|
Striven Hydro-Electric Scheme
Striven Hydro-Electric Scheme is a small-scale hydro-electric power station, built by the North of Scotland Hydro-Electric Board and commissioned in 1951. It is located near Ardtaraig on the Cowal Peninsula, part of Argyll and Bute, west of Scotland. It is sometimes known as the Cowal Hydro-Electric Scheme. It was originally designed to supply power to the remote communities on the peninsula, but is now connected to the National Grid. History The North of Scotland Hydro-Electric Board was created by the Hydro-electric Development (Scotland) Act 1943, a measure championed by the politician Tom Johnston while he was Secretary of State for Scotland. Johnston's vision was for a public body that could build hydro-electric stations throughout the Highlands. Profits made by selling bulk electricity to the Scottish lowlands would be used to fund "the economic development and social improvement of the North of Scotland." Private consumers would be offered a supply of cheap electricity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ardtaraig
Ardtaraig is a hamlet lying at the head of Loch Striven on the Cowal Peninsula, in Argyll and Bute, West of Scotland. The hamlet is on the single track B836 road. Cowal Hydro Scheme The Cowal Hydro Scheme is part of the Sloy/Awe Hydro-Electric Scheme and produces 8MW from the stored waters of Loch Tarsan (artificial reservoir), located close by in Glen Lean. The generating house is located at Ardtaraig and is supplied by pipe. The scheme opened in 1951. History Ardtaraig Chapel Ardtaraig Chapel no longer stands, but the foundations are still visible. World War II Ardtaraig was known as HMS Varbel II, a secondary base to HMS Varbel, where navigation was taught to the men who manned the midget submarines or X-craft. Transportation National Cycle Route 75 Ardtaraig is on the NCR75 a route from Edinburgh to Tarbert on the Kintyre peninsula. The National Cycle Network is maintained by sustrans Sustrans ( ) is a United Kingdom-based walking, wheeling and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harold Tarbolton
Harold Ogle Tarbolton FRIBA (1869–1947) was a 19th/20th century British architect, mainly working in Scotland. He was affectionately known as Tarrybreeks. In later life he went into partnership with Sir Matthew Ochterlony to create Tarbolton & Ochterlony. He was involved in electricity schemes from at least 1902, and ended his career overseeing several hydro-electric schemes in Scotland. Life Tarbolton was born in Nottingham in 1869, the son of Marriott Ogle Tarbotton, Marriot Tarbolton, a civil engineer, and his wife, E. M. Stanfield. The family moved around and he was mainly educated at Chigwell in Essex. He was articled to train as an architect with George Thomas Hine around 1885. After training he joined the office of Gerald Horsley in London. Here he was able to also study at the Royal Academy of Art, Royal Academy Schools from 1893 to 1895. He appears to have also spent some time during the same period at the University of Bonn in Germany. In 1895 he set up prac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Framework Directive
The Water Framework Directive (WFD; 2000/60/EC) is an EU directive to establish a framework for the protection of all water bodies (including marine waters up to one nautical mile from shore) by 2015. The WFD establishes a programme and timetable for Member States to set up river basin management plans by 2009. The Directive's aim is for all water bodies in EU member states to achieve "good status", with 47% of EU water bodies covered by the Directive failing this standard. Objectives of the Directive The Directive aims for "good status" for all ground and surface waters (rivers, lakes, transitional waters, and coastal waters) in the EU. The purpose of the WFD is to prevent deterioration of the water bodies, enhance status of aquatic ecosystems, reduce pollution from priority substances, promote sustainable water use and contribute to mitigate the effects of floods and droughts. The ecological and chemical status of surface waters are assessed according to the following c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish Environment Protection Agency
The Scottish Environment Protection Agency (SEPA; ) is Scotland's Environmental regulation, environmental regulator and national flood forecasting, flood warning and strategic flood risk management authority.Environment Act (1995). (c.2), London, HMSO [Accessed 29 April 2010]. Its main role is to protect and improve Scotland's environment. SEPA does this by helping business and industry to understand their environmental responsibilities, enabling customers to comply with legislation and good practice and to realise the economic benefits of good environmental practice. One of the ways SEPA does this is through the NetRegs environmental guidance service. It protects communities by regulating activities that can cause harmful pollution and by monitoring the quality of Scotland's air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordnance Datum
An ordnance datum (OD) is a vertical datum used by an ordnance survey as the basis for deriving altitudes on maps. A spot height may be expressed as above ordnance datum (AOD). Usually mean sea level (MSL) at a particular place is used for the datum. British Isles * In Great Britain, OD for the Ordnance Survey is Ordnance Datum Newlyn (ODN), defined as the MSL as recorded by the Newlyn Tidal Observatory between 1915 and 1921. **Prior to 1921, OD was Ordnance Datum Liverpool (ODL) defined as MSL as recorded in the Victoria Dock (Liverpool), Victoria Dock, Liverpool, during a short period in 1844. The first datum, in 1840 used a benchmark on St John's Church, Liverpool Central, St. John’s Church, . * In Northern Ireland, OD for the Ordnance Survey of Northern Ireland is Belfast Ordnance Datum: the MSL at Clarendon Dock, Belfast Harbour, between 1951 and 1956. * In Republic of Ireland, Ireland, OD for the Ordnance Survey of Ireland is Malin Ordnance Datum: the MSL at Portmoor Pie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish And Southern Energy
SSE plc (formerly Scottish and Southern Energy plc) is a multinational energy company headquartered in Perth, Scotland. It is listed on the London Stock Exchange, and is a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index. SSE operates in the United Kingdom and Ireland. History Origins The company has its origins in two public sector electricity supply authorities. The former North of Scotland Hydro-Electric Board was founded in 1943 to design, construct and manage hydroelectricity projects in the Highlands of Scotland, and took over further generation and distribution responsibilities on the nationalisation of the electricity industry within the United Kingdom in 1948. The former Southern Electricity Board was created in 1948 to distribute electricity in Southern England. Whilst the Southern Electricity Board was a distribution only authority, with no power generation capacity of its own, the North of Scotland Hydro-Electric board was a broader spectrum organisation, with its own generat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Electric
Southern Electric plc was a public limited energy company in the United Kingdom between 1990 and 1998, when it merged with Scottish Hydro-Electric plc to form Scottish and Southern Energy plc (now SSE plc). The company had its origins in the southern England region of the British nationalised electricity industry. Created in 1948 as the Southern Electricity Board, in 1990 it was privatised by being floated on the London Stock Exchange. History The company originated as the Southern Electricity Board, created in 1948 as part of the nationalisation of the electricity industry by the Electricity Act 1947. The board's assets passed in 1990 to Southern Electric plc, one of the fourteen public electricity suppliers, and that company was privatised in the same year. In 1998 the company merged with Scottish Hydro-Electric plc and became part of Scottish and Southern Energy. SSE used the "Southern Electric" name and logo for a time as a brand name for retail distribution of gas a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish Hydro-Electric
Scottish Hydro-Electric (named North of Scotland Electricity between 1 April 1989 and 1 August 1989) was a public electricity supplier in the United Kingdom. It was listed on the London Stock Exchange and was once a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index. The company merged with Southern Electric in 1998, and is now known as SSE plc. History The company was formed on 1 April 1989 to acquire the assets of the North of Scotland Hydro-Electric Board ahead of electricity privatisation in the United Kingdom under the name ''North of Scotland Electricity plc''. The company was floated on the London Stock Exchange in June 1991. It merged with the English public electricity supplier Southern Electric plc to become Scottish and Southern Energy plc (SSE) on 14 December 1998. Operations The Scottish Hydro name was used as a brand name by SSE plc for supplying gas and electricity in Scotland, and by Scottish Hydro-Electric Power Distribution Ltd, the distribution network operator in the north o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isle Of Cumbrae
Great Cumbrae () is the larger of the two islands known as The Cumbraes in the lower Firth of Clyde in western Scotland. The island is sometimes called Millport, after its main town. Home to the Cathedral of The Isles and the FSC Millport field study centre, the island has a community of 1,300 residents. Geography The island is roughly long by wide, rising to a height of above sea level at The Glaid Stone, which is a large, naturally occurring rock perched on the highest summit on the island. There is a triangulation pillar nearby, as well as an orientation point which indicates the locations of surrounding landmarks. In clear conditions, views extend north over the upper Clyde estuary to Ben Lomond and the Arrochar Alps. To the west, the larger islands of Bute and Arran can be seen, while on the other side of Knapdale the Paps of Jura may be visible. Looking south, Ailsa Craig is visible, around distant beyond Little Cumbrae. Ailsa Craig roughly marks the halfway point ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isle Of Bute
The Isle of Bute (; or '), known as Bute (), is an island in the Firth of Clyde in Scotland, United Kingdom. It is divided into highland and lowland areas by the Highland Boundary Fault. Formerly a constituent island of the larger County of Bute, it is now part of the council area of Argyll and Bute. Bute's resident population was 6,498 in 2011, a decline of just over 10% from the figure of 7,228 recorded in 2001 against a background of Scottish island populations as a whole growing by 4% to 103,702 for the same period. Name The name "Bute" is of uncertain origin. Watson and Mac an Tàilleir support a derivation from Old Irish ' ("fire"), perhaps in reference to signal fires.Watson (1926) pp 95–6Mac an Tàilleir (2003) p. 24 This reference to beacon fires may date from the Viking period, when the island was probably known to the Norse as '. Other possible derivations include Brittonic ''budh'' ("corn"), "victory", , or ', his monastic cell. There is no likely derivatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
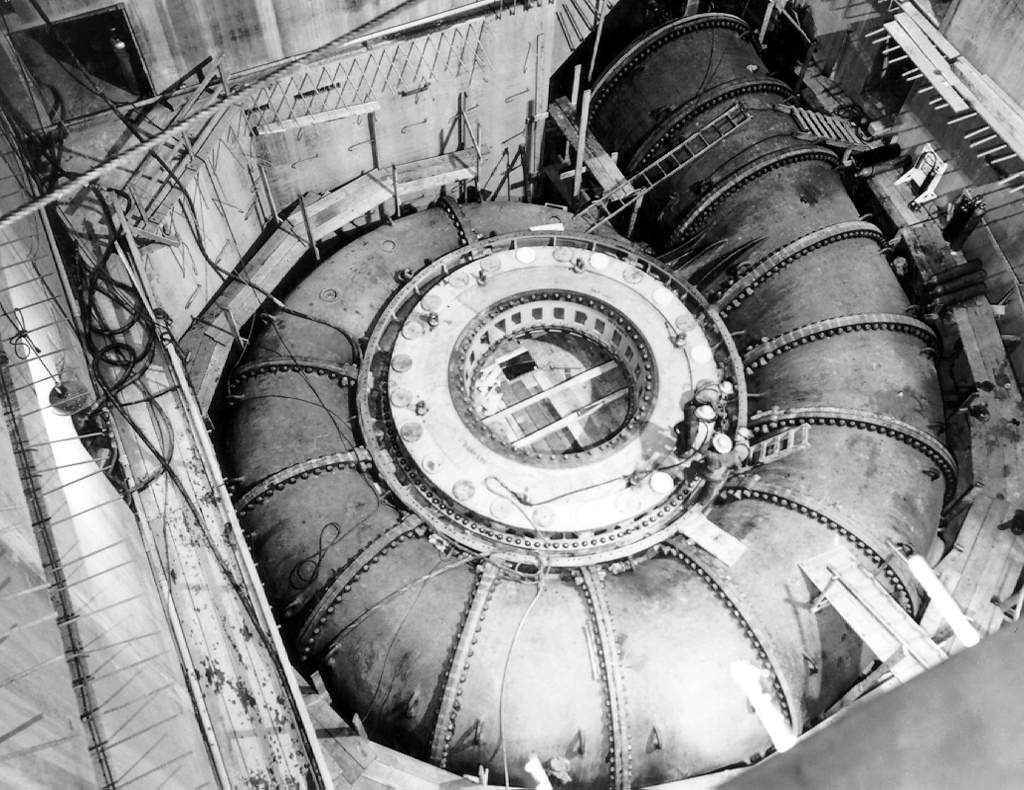
Francis Turbine
The Francis turbine is a type of water turbine. It is an inward-flow reaction turbine that combines radial and axial flow concepts. Francis turbines are the most common water turbine in use today, and can achieve over 95% efficiency. The process of arriving at the modern Francis runner design took from 1848 to approximately 1920. It became known as the Francis turbine around 1920, being named after British-American engineer James B. Francis who in 1848 created a new turbine design. Francis turbines are primarily used for producing electricity. The power output of the electric generators generally ranges from just a few kilowatts up to 1000 MW, though mini-hydro installations may be lower. The best performance is seen when the head height is between . Penstock diameters are between . The speeds of different turbine units range from 70 to 1000 rpm. A wicket gate around the outside of the turbine's rotating runner controls the rate of water flow through the turbine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |