|
String Quartet No. 1 (Gerhard)
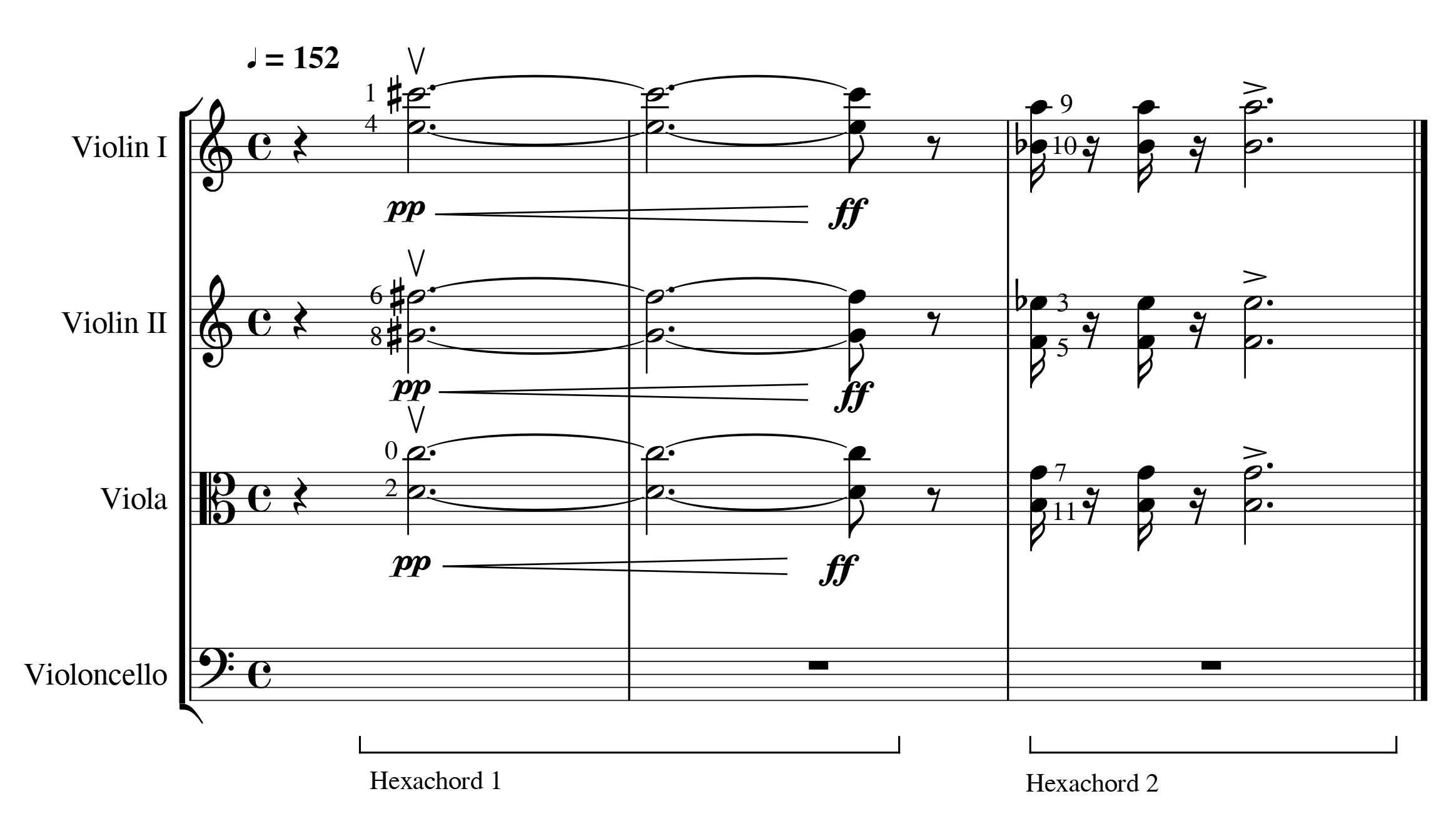
The ''String Quartet No.1'' is a piece for two violins, viola and cello, composed by Robert Gerhard between 1951 and 1955, premiered at Dartington in 1956. This work marks a turning point in Gerhard's style and composition processes, because in one hand, he recovers some old techniques such as the sonata form in the first movement, along with others not as old like the 12-tone technique. Gerhard brilliantly develops, combines and transforms these resources along with new systematic processes created by himself, so that it leads to a new and broad theoretical framework that will be essential to his music thereafter. Background Robert Gerhard began writing this string quartet in 1951 in Cambridge, where he lived in exile since 1939 as a result of Francoist Spain, Franco's dictatorship, within a significant historical and personal context. He had been one of the most important disciples (from the few who remained alive) of Arnold Schoenberg, who died in the same year of 1951. At t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Gerhard
Robert Gerhard i Ottenwaelder (; 25 September 1896 – 5 January 1970) was a Spanish Catalan composer and musical scholar and writer, generally known outside Catalonia as Roberto Gerhard.Malcolm MacDonald. 'Gerhard, Roberto' in ''Grove Music Online'' (2001) Life Gerhard was born in Valls, near Tarragona, Spain, the son of a German-Swiss father and an Alsatian mother. He was predisposed to an international, multilingual outlook. He studied piano with Enrique Granados and composition with scholar-composer Felip Pedrell, teacher of Isaac Albéniz, Granados and Manuel de Falla. When Pedrell died in 1922, Gerhard tried unsuccessfully to become a pupil of Falla and considered studying with Charles Koechlin in Paris but then approached Arnold Schoenberg, who on the strength of a few early compositions accepted him as his only Spanish pupil. Gerhard spent several years with Schoenberg in Vienna and Berlin. Returning to Barcelona in 1928, he devoted his energies to new music through co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitch (music)
Pitch is a perceptual property of sounds that allows their ordering on a frequency-related scale, or more commonly, pitch is the quality that makes it possible to judge sounds as "higher" and "lower" in the sense associated with musical melodies. Pitch is a major auditory attribute of musical tones, along with duration, loudness, and timbre. Pitch may be quantified as a frequency, but pitch is not a purely objective physical property; it is a subjective psychoacoustical attribute of sound. Historically, the study of pitch and pitch perception has been a central problem in psychoacoustics, and has been instrumental in forming and testing theories of sound representation, processing, and perception in the auditory system. Perception Pitch and frequency Pitch is an auditory sensation in which a listener assigns musical tones to relative positions on a musical scale based primarily on their perception of the frequency of vibration. Pitch is closely related to frequency, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Society For Contemporary Music
The International Society for Contemporary Music (ISCM) is a music organization that promotes contemporary classical music. The organization was established in Salzburg in 1922 as Internationale Gesellschaft für Neue Musik (IGNM) following the Internationale Kammermusikaufführungen Salzburg, a festival of modern chamber music held as part of the Salzburg Festival. It was founded by the Austrian (later British) composer Egon Wellesz and the Cambridge academic Edward J Dent, who first met when Wellesz visited England in 1906. In 1936 the rival Permanent Council for the International Co-operation of Composers, set up under Richard Strauss, was accused of furthering Nazi Party cultural ambitions in opposition to the non-political ISCM. British composer Herbert Bedford, acting as co-Secretary, defended its neutrality. Aside from hiatuses in 1940 and 1943-5 due to World War II and in 2020–21 due to the global COVID-19 pandemic, the ISCM's core activity has been an annual fest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symphony No
A symphony is an extended musical composition in Western classical music, most often for orchestra. Although the term has had many meanings from its origins in the ancient Greek era, by the late 18th century the word had taken on the meaning common today: a work usually consisting of multiple distinct sections or movements, often four, with the first movement in sonata form. Symphonies are almost always scored for an orchestra consisting of a string section (violin, viola, cello, and double bass), brass, woodwind, and percussion instruments which altogether number about 30 to 100 musicians. Symphonies are notated in a musical score, which contains all the instrument parts. Orchestral musicians play from parts which contain just the notated music for their own instrument. Some symphonies also contain vocal parts (e.g., Beethoven's Ninth Symphony). Etymology and origins The word ''symphony'' is derived from the Greek word (), meaning "agreement or concord of sound", "c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mode (music)
In music theory, the term mode or ''modus'' is used in a number of distinct senses, depending on context. Its most common use may be described as a type of musical scale coupled with a set of characteristic melodic and harmonic behaviors. It is applied to major and minor keys as well as the seven diatonic modes (including the former as Ionian and Aeolian) which are defined by their starting note or tonic. ( Olivier Messiaen's modes of limited transposition are strictly a scale type.) Related to the diatonic modes are the eight church modes or Gregorian modes, in which authentic and plagal forms of scales are distinguished by ambitus and tenor or reciting tone. Although both diatonic and gregorian modes borrow terminology from ancient Greece, the Greek ''tonoi'' do not otherwise resemble their mediaeval/modern counterparts. In the Middle Ages the term modus was used to describe both intervals and rhythm. Modal rhythm was an essential feature of the modal notation syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harpsichord Concerto (Gerhard)
A harpsichord concerto is a piece of music for an orchestra with the harpsichord in a solo role (though for another sense, see below). Sometimes these works are played on the modern piano (see ''piano concerto''). For a period in the late 18th century, Joseph Haydn and Thomas Arne wrote concertos that could be played interchangeably on harpsichord, fortepiano, and (in some cases) pipe organ. The Baroque harpsichord concerto The harpsichord was a common instrument in the 1730s, but never as popular as string or wind instruments in the concerto role in the orchestra, probably due to its relative lack of volume in an orchestral setting. In this context, harpsichords were more usually employed as a continuo instrument, playing a harmonised bass part in nearly all orchestral music, the player often also directing the orchestra. Bach's Brandenburg Concerto No.5 in D major, BWV 1050, may be the first work in which the harpsichord appears as a concerto soloist. In this piece, its usual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piano Concerto (Gerhard)
A piano concerto is a type of concerto, a solo composition in the classical music genre which is composed for a piano player, which is typically accompanied by an orchestra or other large ensemble. Piano concertos are typically virtuoso showpieces which require an advanced level of technique on the instrument. These concertos are typically written out in music notation, including sheet music for the pianist (which they typically memorize for a more virtuosic performance), orchestra parts for the orchestra members, and a full score for the conductor, who leads the orchestra in the accompaniment of the soloist. Depending on the era in which a piano concerto was composed, the orchestra parts may provide a fairly subordinate accompaniment role, setting out the bassline and chord progression over which the piano plays solo parts (more typical during the Baroque music era, from 1600 to 1750 and the Classical period, from 1730 to 1800), or the orchestra may be given an almost equal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Béla Bartók
Béla Viktor János Bartók (; ; 25 March 1881 – 26 September 1945) was a Hungarian composer, pianist, and ethnomusicologist. He is considered one of the most important composers of the 20th century; he and Franz Liszt are regarded as Hungary's greatest composers. Through his collection and analytical study of folk music, he was one of the founders of comparative musicology, which later became ethnomusicology. Biography Childhood and early years (1881–98) Bartók was born in the Banatian town of Nagyszentmiklós in the Kingdom of Hungary (present-day Sânnicolau Mare, Romania) on 25 March 1881. On his father's side, the Bartók family was a Hungarian lower noble family, originating from Borsodszirák, Borsod. His paternal grandmother was a Catholic of Bunjevci origin, but considered herself Hungarian. Bartók's father (1855–1888) was also named Béla. Bartók's mother, Paula (née Voit) (1857–1939), also spoke Hungarian fluently. A native of Turócszentmár ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orchestration
Orchestration is the study or practice of writing music for an orchestra (or, more loosely, for any musical ensemble, such as a concert band) or of adapting music composed for another medium for an orchestra. Also called "instrumentation", orchestration is the assignment of different instruments to play the different parts (e.g., melody, bassline, etc.) of a musical work. For example, a work for solo piano could be adapted and orchestrated so that an orchestra could perform the piece, or a concert band piece could be orchestrated for a symphony orchestra. In classical music, composers have historically orchestrated their own music. Only gradually over the course of music history did orchestration come to be regarded as a separate compositional art and profession in itself. In modern classical music, composers almost invariably orchestrate their own work. However, in musical theatre, film music and other commercial media, it is customary to use orchestrators and arranger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Music Of Catalonia
The music of Catalonia comprises one of the oldest documented musical traditions in Europe. In tandem with the rest of Western Europe, it has a long musical tradition, incorporating a number of different styles and genres over the past two thousand years. History Among the earliest references to music from Catalonia date to the Middle Ages, when Barcelona and the surrounding area were relatively prosperous, allowing both music and arts to be cultivated actively. Catalonia and adjacent areas were the home for several troubadours, the itinerant composer-musicians whose influence and aesthetics was decisive on the formation of late medieval secular music, and who traveled into Italy and Northern France after the destruction of Occitann culture by the Albigensian Crusade in the early 13th century. The so-called Llibre Vermell de Montserrat ("Red Book of Montserrat") stands as an important source for 14th-century music. Renaissance polyphony flourished in Catalonia, though local compo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Form (music)
In music, ''form'' refers to the structure of a musical composition or performance. In his book, ''Worlds of Music'', Jeff Todd Titon suggests that a number of organizational elements may determine the formal structure of a piece of music, such as "the arrangement of musical units of rhythm, melody, and/or harmony that show repetition or variation, the arrangement of the instruments (as in the order of solos in a jazz or bluegrass performance), or the way a symphonic piece is orchestrated", among other factors. It is, "the ways in which a composition is shaped to create a meaningful musical experience for the listener."Kostka, Stefan and Payne, Dorothy (1995). ''Tonal Harmony'', p.152. McGraw-Hill. . These organizational elements may be broken into smaller units called phrases, which express a musical idea but lack sufficient weight to stand alone. Musical form unfolds over time through the expansion and development of these ideas. In tonal harmony, form is articulated primar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metre (music)
In music, metre ( Commonwealth spelling) or meter ( American spelling) refers to regularly recurring patterns and accents such as bars and beats. Unlike rhythm, metric onsets are not necessarily sounded, but are nevertheless implied by the performer (or performers) and expected by the listener. A variety of systems exist throughout the world for organising and playing metrical music, such as the Indian system of ''tala'' and similar systems in Arabic and African music. Western music inherited the concept of metre from poetry, where it denotes: the number of lines in a verse; the number of syllables in each line; and the arrangement of those syllables as long or short, accented or unaccented. The first coherent system of rhythmic notation in modern Western music was based on rhythmic modes derived from the basic types of metrical unit in the quantitative metre of classical ancient Greek and Latin poetry. Later music for dances such as the pavane and galliard consisted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |








.jpg)