|
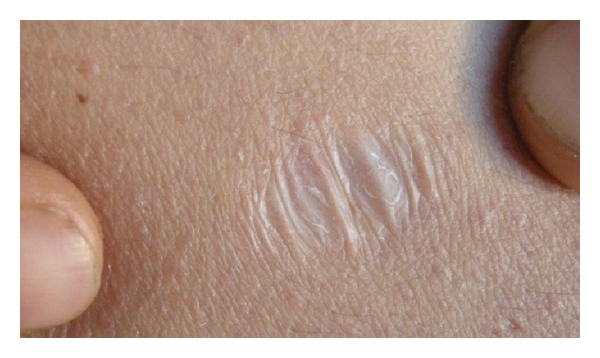
Striae
Stretch marks, also known as striae () or striae distensae, are a form of scarring on the skin with an off-color hue. Over time, they may diminish, but will not disappear completely. Striae are caused by tearing of the dermis during periods of rapid growth of the body, such as during puberty or pregnancy, in which they usually form during the last trimester. Usually on the belly, these striae also commonly occur on the breasts, thighs, hips, lower back, and buttocks. Pregnancy-related striae are known as ''striae gravidarum''. Striae may also be influenced by the hormonal changes associated with puberty, pregnancy, bodybuilding, or hormone replacement therapy. There is no evidence that creams used during pregnancy prevent stretch marks. Once they have formed, there is no clearly effective treatment, though various methods have been attempted and studied. Signs and symptoms Striae, or "stretch marks", begin as reddish or purple lesions which can appear anywhere on the body, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scarring
A scar (or scar tissue) is an area of fibrous tissue that replaces normal skin after an injury. Scars result from the biological process of wound repair in the skin, as well as in other organs, and tissues of the body. Thus, scarring is a natural part of the healing process. With the exception of very minor lesions, every wound (e.g., after accident, disease, or surgery) results in some degree of scarring. An exception to this are animals with complete regeneration, which regrow tissue without scar formation. Scar tissue is composed of the same protein (collagen) as the tissue that it replaces, but the fiber composition of the protein is different; instead of a random basketweave formation of the collagen fibers found in normal tissue, in fibrosis the collagen cross-links and forms a pronounced alignment in a single direction. This collagen scar tissue alignment is usually of inferior functional quality to the normal collagen randomised alignment. For example, scars in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scar
A scar (or scar tissue) is an area of fibrosis, fibrous tissue that replaces normal skin after an injury. Scars result from the biological process of wound repair in the skin, as well as in other Organ (anatomy), organs, and biological tissue, tissues of the body. Thus, scarring is a natural part of the healing process. With the exception of very minor lesions, every wound (e.g., after accident, disease, or surgery) results in some degree of scarring. An exception to this are animals with complete Regeneration (biology), regeneration, which regrow tissue without scar formation. Scar tissue is composed of the same protein (collagen) as the tissue that it replaces, but the fiber composition of the protein is different; instead of a random basketweave formation of the collagen fibers found in normal tissue, in fibrosis the collagen cross-links and forms a pronounced alignment in a single direction. This collagen scar tissue alignment is usually of inferior functional quality to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cushing's Syndrome
Cushing's syndrome is a collection of signs and symptoms due to prolonged exposure to glucocorticoids such as cortisol. Signs and symptoms may include high blood pressure, abdominal obesity but with thin arms and legs, reddish stretch marks, a round red face due to facial plethora, a fat lump between the shoulders, weak muscles, weak bones, acne, and fragile skin that heals poorly. Women may have more hair and irregular menstruation or loss of menses, with the exact mechanisms of why still unknown. Occasionally there may be changes in mood, headaches, and a chronic feeling of tiredness. Cushing's syndrome is caused by either excessive cortisol-like medication, such as prednisone, or a tumor that either produces or results in the production of excessive cortisol by the adrenal glands. Cases due to a pituitary adenoma are known as Cushing's disease, which is the second most common cause of Cushing's syndrome after medication. A number of other tumors, often referred to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
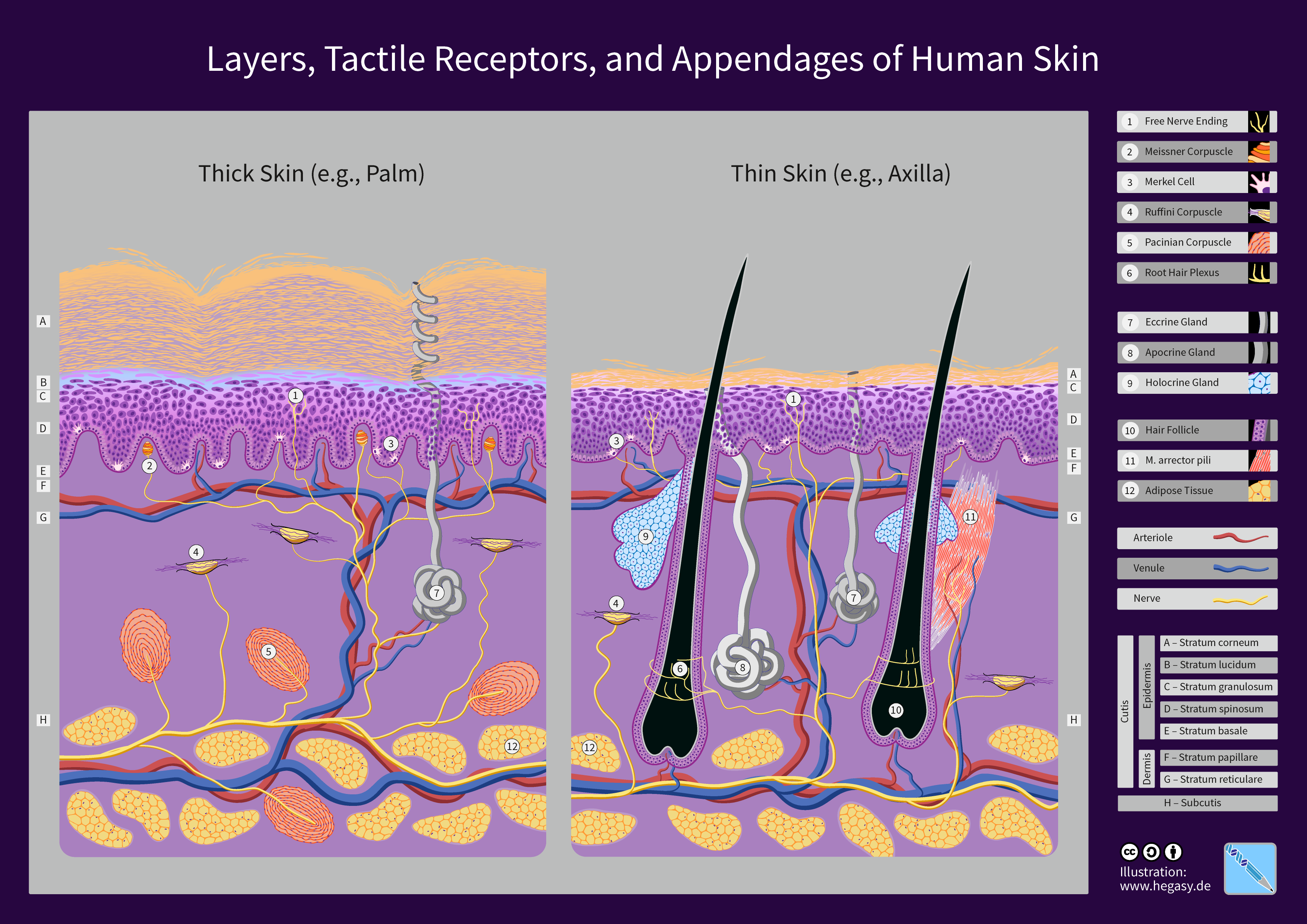
Human Skin
The human skin is the outer covering of the body and is the largest organ of the integumentary system. The skin has up to seven layers of ectodermal tissue (biology), tissue guarding Skeletal muscle, muscles, bones, ligaments and organ (anatomy), internal organs. Human skin is similar to most of the other mammals' skin, and it is very similar to pig skin. Though nearly all human skin is covered with hair follicles, it can appear Nudity#Evolution of hairlessness, hairless. There are two general types of skin: hairy and glabrous skin (hairless). The adjective List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes#C, ''cutaneous'' literally means "of the skin" (from Latin ''cutis'', skin). Skin plays an important immunity (medical), immunity role in protecting the body against pathogens and excessive transepidermal water loss, water loss. Its other functions are Thermal insulation, insulation, thermoregulation, temperature regulation, sensation, synthesis of vitamin D, and the protection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marfan Syndrome
Marfan syndrome (MFS) is a multi-systemic genetic disorder that affects the connective tissue. Those with the condition tend to be tall and thin, with dolichostenomelia, long arms, legs, Arachnodactyly, fingers, and toes. They also typically have hypermobility (joints), exceptionally flexible joints and scoliosis, abnormally curved spines. The most serious complications involve the heart and aorta, with an increased risk of mitral valve prolapse and aortic aneurysm. The lungs, eyes, bones, and the dura mater, covering of the spinal cord are also commonly affected. The severity of the symptoms is variable. MFS is caused by a mutation in ''FBN1'', one of the genes that make fibrillin, which results in abnormal connective tissue. It is an autosomal dominant disorder. In about 75% of cases, it is inherited from a parent with the condition, while in about 25% it is a new mutation. Diagnosis is often based on the Ghent criteria, family history and genetic testing (DNA analysis). Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ehlers–Danlos Syndrome
Ehlers–Danlos syndromes (EDS) is a group of 14 genetic connective-tissue disorders. Symptoms often include loose joints, joint pain, stretchy velvety skin, and abnormal scar formation. These may be noticed at birth or in early childhood. Complications may include aortic dissection, joint dislocations, scoliosis, chronic pain, or early osteoarthritis. The existing classification was last updated in 2017, when a number of rarer forms of EDS were added. EDS occurs due to mutations in one or more particular genes—there are 19 genes that can contribute to the condition. The specific gene affected determines the type of EDS, though the genetic causes of hypermobile Ehlers–Danlos syndrome are still unknown. Some cases result from a new variation occurring during early development, while others are inherited in an autosomal dominant or recessive manner. Typically, these variations result in defects in the structure or processing of the protein collagen or tenascin. Diagnos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squircle Belly (19004951)
A squircle is a shape intermediate between a square and a circle. There are at least two definitions of "squircle" in use, one based on the superellipse, the other arising from work in optics. The word "squircle" is a portmanteau of the words "square" and "circle". Squircles have been applied in design and optics. Superellipse-based squircle In a Cartesian coordinate system, the superellipse is defined by the equation \left, \frac\^n + \left, \frac\^n = 1, where and are the semi-major and semi-minor axes, and are the and coordinates of the centre of the ellipse, and is a positive number. The squircle is then defined as the superellipse where and . Its equation is:\left, x - a\^4 + \left, y - b\^4 = r^4where is the radius of the squircle. Compare this to the equation of a circle. When the squircle is centred at the origin, then , and it is called Lamé's special quartic. The area inside the squircle can be expressed in terms of the beta function or the gamma funct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asian People
"Asian people" (sometimes "Asiatic people")United States National Library of Medicine. Medical Subject Headings. 2004. November 17, 200Nlm.nih.gov: ''Asian Continental Ancestry Group'' is also used for categorical purposes. is an umbrella term for people who belong to any ethnic, racial, or national group with origins in Asia. It is most often used in contexts concerning the Asian diaspora, which consists of Asian people and their descendants living outside of the continent. The exact definition of the term may vary by country; some classifications of "Asian" may only refer to certain Asian-origin groups, as opposed to the population of the entire continent. Meanings by region Anglophone Africa and the Caribbean In parts of anglophone Africa, especially East Africa and in parts of the Caribbean, the term "Asian" is more commonly associated with people of South Asian origin, particularly Indians, Pakistanis, Bangladeshis and Sri Lankans. In South Africa the term "Asian" i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adrenal Gland Disorder
Adrenal gland disorders (or diseases) are conditions that interfere with the normal functioning of the adrenal glands. Your body produces too much or too little of one or more hormones when you have an adrenal gland dysfunction. The type of issue you have and the degree to which it affects your body's hormone levels determine the symptoms. The adrenal gland produces hormones that affects growth, development and stress, and also helps to regulate kidney function. There are two parts of the adrenal glands, the adrenal cortex and the adrenal medulla. The adrenal cortex produces mineralocorticoids, which regulate salt and water balance within the body, glucocorticoids (including cortisol) which have a wide number of roles within the body, and androgens, hormones with testosterone-like function.Adre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
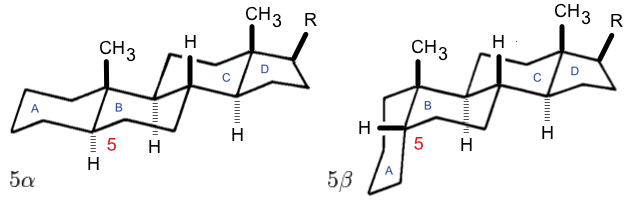
Steroid
A steroid is an organic compound with four fused compound, fused rings (designated A, B, C, and D) arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and as signal transduction, signaling molecules. Examples include the lipid cholesterol, sex hormones estradiol and testosterone, anabolic steroids, and the anti-inflammatory corticosteroid drug dexamethasone. Hundreds of steroids are found in Fungus, fungi, plants, and animals. All steroids are manufactured in cells from a sterols, sterol: Cholesterol, cholesterol (animals), lanosterol (opisthokonts), or cycloartenol (plants). All three of these molecules are produced via Cyclic compound, cyclization of the triterpene squalene. Structure The steroid nucleus (parent structure, core structure) is called gonane (cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene). It is typically composed of seventeen carbon atoms, bonded in fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are involved in a wide range of physiological processes, including stress response, immune response, and regulation of inflammation, carbohydrate metabolism, protein catabolism, blood electrolyte levels, and behavior. Some common naturally occurring steroid hormones are cortisol (), corticosterone (), cortisone () and aldosterone () (cortisone and aldosterone are isomers). The main corticosteroids produced by the adrenal cortex are cortisol and aldosterone. The etymology of the '' cortico-'' part of the name refers to the adrenal cortex, which makes these steroid hormones. Thus a corticosteroid is a "cortex steroid". Classes * Glucocorticoids such as cortisol affect carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism, and have anti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Growth Spurt
Human height or stature is the distance from the bottom of the feet to the top of the head in a human body, standing erect. It is measured using a stadiometer, in centimetres when using the metric system or SI system, or feet and inches when using United States customary units or the imperial system. In the early phase of anthropometric research history, questions about height measuring techniques for measuring nutritional status often concerned genetic differences. Height is also important because it is closely correlated with other health components, such as life expectancy. Studies show that there is a correlation between small stature and a longer life expectancy. Individuals of small stature are also more likely to have lower blood pressure and are less likely to acquire cancer. The University of Hawaii has found that the "longevity gene" FOXO3 that reduces the effects of aging is more commonly found in individuals of small body size. Short stature decreases the risk of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |