Witwatersrand on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Witwatersrand (, ; ; locally the Rand or, less commonly, the Reef) is a , north-facing scarp in
 The Witwatersrand plateau consists of a layer of mainly sedimentary rocks laid down over a period of about 260 million years, starting approximately 2.97 billion years ago. The entire series of rocks, known as the "Witwatersrand Supergroup", consists of very hard erosion resistant quartzites, banded ironstones and some marine
The Witwatersrand plateau consists of a layer of mainly sedimentary rocks laid down over a period of about 260 million years, starting approximately 2.97 billion years ago. The entire series of rocks, known as the "Witwatersrand Supergroup", consists of very hard erosion resistant quartzites, banded ironstones and some marine
 The Witwatersrand Basin is a largely underground geological formation which surfaces in the Witwatersrand. It holds the world's largest known
The Witwatersrand Basin is a largely underground geological formation which surfaces in the Witwatersrand. It holds the world's largest known
 There were no continents during the early stages of the Archean Eon, but island arcs did form. It was the coalescence of several of these island arcs that led to the formation of the Kaapvaal craton, one of the first microcontinents to form on Earth about 3.9 billion years ago. Its size and position relative to
There were no continents during the early stages of the Archean Eon, but island arcs did form. It was the coalescence of several of these island arcs that led to the formation of the Kaapvaal craton, one of the first microcontinents to form on Earth about 3.9 billion years ago. Its size and position relative to 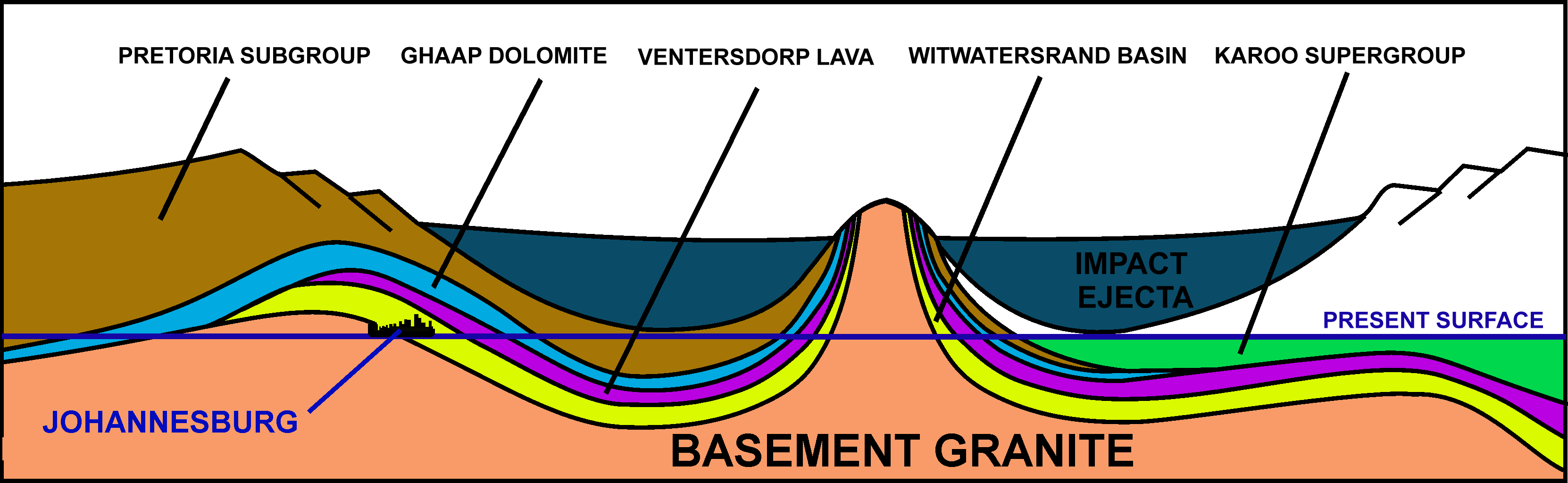 There was no free oxygen in Earth's atmosphere until about 2 billion years ago, before the appearance and sufficient development of photosynthesizing
There was no free oxygen in Earth's atmosphere until about 2 billion years ago, before the appearance and sufficient development of photosynthesizing  A final event that had a major impact on the geology of the Witwatersrand Basin and its exposure in the Johannesburg region, was a massive meteor impact 110 km to the south-west of Johannesburg 2.02 billion years ago. The impact was close to the present village of Vredefort, which has given its name to the geological remnant of this immense event: the Vredefort Dome. Not only are the remains of this impact among the oldest on Earth, but it is also one of the largest meteor impacts to have left its imprint on present-day Earth geology. A meteor 10–15 km across created a 300 km diameter crater, distorting all the rock strata within that circle. Johannesburg is just within the outer edge of this impact crater. In the immediate vicinity of the impact all the subterranean strata were uplifted and upturned, so that Witwatersrand rocks are exposed in an arc 25 km away from the impact centre. There are no gold deposits in these outcrops. The meteor impact, however, lowered the Witwatersrand basin inside the crater. This protected it from erosion later on; but, possibly more importantly, bringing it to the surface close to the crater rim, near Johannesburg. In fact, apart from the Witwatersrand outcrops (i.e. where these rocks are exposed at the surface) in the immediate vicinity of the Vredefort Dome, virtually all the other outcrops occur in an arc approximately 80–120 km from the centre of the impact crater, to the west, north-west, north and north-east. Thus, it is possible that if it had not been for the Vredefort asteroid strike 2 billion years ago, humanity would either never have discovered the rich gold deposits beneath the Southern African surface, or they would have been eroded away during the uninterrupted removal of a several kilometres thick layer of deposits from the surface of the Southern African Plateau in the relatively recent geological past: i.e. the past 150 million years, but especially during the last 20 million years.
A final event that had a major impact on the geology of the Witwatersrand Basin and its exposure in the Johannesburg region, was a massive meteor impact 110 km to the south-west of Johannesburg 2.02 billion years ago. The impact was close to the present village of Vredefort, which has given its name to the geological remnant of this immense event: the Vredefort Dome. Not only are the remains of this impact among the oldest on Earth, but it is also one of the largest meteor impacts to have left its imprint on present-day Earth geology. A meteor 10–15 km across created a 300 km diameter crater, distorting all the rock strata within that circle. Johannesburg is just within the outer edge of this impact crater. In the immediate vicinity of the impact all the subterranean strata were uplifted and upturned, so that Witwatersrand rocks are exposed in an arc 25 km away from the impact centre. There are no gold deposits in these outcrops. The meteor impact, however, lowered the Witwatersrand basin inside the crater. This protected it from erosion later on; but, possibly more importantly, bringing it to the surface close to the crater rim, near Johannesburg. In fact, apart from the Witwatersrand outcrops (i.e. where these rocks are exposed at the surface) in the immediate vicinity of the Vredefort Dome, virtually all the other outcrops occur in an arc approximately 80–120 km from the centre of the impact crater, to the west, north-west, north and north-east. Thus, it is possible that if it had not been for the Vredefort asteroid strike 2 billion years ago, humanity would either never have discovered the rich gold deposits beneath the Southern African surface, or they would have been eroded away during the uninterrupted removal of a several kilometres thick layer of deposits from the surface of the Southern African Plateau in the relatively recent geological past: i.e. the past 150 million years, but especially during the last 20 million years.
, New York Times, 24 October 2005. (PDF). Retrieved on 4 May 2012. The tailings ponds contain an average of 100 mg/kg of U3O8, and uranium levels are measureable in human hair. Sulfuric acid also erodes concrete and cement structures, resulting in structural damage to buildings and bridges.
 Harrison's original Zoekers' (in English: seekers', or prospectors') Claim No 19 was declared a national monument in 1944, and named Harrison's Park. The park is on the busy Main Reef Road, immediately west of Nasrec Road.
In 1887
Harrison's original Zoekers' (in English: seekers', or prospectors') Claim No 19 was declared a national monument in 1944, and named Harrison's Park. The park is on the busy Main Reef Road, immediately west of Nasrec Road.
In 1887
South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic O ...
. It consists of a hard, erosion-resistant quartzite metamorphic rock, over which several north-flowing rivers form waterfalls, which account for the name Witwatersrand, meaning 'white water ridge' in Afrikaans
Afrikaans is a West Germanic languages, West Germanic language spoken in South Africa, Namibia and to a lesser extent Botswana, Zambia, Zimbabwe and also Argentina where there is a group in Sarmiento, Chubut, Sarmiento that speaks the Pat ...
.Truswell, J.F. (1977). ''The Geological Evolution of South Africa''. pp. 21, 27–28, 33–36. Cape Town: Purnell. This east-west-running scarp can be traced with only one short gap, from Bedfordview (about west of O.R. Tambo International Airport) in the east, through Johannesburg
Johannesburg ( , , ; Zulu language, Zulu and Xhosa language, Xhosa: eGoli ) (colloquially known as Jozi, Joburg, Jo'burg or "The City of Gold") is the most populous city in South Africa. With 5,538,596 people in the City of Johannesburg alon ...
and Roodepoort, to Krugersdorp
Krugersdorp (Afrikaans for ''Kruger's Town'') is a mining city in the West Rand, Gauteng Province, South Africa founded in 1887 by Marthinus Pretorius and Abner Cohen. Following the discovery of gold on the Witwatersrand, a need arose for a ...
in the west (see the diagram at left below).Norman, N.; Whitfield, G. (2006) ''Geological Journeys''. pp. 38–49, 60–61. Cape Town: Struik Publishers.
The scarp forms the northern edge of a plateau (or ridge) which rises about above the surrounding plains of the Highveld. A number of picturesque Johannesburg suburbs, including Observatory
An observatory is a location used for observing terrestrial, marine, or celestial events. Astronomy, climatology/meteorology, geophysics, oceanography and volcanology are examples of disciplines for which observatories have been constructed.
Th ...
, Linksfield Ridge and Upper Houghton are located along the scarp, overlooking the rest of northern Johannesburg with views up to the Magaliesberg (although locals refer to segments of the scarp using area-specific names, such as ''Linksfield Ridge'', ''Parktown Ridge'' or Observatory Ridge). The entire plateau-like structure is also often called the Witwatersrand. The plateau's elevation above sea-level is between .
The Witwatersrand plateau forms a continental divide, with the run-off to the north draining into the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or approximately 20% of the water area of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia (continent), ...
via the Crocodile
Crocodiles (family (biology), family Crocodylidae) or true crocodiles are large, semiaquatic reptiles that live throughout the tropics in Africa, Asia, the Americas and Australia. The term "crocodile" is sometimes used more loosely to include ...
and Limpopo
Limpopo () is the northernmost Provinces of South Africa, province of South Africa. It is named after the Limpopo River, which forms the province's western and northern borders. The term Limpopo is derived from Rivombo (Livombo/Lebombo), a ...
rivers, while the run-off to the south drains via the Vaal into the Orange River and ultimately into the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ...
.
Because of the extraordinary quantities of gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
that have been extracted from the Witwatersrand rocks, the South African currency was named the ''rand'' in 1961 upon the declaration of the republic.
''Witwatersrand'' and ''the Rand'' are names for the conurbation that developed along the range, although the terms are falling into disuse and ''Witwatersrand'' was the "W" in ''PWV'' (Pretoria-Witwatersrand-Vereeniging), the initial name of Gauteng
Gauteng ( , ; Sotho-Tswana languages, Sotho-Tswana for 'place of gold'; or ) is one of the nine provinces of South Africa.
Situated on the Highveld, Gauteng is the smallest province by land area in South Africa. Although Gauteng accounts f ...
province. In this context, it has lent its name to institutions including the University of the Witwatersrand
The University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg (), commonly known as Wits University or Wits, is a multi-campus Public university, public research university situated in the northern areas of central Johannesburg, South Africa. The universit ...
(Wits University) and the defunct Rand Afrikaans University (RAU, now part of the University of Johannesburg
The University of Johannesburg, colloquially known as UJ, is a public university
A public university, state university, or public college is a university or college that is State ownership, owned by the state or receives significant fundi ...
), and to towns and regions such as the East Rand, West Rand and Randburg.
Geology
 The Witwatersrand plateau consists of a layer of mainly sedimentary rocks laid down over a period of about 260 million years, starting approximately 2.97 billion years ago. The entire series of rocks, known as the "Witwatersrand Supergroup", consists of very hard erosion resistant quartzites, banded ironstones and some marine
The Witwatersrand plateau consists of a layer of mainly sedimentary rocks laid down over a period of about 260 million years, starting approximately 2.97 billion years ago. The entire series of rocks, known as the "Witwatersrand Supergroup", consists of very hard erosion resistant quartzites, banded ironstones and some marine lava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a Natural satellite, moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a Fissure vent, fractu ...
deposits, interspersed with softer, more easily eroded tillite
image:Geschiebemergel.JPG, Closeup of glacial till. Note that the larger grains (pebbles and gravel) in the till are completely surrounded by the matrix of finer material (silt and sand), and this characteristic, known as ''matrix support'', is d ...
s, mudstones and conglomerates. The oldest rocks (laid down 2.97 billion years ago) form the northern scarp of the Witwatersrand plateau; the youngest (laid down 2.71 billion years ago) are those that form the southern edge of the plateau.
Gold is found in the conglomerate strata of the younger members of the Supergroup, locally referred to as banket. The abundance of this gold is without a natural equal anywhere else in the world. Over have been mined from these rocks since this precious metal was first discovered here in 1886. This accounts for approximately 22% of all the gold that is accounted for today.
Not all the conglomerates contain gold, and of those that do (known as "reefs" by the miners), the gold is not uniformly distributed throughout the layer, but tends to occur in streaks, where the pebbles that make up the conglomerate are larger than elsewhere. Here the gold is associated with other minerals, especially iron pyrite and uraninite, as well as carbon rich materials such as kerogen, or bitumen
Bitumen ( , ) is an immensely viscosity, viscous constituent of petroleum. Depending on its exact composition, it can be a sticky, black liquid or an apparently solid mass that behaves as a liquid over very large time scales. In American Engl ...
, which occurs in small balls less than in size, called "flyspeck carbon", or as continuous layers about thick. The gold-bearing conglomerates occur chiefly in the upper, younger layers of the Witwatersrand Supergroup of rocks, on the southern side of the Witwatersrand plateau.
The Witwatersrand Supergroup strata which reach the surface in Johannesburg dip downwards to the south at an angle of about 30°. From there on they are almost everywhere, with very few exceptions (see below), covered by younger rocks.Geological map of South Africa, Lesotho and Swaziland (1970). Council for Geoscience, Geological Survey of South Africa. Gold mining in these buried portions of the Witwatersrand Supergroup is sometimes carried out at depths of below the surface.
Witwatersrand Basin
 The Witwatersrand Basin is a largely underground geological formation which surfaces in the Witwatersrand. It holds the world's largest known
The Witwatersrand Basin is a largely underground geological formation which surfaces in the Witwatersrand. It holds the world's largest known gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
reserves and has produced over , which represents about 22% of all the gold accounted for above the surface. The basin straddles the old provinces of Transvaal and the Orange Free State
The Orange Free State ( ; ) was an independent Boer-ruled sovereign republic under British suzerainty in Southern Africa during the second half of the 19th century, which ceased to exist after it was defeated and surrendered to the British Em ...
, and consists of a 5000–7000 m thick layer of Archean
The Archean ( , also spelled Archaean or Archæan), in older sources sometimes called the Archaeozoic, is the second of the four geologic eons of Earth's history of Earth, history, preceded by the Hadean Eon and followed by the Proterozoic and t ...
, mainly sedimentary rocks laid down over a period of about 260 million years, starting about 3 billion years ago. The entire series of rocks, known as the "Witwatersrand Supergroup" consists of quartzites, banded ironstones, mudstones, tillite
image:Geschiebemergel.JPG, Closeup of glacial till. Note that the larger grains (pebbles and gravel) in the till are completely surrounded by the matrix of finer material (silt and sand), and this characteristic, known as ''matrix support'', is d ...
s, conglomerates and some marine lava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a Natural satellite, moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a Fissure vent, fractu ...
deposits. Most of the basin is deeply buried under younger rocks, but outcrops occur in Gauteng
Gauteng ( , ; Sotho-Tswana languages, Sotho-Tswana for 'place of gold'; or ) is one of the nine provinces of South Africa.
Situated on the Highveld, Gauteng is the smallest province by land area in South Africa. Although Gauteng accounts f ...
, the Free State, as well as in some of the surrounding Provinces. The outcrop in Gauteng forms the Witwatersrand ridge, from which the basin and its rocks derive their name. It was on the southern portion of this ridge that gold was first discovered on the farm Langlaagte in 1886, 5 km west of Johannesburg
Johannesburg ( , , ; Zulu language, Zulu and Xhosa language, Xhosa: eGoli ) (colloquially known as Jozi, Joburg, Jo'burg or "The City of Gold") is the most populous city in South Africa. With 5,538,596 people in the City of Johannesburg alon ...
. Since this gold was embedded in a conglomerate, it was first assumed that this was alluvial gold in an old riverbed, that had been tilted as a result of earth movements. However, when it was found that, traced downdip, the conglomerate was not merely developed for the narrow width of a river, but continued in depth, there came the realisation that this conglomeratic zone was part of a sedimentary succession. The conglomerate was quickly traced east and westward for a total continuous distance of to define what became known as the "Central Rand Gold Field".
It has since been established that the rocks that make up the Witwatersrand Ridge dip downwards and southwards to form the largely underground "Witwatersrand Basin" which covers an elliptical area with a long major axis from Evander in the north-east to Theunissen in the south-west, and wide stretching from Steynsrus in the south-east to Coligny in the north-west, with a small subsidiary basin at Kinross. Gold occurs only along the northern and western margins of this basin, but not in a continuous band. The gold-bearing rocks are limited to six sites where Archean rivers from the north and west formed fan deltas, with many braided channels, before flowing into the "Witwatersrand Sea" to the south, where the earlier sediments that form the older rocks of the Witwatersrand Supergroup had been deposited. Some of these gold bearing fan deltas are now at depths of below the surface.
Although many of the older mines, around Johannesburg, are now nearly exhausted, the Witwatersrand Basin still produces most of South Africa's gold and much of the total world output. Silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. ...
, uranium
Uranium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Ura ...
, and iridium
Iridium is a chemical element; it has the symbol Ir and atomic number 77. This very hard, brittle, silvery-white transition metal of the platinum group, is considered the second-densest naturally occurring metal (after osmium) with a density ...
are recovered as gold-refining by-products.
Geological origin
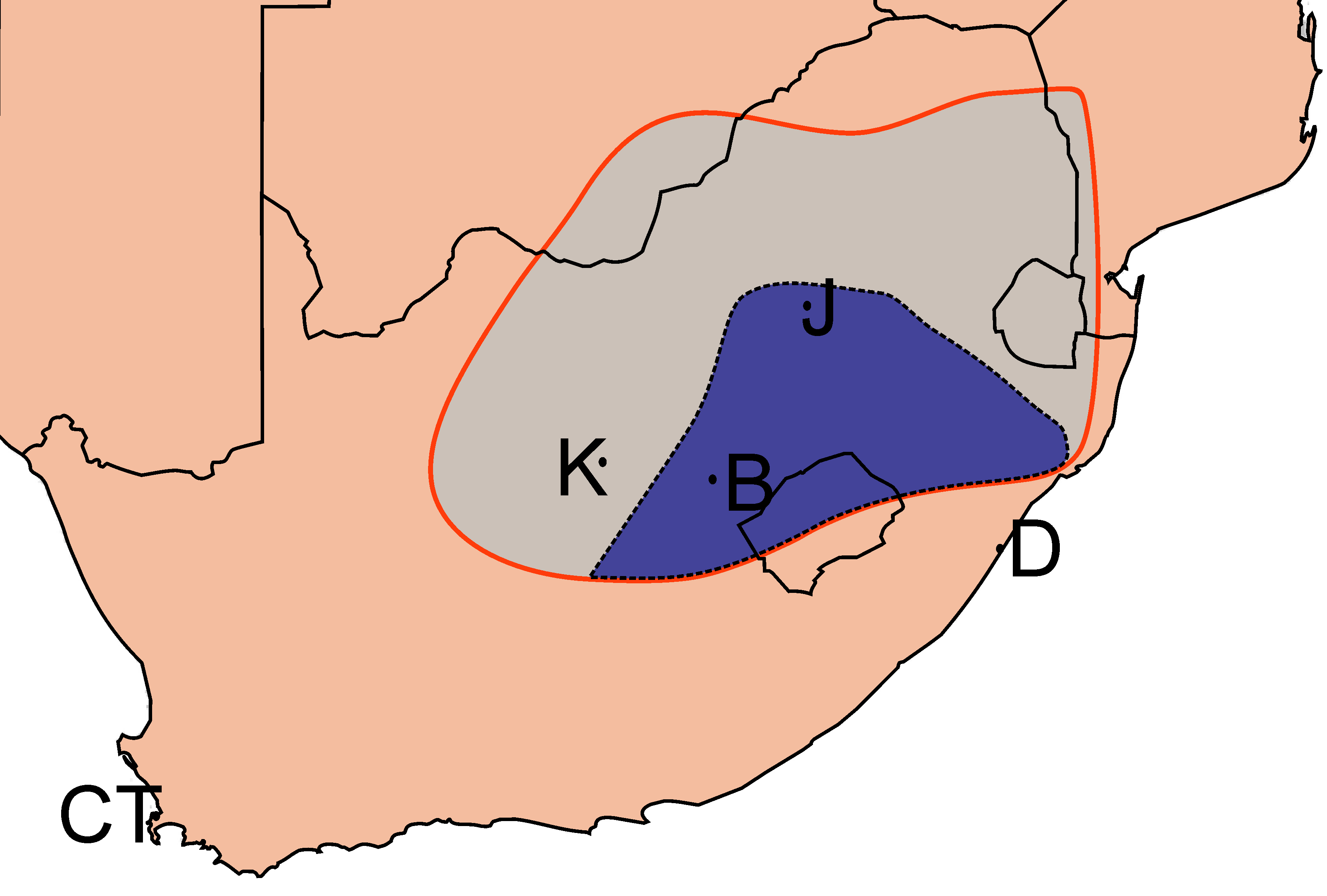
The Witwatersrand basin was created during the Archean Eon, and is therefore amongst the oldest geological structures on Earth. It was laid down in two stages, over the course of 260 million years starting just short of 3 billion years ago. The first phase, lasting 60 million years, consisted of sedimentary deposits in a shallow sea, conveniently named the "Witwatersrand Sea". The resulting 2500–4500 m thick layer of sediments is termed the "West Rand Group" of Witwatersrand rocks. The second phase, which lasted for 200 million years, followed on from the first phase, with on-land deposits, resulting from the retreat of the Witwatersrand Sea, leaving a wide almost flat coastal plain over which rivers from the north formed wide braided river deltas, into some of which rich deposits of gold were deposited. The resulting 2500 m thick layer of rock is termed the "Central Rand Group". The "West Rand Group" and "Central Rand Group" of rocks together form the "Witwatersrand Supergroup", the full horizontal extent of which is termed the Witwatersrand Basin. There were no continents during the early stages of the Archean Eon, but island arcs did form. It was the coalescence of several of these island arcs that led to the formation of the Kaapvaal craton, one of the first microcontinents to form on Earth about 3.9 billion years ago. Its size and position relative to
There were no continents during the early stages of the Archean Eon, but island arcs did form. It was the coalescence of several of these island arcs that led to the formation of the Kaapvaal craton, one of the first microcontinents to form on Earth about 3.9 billion years ago. Its size and position relative to Southern Africa
Southern Africa is the southernmost region of Africa. No definition is agreed upon, but some groupings include the United Nations geoscheme for Africa, United Nations geoscheme, the intergovernmental Southern African Development Community, and ...
today are indicated in the diagram on the left. About 3 billion years ago local cooling of the underlying asthenosphere
The asthenosphere () is the mechanically weak and ductile region of the upper mantle of Earth. It lies below the lithosphere, at a depth between c. below the surface, and extends as deep as . However, the lower boundary of the asthenosphere i ...
caused subsidence of the south eastern portion of this microcontinent below sea level. The floor of this newly formed "Witwatersrand sea" consisted of smoothly eroded granite
Granite ( ) is a coarse-grained (phanerite, phaneritic) intrusive rock, intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly coo ...
s. Sandy sediments brought in by rivers from the north started being deposited on the granite about 2.97 billion years ago. This sandy layer eventually became compressed to form the Orange Grove Quartzite, the lowermost layer of the Witwatersrand Supergroup. This quartzite layer can be seen lying on its granite base in Johannesburg
Johannesburg ( , , ; Zulu language, Zulu and Xhosa language, Xhosa: eGoli ) (colloquially known as Jozi, Joburg, Jo'burg or "The City of Gold") is the most populous city in South Africa. With 5,538,596 people in the City of Johannesburg alon ...
, where it forms a 56 km long east–west ridge over which several rivers running to the north form waterfalls, giving rise to the name Witwatersrand, which in Afrikaans
Afrikaans is a West Germanic languages, West Germanic language spoken in South Africa, Namibia and to a lesser extent Botswana, Zambia, Zimbabwe and also Argentina where there is a group in Sarmiento, Chubut, Sarmiento that speaks the Pat ...
means "Ridge of White Waters".
 There was no free oxygen in Earth's atmosphere until about 2 billion years ago, before the appearance and sufficient development of photosynthesizing
There was no free oxygen in Earth's atmosphere until about 2 billion years ago, before the appearance and sufficient development of photosynthesizing cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria ( ) are a group of autotrophic gram-negative bacteria that can obtain biological energy via oxygenic photosynthesis. The name "cyanobacteria" () refers to their bluish green (cyan) color, which forms the basis of cyanobacteri ...
. The oxygen produced by these microorganisms rapidly reacted with, amongst others, Fe2+ ions dissolved in water, precipitating insoluble red iron oxide
An iron oxide is a chemical compound composed of iron and oxygen. Several iron oxides are recognized. Often they are non-stoichiometric. Ferric oxyhydroxides are a related class of compounds, perhaps the best known of which is rust.
Iron ...
(hematite
Hematite (), also spelled as haematite, is a common iron oxide compound with the formula, Fe2O3 and is widely found in rocks and soils. Hematite crystals belong to the rhombohedral lattice system which is designated the alpha polymorph of . ...
). For various reasons, the sedimentation of the fine grain mud was affected by cyclic episodes with more or less precipitation of iron oxides. The result was alternating red and beige layers of mud which, when consolidated, became banded ironstones.
As the sea deepened, finer grained and muddy sediments accumulated. Changing geographical conditions resulted in the accumulation of a wide variety of sediments, ranging from mud, to sand, to gravel, and banded ironstones. Tillite
image:Geschiebemergel.JPG, Closeup of glacial till. Note that the larger grains (pebbles and gravel) in the till are completely surrounded by the matrix of finer material (silt and sand), and this characteristic, known as ''matrix support'', is d ...
deposits, dating from 2.95 billion years ago, are indicative of the first glaciation episodes on earth.Tankard, A.J., Jackson, M.P.A, Erikson, K.A., Hobday, D.K., Hunter, D.R., Minter, W.E.L. (1982). ''Crustal Evolution of Southern Africa. 3.8 Billion Years of Earth History.''pp. 118–139. Springer-Verlag, New York. Within 60 million years, up to 4500 m of sediment had accumulated on the granite base, to become the "West Rand Group" of rocks that contribute over 60% of the total thickness of the Witwatersrand Supergroup.
Uplifting of the north of the Kaapvaal craton, in addition to orogenesis (mountain formation), towards the end of the deposition of the "West Rand Group" of sediments caused the Witwatersrand sea to retreat. The area of the craton on top of which Johannesburg is now situated, became a vast riverine plain, which extended along the entire northern and western shoreline of the shrunken sea, in an arc extending from Evander in the east, through Johannesburg, Carletonville and then southwards to Klerksdorp and Welkom in the south-west. The rivers formed braided deltas with many interlacing, slow flowing channels where all the heavy materials brought down from the mountains were deposited: large pebbles, and heavy minerals, such as gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
, iron pyrite, and uraninite. The gold was in its free elemental form. Cyanobacteria grew in relative abundance in these mineral rich waters. The kerogen, or bitumen
Bitumen ( , ) is an immensely viscosity, viscous constituent of petroleum. Depending on its exact composition, it can be a sticky, black liquid or an apparently solid mass that behaves as a liquid over very large time scales. In American Engl ...
, that is found in association with the gold deposits almost certainly represents what remains of these Archean photosynthesizing micro-organisms.
It is clear that for the next 200 million years the flood plain was repeatedly inundated, sometimes eroded, and sediments re-deposited. The result was a 2500 m thick layer of rock that is termed the "Central Rand Group", which together with the "West Rand Group", forms the "Witwatersrand Supergroup". It is the younger Central Rand Group that contains most of the gold bearing conglomerates, locally referred to as banket, that are today of great economic importance.
The "Central Rand Group" of deposits was brought to an abrupt end by massive outpourings of lava, which form the Ventersdorp lavas which erupted 2.715 billion years ago. The cause of these lava outpourings is a matter of speculation. It might be related to the collision of the Kaapvaal craton with the Zimbabwe Craton, eventually to become knitted together to form a single continental unit.
 A final event that had a major impact on the geology of the Witwatersrand Basin and its exposure in the Johannesburg region, was a massive meteor impact 110 km to the south-west of Johannesburg 2.02 billion years ago. The impact was close to the present village of Vredefort, which has given its name to the geological remnant of this immense event: the Vredefort Dome. Not only are the remains of this impact among the oldest on Earth, but it is also one of the largest meteor impacts to have left its imprint on present-day Earth geology. A meteor 10–15 km across created a 300 km diameter crater, distorting all the rock strata within that circle. Johannesburg is just within the outer edge of this impact crater. In the immediate vicinity of the impact all the subterranean strata were uplifted and upturned, so that Witwatersrand rocks are exposed in an arc 25 km away from the impact centre. There are no gold deposits in these outcrops. The meteor impact, however, lowered the Witwatersrand basin inside the crater. This protected it from erosion later on; but, possibly more importantly, bringing it to the surface close to the crater rim, near Johannesburg. In fact, apart from the Witwatersrand outcrops (i.e. where these rocks are exposed at the surface) in the immediate vicinity of the Vredefort Dome, virtually all the other outcrops occur in an arc approximately 80–120 km from the centre of the impact crater, to the west, north-west, north and north-east. Thus, it is possible that if it had not been for the Vredefort asteroid strike 2 billion years ago, humanity would either never have discovered the rich gold deposits beneath the Southern African surface, or they would have been eroded away during the uninterrupted removal of a several kilometres thick layer of deposits from the surface of the Southern African Plateau in the relatively recent geological past: i.e. the past 150 million years, but especially during the last 20 million years.
A final event that had a major impact on the geology of the Witwatersrand Basin and its exposure in the Johannesburg region, was a massive meteor impact 110 km to the south-west of Johannesburg 2.02 billion years ago. The impact was close to the present village of Vredefort, which has given its name to the geological remnant of this immense event: the Vredefort Dome. Not only are the remains of this impact among the oldest on Earth, but it is also one of the largest meteor impacts to have left its imprint on present-day Earth geology. A meteor 10–15 km across created a 300 km diameter crater, distorting all the rock strata within that circle. Johannesburg is just within the outer edge of this impact crater. In the immediate vicinity of the impact all the subterranean strata were uplifted and upturned, so that Witwatersrand rocks are exposed in an arc 25 km away from the impact centre. There are no gold deposits in these outcrops. The meteor impact, however, lowered the Witwatersrand basin inside the crater. This protected it from erosion later on; but, possibly more importantly, bringing it to the surface close to the crater rim, near Johannesburg. In fact, apart from the Witwatersrand outcrops (i.e. where these rocks are exposed at the surface) in the immediate vicinity of the Vredefort Dome, virtually all the other outcrops occur in an arc approximately 80–120 km from the centre of the impact crater, to the west, north-west, north and north-east. Thus, it is possible that if it had not been for the Vredefort asteroid strike 2 billion years ago, humanity would either never have discovered the rich gold deposits beneath the Southern African surface, or they would have been eroded away during the uninterrupted removal of a several kilometres thick layer of deposits from the surface of the Southern African Plateau in the relatively recent geological past: i.e. the past 150 million years, but especially during the last 20 million years.
Gold origin
The vast majority of the Earth'sgold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
and other heavy metals are locked up in the earth's core. Evidence from tungsten
Tungsten (also called wolfram) is a chemical element; it has symbol W and atomic number 74. It is a metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively in compounds with other elements. It was identified as a distinct element in 1781 and first ...
isotope
Isotopes are distinct nuclear species (or ''nuclides'') of the same chemical element. They have the same atomic number (number of protons in their Atomic nucleus, nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemica ...
studies indicates that most gold in the crust is derived from gold in the mantle which resulted from a meteorite
A meteorite is a rock (geology), rock that originated in outer space and has fallen to the surface of a planet or Natural satellite, moon. When the original object enters the atmosphere, various factors such as friction, pressure, and chemical ...
bombardment some 3.9 billion years ago (i.e., at approximately the time that the Kaapvaal craton formed). The gold bearing meteorite events occurred millions of years after the segregation of the Earth's core.
The gold in the Witwatersrand Basin area was deposited in Archean river deltas
A river delta is a landform, wikt:archetype#Noun, archetypically triangular, created by the deposition (geology), deposition of the sediments that are carried by the waters of a river, where the river merges with a body of slow-moving water or ...
having been washed down from surrounding gold-rich greenstone belts to the north and west. Rhenium- osmium isotope studies indicate that the gold in those mineral deposits came from unusual 3 billion year old mantle-derived intrusions known as komatiite, present in the greenstone belts.Kirk, Jason; Joakin Ruiz; John Chesley and Spencer Titley; ''The Origin of Gold in South Africa,'' American Scientist, Vol 91, Nov.-Dec 2003, pp. 534–53Consequences of mining the ancient Witwatersrand rocks
Apart from the obvious hollowing out of the rocks below southern Johannesburg, causing unpredictable sinkholes, surface instabilities and earth tremors,Brink, A.B.A. (1996). "Engineering Geology of Southern Africa". pp. 81–160. Building Publications, Pretoria. the bringing to the surface of rocks that had been laid down in oxygen-free conditions had unforeseen effects. Iron pyrite (FeS2), which is relatively plentiful in the gold ores of the Witwatersrand, oxidises to insoluble ferric oxide (Fe2O3) andsulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen, ...
(H2SO4). Thus, when mine waste comes into contact with oxygenated rainwater, sulfuric acid is released into the ground water. Acid mine drainage
Acid mine drainage, acid and metalliferous drainage (AMD), or acid rock drainage (ARD) is the outflow of acidic water from metal mines and coal mines.
Acid rock drainage occurs naturally within some environments as part of the rock weatherin ...
, as the phenomenon is called, has become a major ecological problem, because it dissolves many of the heavy elements, such as the uranium
Uranium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Ura ...
, cadmium
Cadmium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, silvery-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12 element, group 12, zinc and mercury (element), mercury. Like z ...
, lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleabl ...
, zinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic tabl ...
, copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
, arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol As and atomic number 33. It is a metalloid and one of the pnictogens, and therefore shares many properties with its group 15 neighbors phosphorus and antimony. Arsenic is not ...
and mercury found in the mine dumps, facilitating their passage into surface water and ground water.Behind gold's glitter, torn lands and pointed questions, New York Times, 24 October 2005. (PDF). Retrieved on 4 May 2012. The tailings ponds contain an average of 100 mg/kg of U3O8, and uranium levels are measureable in human hair. Sulfuric acid also erodes concrete and cement structures, resulting in structural damage to buildings and bridges.
History
Although gold had been discovered in various locations in South Africa, such as Barberton and Pilgrim's Rest, as well as at several sites near the Witwatersrand, these were alluvial concentrates in contemporary rivers, or in quartz veins, in the form that gold had always been found elsewhere on earth. When George Harrison, probably accompanied by George Walker, found gold on the farm Langlaagte, west of what would become the city of Johannesburg, in an outcrop of conglomerate rocks, in February 1886, they assumed that this was alluvial gold in an old riverbed, that had been tilted as a result of earth movements. However, when it was found that, traced downdip, the conglomerate was not merely developed for the narrow width of a river, but continued in depth, there came the realisation that this conglomeratic zone was part of a sedimentary succession. Harrison had stumbled on the Main Reef conglomerate (part of the "Johannesburg Subgroup" of rocks — see illustration above). The conglomerate was quickly traced east and westward for a total continuous distance of to define what became known as the "Central Rand Gold Field". Harrison declared his claim to the government of the Zuid Afrikaanse Republiek (ZAR), and in September 1886 President Paul Kruger issued a proclamation declaring nine farms public mining diggings, starting on 20 September 1886. This heralded the historic Witwatersrand Gold Rush. Harrison is believed to have sold his claim for less than £10 before leaving the area, and he was never heard from again. Harrison's original Zoekers' (in English: seekers', or prospectors') Claim No 19 was declared a national monument in 1944, and named Harrison's Park. The park is on the busy Main Reef Road, immediately west of Nasrec Road.
In 1887
Harrison's original Zoekers' (in English: seekers', or prospectors') Claim No 19 was declared a national monument in 1944, and named Harrison's Park. The park is on the busy Main Reef Road, immediately west of Nasrec Road.
In 1887 Cecil John Rhodes
Cecil John Rhodes ( ; 5 July 185326 March 1902) was an English-South African mining magnate and politician in southern Africa who served as Prime Minister of the Cape Colony from 1890 to 1896. He and his British South Africa Company founded ...
registered "The Gold Fields of South Africa" in London, South Africa's first mining house, with a capital of . His brother Thomas was the first chairman.
See also
* Geography of South Africa * Great Escarpment, Southern Africa * Borakalalo Game Reserve * Pilanesberg * List of mountain ranges of South Africa * Witwatersrand Gold Rush * ThuchomycesFurther reading
* Breckenridge, Keith Derek (1995) ''An Age of Consent: law, discipline, and violence on the South African gold mines, 1910–1933''. Ph.D. thesis, Northwestern University, Evanston, Ill. * Cammack, Diana (1990) ''The Rand at War: the Witwatersrand and the Anglo-Boer war 1899–1902''. London: James Currey * Herd, Norman (1966) ''1922: the revolt on the Rand''. Johannesburg: Blue Crane BooksReferences
External links
* * {{Authority control Landforms of Gauteng Landforms of South Africa Geography of Johannesburg Mountain ranges of South Africa Escarpments of Africa