Soler (1729–1783), Spanish baroque/classical era composer usually known as Padre ('Father') Antonio Soler * Carlos Soler (footballer) (born 1997), Spanish footballer * Domingo Soler (1901–1961), Mexican actor * Fernando Soler (1896–1979), Mexican film actor and film director * Francesc Fàbregas Soler (born 1987), Spanish footballer * Francisco Gabilondo Soler (1907–1990), also known as ''Cri-Cri'', Mexican composer and perfor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loganiaceae
The Loganiaceae are a family of flowering plants classified in order Gentianales. The family includes up to 13 genera, distributed around the world's tropics. There are not any great morphological characteristics to distinguish these taxa from others in the order Gentianales. Many members of the Loganiaceae are extremely poisonous, causing death by convulsion. Poisonous properties are largely due to alkaloids such as those found in '' Strychnos''. Glycosides are also present as loganin in ''Strychnos''.Flowering Plants of the World by consultant editor Vernon H. Heywood, 1978, Oxford University Press, Walton Street, Oxford OX2 6DP, England, Earlier treatments of the family have included up to 29 genera. Phylogenetic studies have demonstrated that this broadly defined Loganiaceae was a polyphyletic assemblage, and numerous genera have been removed from Loganiaceae to other families (sometimes in other orders), e.g., Gentianaceae, Gelsemiaceae, Plocospermataceae ''Pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring countries of Namibia, Botswana, and Zimbabwe; and to the east and northeast by Mozambique and Eswatini. It also completely enclaves the country Lesotho. It is the southernmost country on the mainland of the Old World, and the second-most populous country located entirely south of the equator, after Tanzania. South Africa is a biodiversity hotspot, with unique biomes, plant and animal life. With over 60 million people, the country is the world's 24th-most populous nation and covers an area of . South Africa has three capital cities, with the executive, judicial and legislative branches of government based in Pretoria, Bloemfontein, and Cape Town respectively. The largest city is Johannesburg. About 80% of the population are Black Sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Witwatersrand
The Witwatersrand () (locally the Rand or, less commonly, the Reef) is a , north-facing scarp in South Africa. It consists of a hard, erosion-resistant quartzite metamorphic rock, over which several north-flowing rivers form waterfalls, which account for the name Witwatersrand, meaning "white water ridge" in Afrikaans.Truswell, J.F. (1977). ''The Geological Evolution of South Africa''. pp. 21, 27–28, 33–36. Cape Town: Purnell. This east-west-running scarp can be traced with only one short gap, from Bedfordview (about west of O.R. Tambo International Airport) in the east, through Johannesburg and Roodepoort, to Krugersdorp in the west (see the diagram at left below).Norman, N.; Whitfield, G. (2006) ''Geological Journeys''. pp. 38–49, 60–61. Cape Town: Struik Publishers. The scarp forms the northern edge of a plateau (or ridge) which rises about above the surrounding plains of the Highveld. A number of picturesque Johannesburg suburbs, including Observatory, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
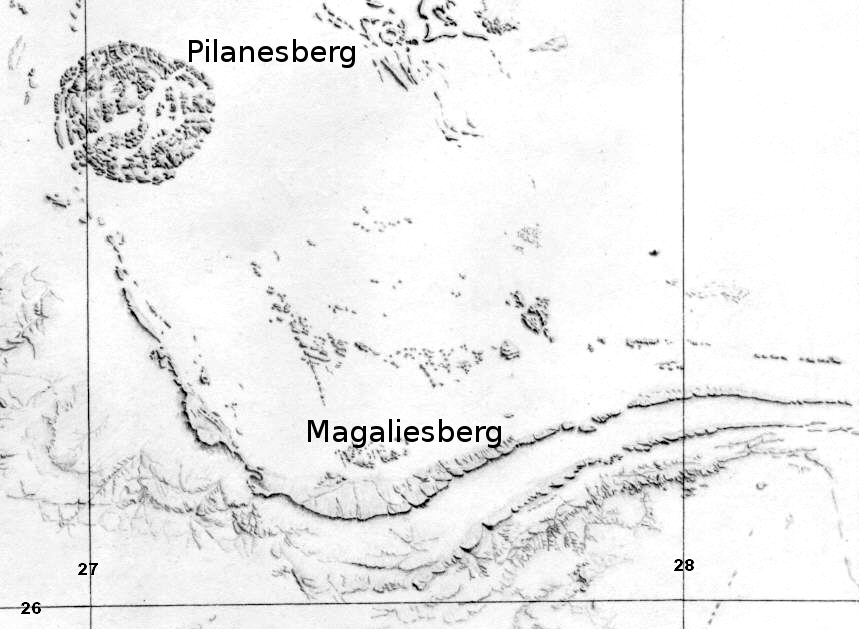
Magaliesberg
The Magaliesberg (historically also known as ''Macalisberg'' or ''Cashan Mountains'') of northern South Africa, is a modest but well-defined mountain range composed mainly of quartzites. It rises at a point south of the Pilanesberg (and the Pilanesberg National Park) to form a curved prominence that intersects suburban Pretoria before it peters out some to the east, just south of Bronkhorstspruit. The highest point of the Magaliesberg is reached at Nooitgedacht, about above sea level. A cableway reaching to the top of the mountain range is located at Hartbeespoort Dam, providing sweeping views of the Magaliesberg and surrounding area. Geology The Magaliesberg has ancient origins. Its composition is ascribed to successive geological processes over a very protracted history. Its quartzites, shales, chert and dolomite were deposited as sediments in an inland basin on top of a 3 billion year old Archaean Basement Complex, known as the Kaapvaal Craton. This process of sedimentatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Namibia
Namibia (, ), officially the Republic of Namibia, is a country in Southern Africa. Its western border is the Atlantic Ocean. It shares land borders with Zambia and Angola to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south and east. Although it does not border Zimbabwe, less than 200 metres (660 feet) of the Botswanan right bank of the Zambezi River separates the two countries. Namibia gained independence from South Africa on 21 March 1990, following the Namibian War of Independence. Its capital and largest city is Windhoek. Namibia is a member state of the United Nations (UN), the Southern African Development Community (SADC), the African Union (AU) and the Commonwealth of Nations. The driest country in sub-Saharan Africa, Namibia has been inhabited since pre-historic times by the San, Damara and Nama people. Around the 14th century, immigrating Bantu peoples arrived as part of the Bantu expansion. Since then, the Bantu groups, the largest being the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botswana
Botswana (, ), officially the Republic of Botswana ( tn, Lefatshe la Botswana, label= Setswana, ), is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. Botswana is topographically flat, with approximately 70 percent of its territory being the Kalahari Desert. It is bordered by South Africa to the south and southeast, Namibia to the west and north, and Zimbabwe to the northeast. It is connected to Zambia across the short Zambezi River border by the Kazungula Bridge. A country of slightly over 2.3 million people, Botswana is one of the most sparsely populated countries in the world. About 11.6 percent of the population lives in the capital and largest city, Gaborone. Formerly one of the world's poorest countries—with a GDP per capita of about US$70 per year in the late 1960s—it has since transformed itself into an upper-middle-income country, with one of the world's fastest-growing economies. Modern-day humans first inhabited the country over 200,000 years ago. The Tswa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe (), officially the Republic of Zimbabwe, is a landlocked country located in Southeast Africa, between the Zambezi and Limpopo Rivers, bordered by South Africa to the south, Botswana to the south-west, Zambia to the north, and Mozambique to the east. The capital and largest city is Harare. The second largest city is Bulawayo. A country of roughly 15 million people, Zimbabwe has 16 official languages, with English, Shona language, Shona, and Northern Ndebele language, Ndebele the most common. Beginning in the 9th century, during its late Iron Age, the Bantu peoples, Bantu people (who would become the ethnic Shona people, Shona) built the city-state of Great Zimbabwe which became one of the major African trade centres by the 11th century, controlling the gold, ivory and copper trades with the Swahili coast, which were connected to Arab and Indian states. By the mid 15th century, the city-state had been abandoned. From there, the Kingdom of Zimbabwe was established, fol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Citric Acid
Citric acid is an organic compound with the chemical formula HOC(CO2H)(CH2CO2H)2. It is a colorless weak organic acid. It occurs naturally in citrus fruits. In biochemistry, it is an intermediate in the citric acid cycle, which occurs in the metabolism of all aerobic organisms. More than two million tons of citric acid are manufactured every year. It is used widely as an acidifier, as a flavoring, and a chelating agent. A citrate is a derivative of citric acid; that is, the salts, esters, and the polyatomic anion found in solution. An example of the former, a salt is trisodium citrate; an ester is triethyl citrate. When part of a salt, the formula of the citrate anion is written as or . Natural occurrence and industrial production Citric acid occurs in a variety of fruits and vegetables, most notably citrus fruits. Lemons and limes have particularly high concentrations of the acid; it can constitute as much as 8% of the dry weight of these fruits (about 47&nb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strychnine Tree
''Strychnos nux-vomica'', the strychnine tree, also known as nux vomica, poison fruit, semen strychnos, and quaker buttons, is a deciduous tree native to India and to southeast Asia. It is a medium-sized tree in the family Loganiaceae that grows in open habitats. Its leaves are ovate and in size. It is known for being the natural source of the extremely poisonous compound strychnine. Description and properties ''Strychnos nux-vomica'' is a medium-sized tree with a short, thick trunk. The wood is dense, hard white, and close-grained. The branches are irregular and are covered with a smooth ashen bark. The young shoots are a deep green colour with a shiny coat. The leaves have an opposite decussate arrangement (each opposing pair of leaves at right angles to the next pair along the stem), are short stalked and oval shaped, have a shiny coat, and are smooth on both sides. The leaves are about long and wide. The flowers are small with a pale green colour and a funnel shape. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strychnine
Strychnine (, , US chiefly ) is a highly toxic, colorless, bitter, crystalline alkaloid used as a pesticide, particularly for killing small vertebrates such as birds and rodents. Strychnine, when inhaled, swallowed, or absorbed through the eyes or mouth, causes poisoning which results in muscular convulsions and eventually death through asphyxia. While it is no longer used medicinally, it was used historically in small doses to strengthen muscle contractions, such as a heart and bowel stimulant and performance-enhancing drug. The most common source is from the seeds of the '' Strychnos nux-vomica'' tree. Biosynthesis Strychnine is a terpene indole alkaloid belonging to the '' Strychnos'' family of ''Corynanthe'' alkaloids, and it is derived from tryptamine and secologanin. The biosynthesis of strychine was solved in 2022. The enzyme, strictosidine synthase, catalyzes the condensation of tryptamine and secologanin, followed by a Pictet-Spengler reaction to form strict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strychnos
''Strychnos'' is a genus of flowering plants, belonging to the family Loganiaceae (sometimes Strychnaceae). The genus includes about 100 accepted species of trees and lianas, and more than 200 that are as yet unresolved. The genus is widely distributed around the world's tropics and is noted for the presence of poisonous indole alkaloids in the roots, stems and leaves of various species. Among these alkaloids are the well-known and virulent poisons strychnine and curare. Etymology The name ''strychnos'' was applied by Pliny the Elder in his '' Natural History'' to ''Solanum nigrum''. The word is derived from the Ancient Greek στρύχνον (''strúkhnon'') – "acrid", "bitter". The meaning of the word ''strychnos'' was not fixed in Ancient Greece, where it could designate a variety of different plants having in common the property of toxicity. Distribution The genus has a pantropical distribution. Taxonomy The genus is divided into 12 sections, though it is conceded that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |