|
Structured Geospatial Analytic Method
The Structured Geospatial Analytic Method (SGAM) is both as an analytic method and pedagogy for the Geospatial Intelligence professional. This model was derived from and incorporates aspects of both Pirolli and Card’s sensemaking process and Richards Heuer’s Analysis of Competing Hypotheses model. This is a simplified view of the geospatial analytic process within the larger intelligence cycle. The SGAM is intended to advance the Geospatial Intelligence tradecraft by providing an approach not only to teach the analyst how forage and repackage data, but also how to analyze the data in a meaningful way. It has been long known that without specific prompting, people may be unaware of spatial patterns of an environment and, similar to other areas of intelligence analysis, the geospatial analyst has the human tendency to: * unconsciously discount much of the relevant information * mentally simplify the task and likely oversimplify the results * make judgments that are subject to u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geospatial Intelligence
In the United States, geospatial intelligence (GEOINT) is intelligence about the human activity on earth derived from the exploitation and analysis of imagery, signals, or signatures with geospatial information. GEOINT describes, assesses, and visually depicts physical features and geographically referenced activities on the Earth. GEOINT, as defined in US Code, consists of imagery, imagery intelligence (IMINT) and geospatial information. GEOINT knowledge and related tradecraft is no longer confined to the U.S. government, or even the world's leading military powers. Additionally, countries such as India are holding GEOINT-specific conferences. While other countries may define geospatial intelligence somewhat differently than does the U.S., the use of GEOINT data and services is the same. Geospatial Intelligence can also be referred to as “Location Intelligence.”Although GEOINT is inclusive, Hydrospatial is preferably used to refer and to focus on the aquatic and costal zon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensemaking
Sensemaking or sense-making is the process by which people give meaning to their collective experiences. It has been defined as "the ongoing retrospective development of plausible images that rationalize what people are doing" ( Weick, Sutcliffe, & Obstfeld, 2005, p. 409). The concept was introduced to organizational studies by Karl E. Weick in the 1970s and has affected both theory and practice. Weick intended to encourage a shift away from the traditional focus of organization theorists on decision-making and towards the processes that constitute the meaning of the decisions that are enacted in behavior. Definition There is no single agreed upon definition of sensemaking, but there is consensus that it is a process that allows people to understand ambiguous, equivocal or confusing issues or events. Disagreements about the meaning of sensemaking exist around whether sensemaking is a mental process within the individual, a social process or a process that occurs as part of discu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richards Heuer
Richards "Dick" J. Heuer, Jr. was a CIA veteran of 45 years and most known for his work on analysis of competing hypotheses and his book, Psychology of Intelligence Analysis'' This is the Introduction to Heuer's book ''Psychology of Intelligence Analysis''. The former provides a methodology for overcoming intelligence biases while the latter outlines how mental models and natural biases impede clear thinking and analysis. Throughout his career, he worked in collection operations, counterintelligence, intelligence analysis and personnel security. In 2010 he co-authored a book with Randolph (Randy) H. Pherson titled ''Structured Analytic Techniques for Intelligence Analysis''. Background Richards Heuer graduated in 1950 from Williams College with a Bachelor of Arts in Philosophy. One year later, while a graduate student at the University of California in Berkeley, future CIA Director Richard Helms recruited Heuer to work at the Central Intelligence Agency. Helms, also a graduate of Wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analysis Of Competing Hypotheses
The analysis of competing hypotheses (ACH) is a methodology for evaluating multiple competing hypotheses for observed data. It was developed by Richards (Dick) J. Heuer, Jr., a 45-year veteran of the Central Intelligence Agency, in the 1970s for use by the Agency. ACH is used by analysts in various fields who make judgments that entail a high risk of error in reasoning. ACH aims to help an analyst overcome, or at least minimize, some of the cognitive limitations that make prescient intelligence analysis so difficult to achieve. ACH was a step forward in intelligence analysis methodology, but it was first described in relatively informal terms. Producing the best available information from uncertain data remains the goal of researchers, tool-builders, and analysts in industry, academia and government. Their domains include data mining, cognitive psychology and visualization, probability and statistics, etc. Abductive reasoning is an earlier concept with similarities to ACH. Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
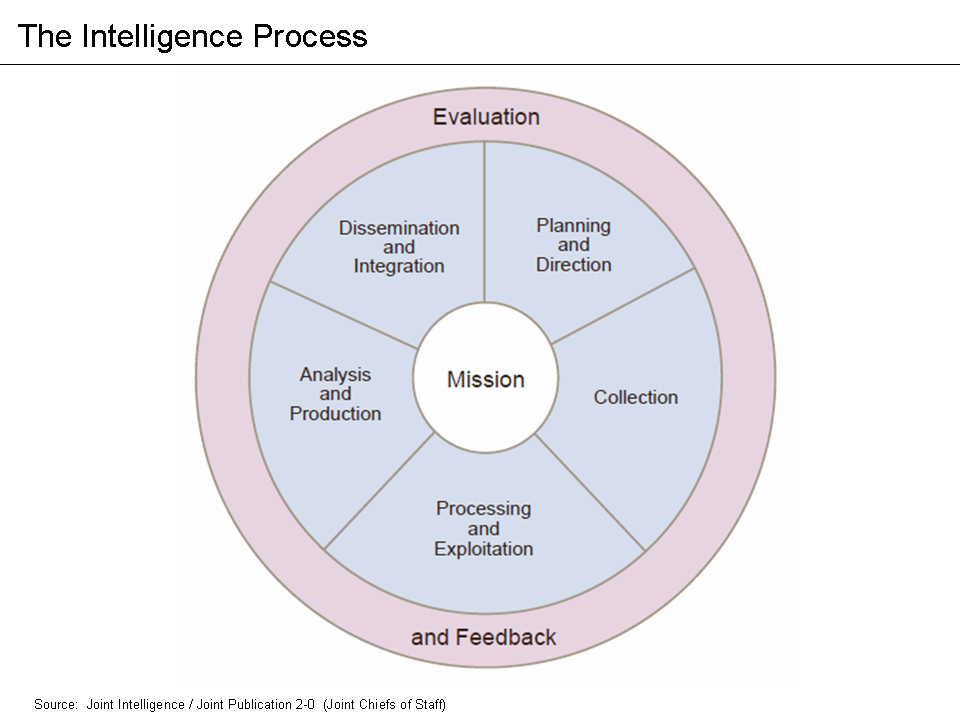
Intelligence Cycle
The Intelligence cycle describes how intelligence is ideally processed in civilian and military intelligence agencies, and law enforcement organizations. It is a closed path consisting of repeating nodes, which (if followed) will result in finished intelligence. The stages of the intelligence cycle include the issuance of requirements by decision makers, collection, processing, analysis, and publication (i.e., dissemination) of intelligence. The circuit is completed when decision makers provide feedback and revised requirements. The intelligence cycle is also called the Intelligence Process by the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) and the uniformed services. Conceptual model Direction Intelligence requirements are determined by a decision maker to meet his/her objectives. In the federal government of the United States, requirements (or priorities) can be issued from the White House or the Congress. In NATO, a commander uses requirements (sometimes called Essential elements of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reginald Golledge
Reginald George Golledge (born 6 December 1937 in Dungog, New South Wales; died 29 May 2009 in Goleta, California) was an Australian-born American Professor of Geography at the University of California, Santa Barbara. He was named Faculty Research Lecturer for 2009. During his career he wrote or edited 16 books and 100 chapters for other books, and wrote more than 150 academic papers. Golledge was a pioneer in the field of behavioral geography. When behavioral geography divided into a humanistic and an analytical approach by the early 1970s, Golledge became the chief proponent of the latter one.Kitchin, R. (2004): Reginald Golledge. In: Hubbard, P., R. Kitchin and G. Valentine (Eds.): Key thinkers on space and place. London: Sage Pubn Inc. pp. 136–142. In 1984 he became blind, and moved his focus to the geography of disability. Golledge was one of the developers (the others being psychologists Jack Loomis and Roberta Klatzky) of the UCSB Personal Guidance System. Academic c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Foraging
Information foraging is a theory that applies the ideas from optimal foraging theory to understand how human users search for information. The theory is based on the assumption that, when searching for information, humans use "built-in" foraging mechanisms that evolved to help our animal ancestors find food. Importantly, a better understanding of human search behavior can improve the usability of websites or any other user interface. History of the theory In the 1970s optimal foraging theory was developed by anthropologists and ecologists to explain how animals hunt for food. It suggested that the eating habits of animals revolve around maximizing energy intake over a given amount of time. For every predator, certain prey is worth pursuing, while others would result in a net loss of energy. In the early 1990s, Peter Pirolli and Stuart Card from PARC noticed the similarities between users' information searching patterns and animal food foraging strategies. Working together wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensemaking
Sensemaking or sense-making is the process by which people give meaning to their collective experiences. It has been defined as "the ongoing retrospective development of plausible images that rationalize what people are doing" ( Weick, Sutcliffe, & Obstfeld, 2005, p. 409). The concept was introduced to organizational studies by Karl E. Weick in the 1970s and has affected both theory and practice. Weick intended to encourage a shift away from the traditional focus of organization theorists on decision-making and towards the processes that constitute the meaning of the decisions that are enacted in behavior. Definition There is no single agreed upon definition of sensemaking, but there is consensus that it is a process that allows people to understand ambiguous, equivocal or confusing issues or events. Disagreements about the meaning of sensemaking exist around whether sensemaking is a mental process within the individual, a social process or a process that occurs as part of discu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brainstorming
Brainstorming is a group creativity technique by which efforts are made to find a conclusion for a specific problem by gathering a list of ideas spontaneously contributed by its members. In other words, brainstorming is a situation where a group of people meet to generate new ideas and solutions around a specific domain of interest by removing inhibitions. People are able to think more freely and they suggest as many spontaneous new ideas as possible. All the ideas are noted down without criticism and after the brainstorming session the ideas are evaluated. The term was popularized by Alex Faickney Osborn in the classic work '' Applied Imagination'' (1953). History In 1939, advertising executive Alex F. Osborn began developing methods for creative problem-solving. He was frustrated by employees' inability to develop creative ideas individually for ad campaigns. In response, he began hosting group-thinking sessions and discovered a significant improvement in the quality and qua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Visualization
Data and information visualization (data viz or info viz) is an interdisciplinary field that deals with the graphic representation of data and information. It is a particularly efficient way of communicating when the data or information is numerous as for example a time series. It is also the study of visual representations of abstract data to reinforce human cognition. The abstract data include both numerical and non-numerical data, such as text and geographic information. It is related to infographics and scientific visualization. One distinction is that it's information visualization when the spatial representation (e.g., the page layout of a graphic design) is chosen, whereas it's scientific visualization when the spatial representation is given. From an academic point of view, this representation can be considered as a mapping between the original data (usually numerical) and graphic elements (for example, lines or points in a chart). The mapping determines how the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
