|
Straußenwirtschaft
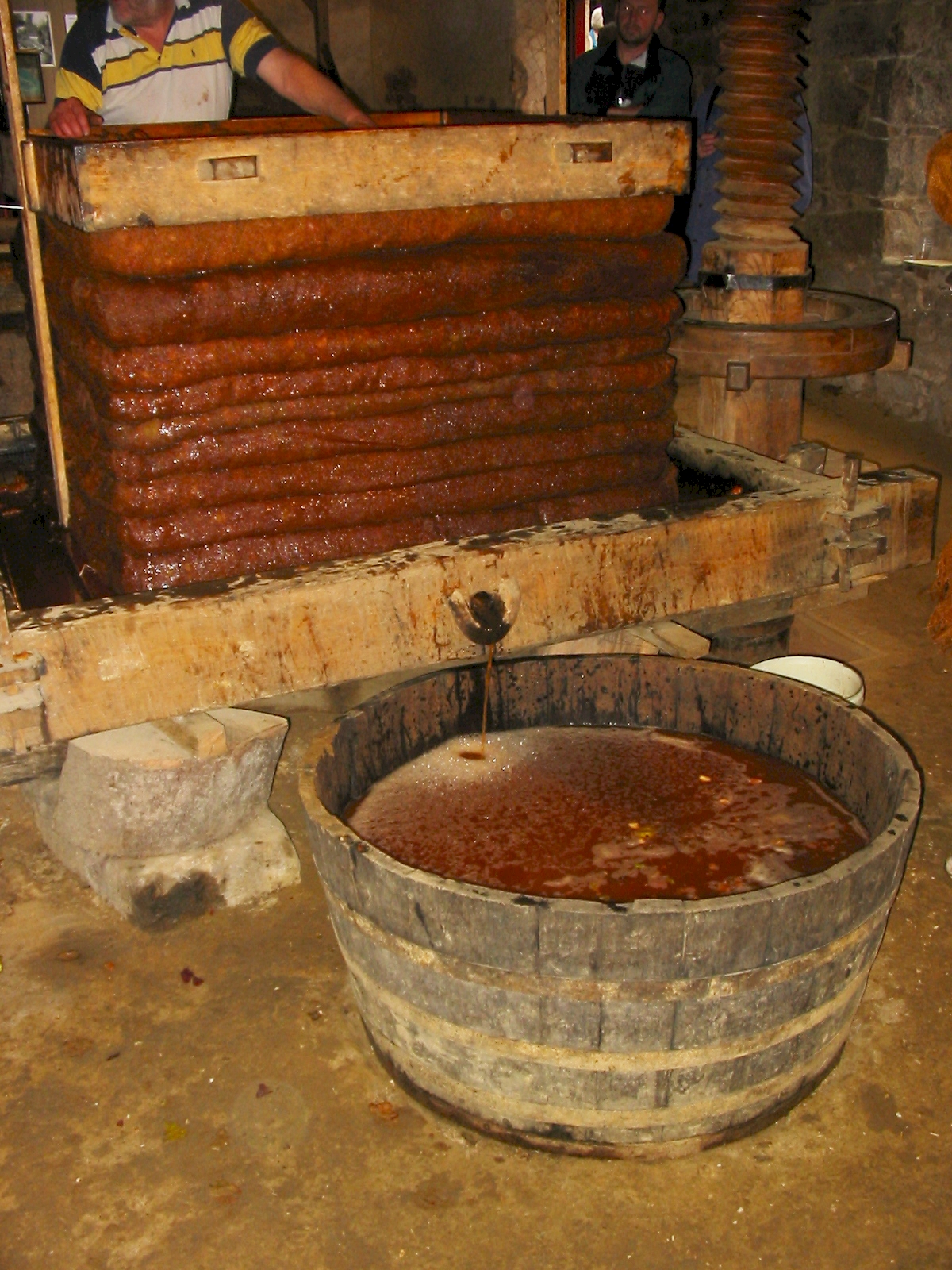
A ''Strausse'' or ''Strausswirtschaft'' (also ''Strauße'' or ''Straußwirtschaft'') is a type of wine tavern in winegrowing areas of German-speaking countries that is only open during certain times of the year. Typically it is a pub run by winegrowers and winemakers themselves, in which they sell their own wine directly to the public. The food served needs to be simple, regional cold dishes. Other expressions like ''Besenwirtschaft'' and ''Besenschänke'' ("broom pub"), ''Rädlewirtschaft'' ("cyclists' pub") as well as ''Hecken-'' or ''Häckerwirtschaft'' are also common. Characterization A ''Strausswirtschaft'' is essentially understood to be a winemaker serving his own wine on his own premises. These seasonal inns are not subject to normal business laws and are thus not obliged to have a licence or to pay extra taxes. They must, however, fulfil certain conditions instead. These conditions vary from state to state but they are in general agreement on certain essential points (s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Private Wine Licence Sign
Private or privates may refer to: Music * "In Private", by Dusty Springfield from the 1990 album ''Reputation'' * Private (band), a Denmark-based band * "Private" (Ryōko Hirosue song), from the 1999 album ''Private'', written and also recorded by Ringo Sheena * "Private" (Vera Blue song), from the 2017 album ''Perennial'' Literature * ''Private'' (novel), 2010 novel by James Patterson * ''Private'' (novel series), young-adult book series launched in 2006 Film and television * ''Private'' (film), 2004 Italian film * ''Private'' (web series), 2009 web series based on the novel series * ''Privates'' (TV series), 2013 BBC One TV series * Private, a penguin character in ''Madagascar'' Other uses * Private (rank), a military rank * ''Privates'' (video game), 2010 video game * Private (rocket), American multistage rocket * Private Media Group, Swedish adult entertainment production and distribution company * ''Private (magazine)'', flagship magazine of the Private Media Group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palatinate (region)
The Palatinate (; ; Palatine German language, Palatine German: ''Palz''), or the Rhenish Palatinate (''Rheinpfalz''), is a historical region of Germany. The Palatinate occupies most of the Southern Germany, southern quarter of the German States of Germany, federal state of Rhineland-Palatinate (''Rheinland-Pfalz''), covering an area of with about 1.4 million inhabitants. Its residents are known as Palatines (''Pfälzer''). Geography The Palatinate borders Saarland in the west, historically also comprising the state's Saarpfalz-Kreis, Saarpfalz District. In the northwest, the Hunsrück mountain range forms the border with the Rhineland region. The eastern border with Hesse and the Baden-Württemberg, Baden region runs along the Upper Rhine river, while the left bank, with Mainz and Worms, Germany, Worms as well as the Selz basin around Alzey, belong to the Rhenish Hesse region. In the south, the German-France, French border separates the Palatinate from Alsace. One-thir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Wine
German wine is primarily produced in the west of Germany, along the river Rhine and its tributaries, with the oldest plantations going back to the Celts and Ancient Rome, Roman eras. Approximately 60 percent of German wine is produced in the state of Rhineland-Palatinate, where 6 of the 13 regions (''Anbaugebiete'') for quality wine are situated. Germany has about 104,000 hectares (252,000 acres or 1,030 square kilometers) of vineyard, which is around one tenth of the vineyard surface in Spain, France or Italy. The total wine production is usually around 10 million hectoliters annually, corresponding to 1.3 billion bottles, which places Germany as the Wine#Producing countries, ninth-largest wine-producing country and seventh by export market share in the world. White wine accounts for almost two thirds of the total production. As a wine country, Germany has a mixed reputation internationally, with some consumers on the export markets associating Germany with the world's most ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cider
Cider ( ) is an alcoholic beverage made from the Fermented drink, fermented Apple juice, juice of apples. Cider is widely available in the United Kingdom (particularly in the West Country) and Ireland. The United Kingdom has the world's highest per capita consumption, as well as the largest cider-producing companies. Ciders from the South West of England are generally higher in alcoholic content. Cider is also popular in many Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth countries, such as India, South Africa, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, and New England. As well as the UK and its former colonies, cider is popular in Portugal (mainly in Entre-Douro-e-Minho Province, Minho and Madeira), France (particularly Normandy and Brittany), northern Italy (specifically Friuli), and northern Spain (specifically Asturias and Basque Country (greater region), Basque Country). Germany also has its own types of cider with Rhineland-Palatinate and Hesse producing a particularly tart version known as A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beer
Beer is an alcoholic beverage produced by the brewing and fermentation of starches from cereal grain—most commonly malted barley, although wheat, maize (corn), rice, and oats are also used. The grain is mashed to convert starch in the grain to sugars, which dissolve in water to form wort. Fermentation of the wort by yeast produces ethanol and carbonation in the beer. Beer is one of the oldest and most widely consumed alcoholic drinks in the world, and one of the most popular of all drinks. Most modern beer is brewed with hops, which add bitterness and other flavours and act as a natural preservative and stabilising agent. Other flavouring agents, such as gruit, herbs, or fruits, may be included or used instead of hops. In commercial brewing, natural carbonation is often replaced with forced carbonation. Beer is distributed in bottles and cans, and is commonly available on draught in pubs and bars. The brewing industry is a global business, consisting of several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhineland-Palatinate
Rhineland-Palatinate ( , ; ; ; ) is a western state of Germany. It covers and has about 4.05 million residents. It is the ninth largest and sixth most populous of the sixteen states. Mainz is the capital and largest city. Other cities are Ludwigshafen am Rhein, Koblenz, Trier, Kaiserslautern, Worms, and Neuwied. It is bordered by North Rhine-Westphalia, Saarland, Baden-Württemberg and Hesse and by France, Luxembourg and Belgium. Rhineland-Palatinate was established in 1946 after World War II, from parts of the former states of Prussia (part of its Rhineland and Nassau provinces), Hesse ( Rhenish Hesse) and Bavaria (its former outlying Palatinate kreis or district), by the French military administration in Allied-occupied Germany. Rhineland-Palatinate became part of the Federal Republic of Germany in 1949 and shared the country's only border with the Saar Protectorate until the latter was returned to German control in 1957. Rhineland-Palatinate's natural and c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camembert (cheese)
Camembert ( , , ) is a moist, soft, creamy, surface-ripened cow's milk cheese. It was first made in the late 18th century in Camembert, Normandy, in northwest France. It is sometimes compared in look, taste and texture to brie cheese, albeit with a slightly lower butterfat content than brie's typical 20% – 25% by weight. Production The first camembert was made from unpasteurized milk, and the AOC variety "Camembert de Normandie" (approximately 10% of the production) is required by law to be made only with unpasteurized milk. Many modern cheesemakers outside of Normandy, France, however, use pasteurized milk for reasons of safety, compliance with regulations, or convenience. The cheese is made by inoculating warmed cow milk with mesophilic bacteria, then adding rennet and allowing the mixture to coagulate. The curd is then cut into roughly 1 cm (1/2 inch) cubes, salted, and transferred to low cylindrical camembert molds. The molds are turned every six to twelve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
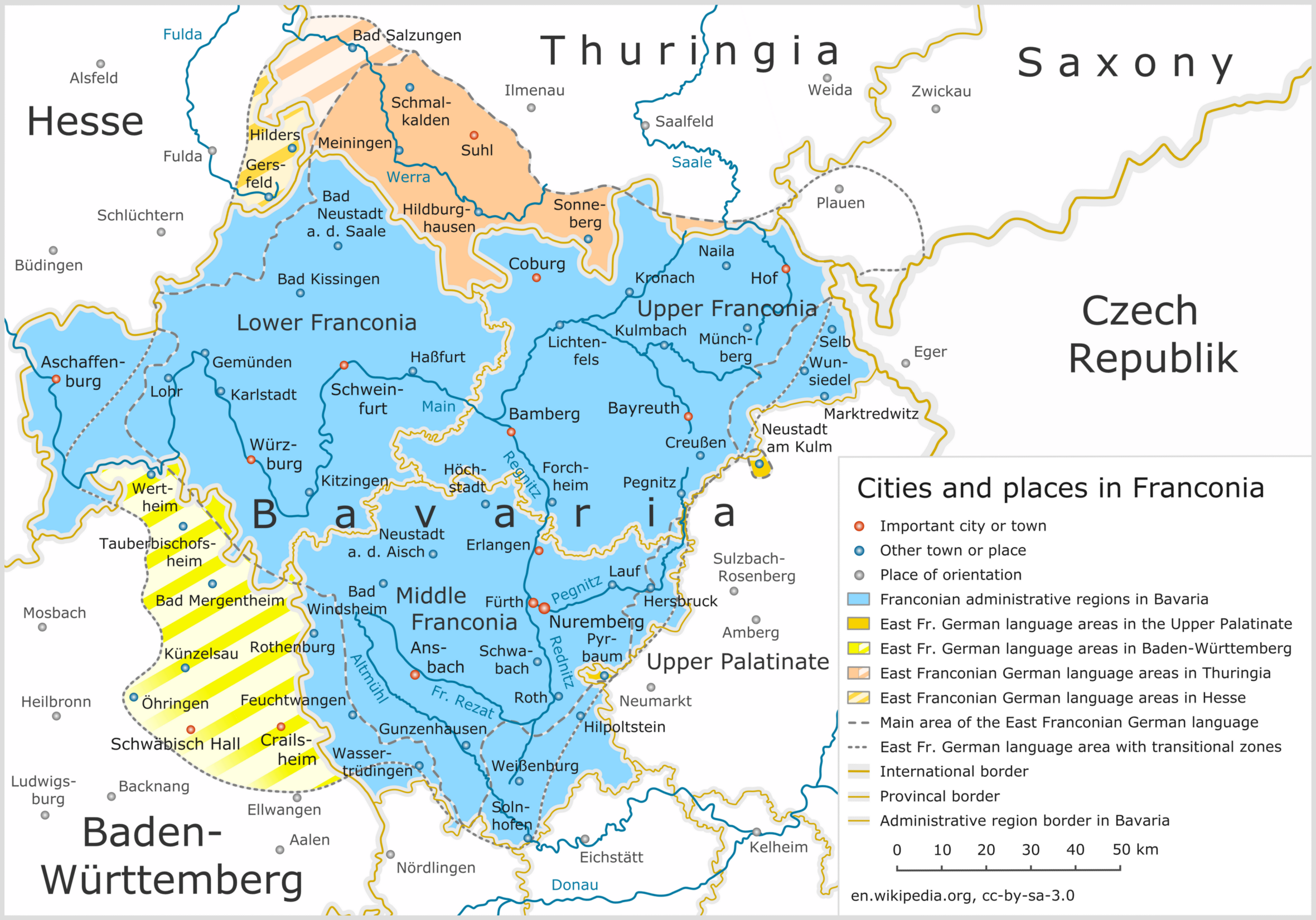
Franconia
Franconia ( ; ; ) is a geographical region of Germany, characterised by its culture and East Franconian dialect (). Franconia is made up of the three (governmental districts) of Lower Franconia, Lower, Middle Franconia, Middle and Upper Franconia in Bavaria, the adjacent, East Franconian, Franconian-speaking South Thuringia, south of the Thuringian Forest—which constitutes the language boundary between Franconian and Thuringian—and the eastern parts of Heilbronn-Franconia in Baden-Württemberg. Those parts of the Vogtland lying in Saxony (largest city: Plauen) are sometimes regarded as Franconian as well, because the Vogtlandian dialects are mostly East Franconian. The inhabitants of Saxon Vogtland, however, mostly do not consider themselves Franconian. On the other hand, the inhabitants of the Hessian dialect, Hessian-speaking parts of Lower Franconia west of the Spessart (largest city: Aschaffenburg) do consider themselves Franconian, although not speaking the dialect. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kraut
''Kraut'' is a German language, German word recorded in English from 1918 onwards as an List of terms used for Germans, ethnic slur for a German, particularly a German soldier during World War I and World War II. Its earlier meaning in English was as a synonym for sauerkraut, a traditional Central and Eastern European food. Etymological foundations In German, the term means "herb", or designates the leaves and stem of a plant as opposed to the root. The term is more often used in compound nouns for herbs, and also for cabbage and cabbage products: * ''Weißkraut'' = white cabbage (also called ''Weißkohl'') * ''Blaukraut'' or ''Rotkraut'' = red cabbage (also called ''Rotkohl'') * ''Sauerkraut'' = fermented white cabbage or 'sour cabbage' * ''Unkraut'' = weed * ''Bohnenkraut'' = Savory (herb), savory * ''Rübenkraut'' = thick sugar beet syrup The plural ''Kräuter'' is commonly used (herbs, weeds) when talking about spices, but is often replaced by ''Gewürz'' which can refer t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bratwurst
''Bratwurst'' () is a type of German sausage made from pork or, less commonly, beef or veal. The name is derived from the Old High German , from , finely chopped meat, and , sausage, although in modern German it is often associated with the verb , to pan fry or roast. Beef and veal are usually incorporated amongst a blend often including pork. Beef or veal is usual in halal and kosher ''Bratwurst'' sausages, which never include pork for religious reasons. History The first documented evidence of the ''Bratwurst'' in Germany dates to 1313 in the Franconian city of Nuremberg, which is still internationally renowned for the production of grilling sausages. Types and traditions Germany In Germany, a bratwurst is considered genuine if its main ingredient is pork. Recipes for the sausage vary by region and even locality; some sources list over 40 different varieties of German cuisine, German ''Bratwurst'', many of the best known originating in Franconia (today for the most part si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarte Flambée
Flammekueche (Alsatian dialect, Alsatian), Flammkuchen (Standard German), or tarte flambée (French language, French), is a speciality of the region of Alsace, German-speaking Mosel (wine region), Moselle, Baden and the Palatinate (region), Palatinate. It is composed of bread dough rolled out very thinly in the shape of a rectangle or oval, which is covered with ''fromage frais, fromage blanc'' or ''crème fraîche'', thinly sliced onions and lardons. The name of the dish varies in local dialects; it is called ''Flàmmeküeche'', or ''Flàmmaküacha'' in Alsatian dialect, Alsatian, or ''Flammkuche'' in Lorraine Franconian – compare (Standard) German language, German ''Flammkuchen''. All these names translate as "(pie) baked in the flames". Interestingly, the French name "tarte flambée" is the most common name for the dish in Alsace, while it is known as its Alsatian name "flammekueche" in the rest of France. Contrary to what the direct translation would suggest, ''tarte flamb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zwiebelkuchen
(, ) is a savory German onion cake made of steamed onions, diced bacon, cream, and caraway seeds on either a yeast or leavened dough. It is not to be confused with Flammkuchen, a similar dish that is dryer. History Most of Zwiebelkuchen's history is unknown, but has been mentioned as early as the 19th century and originates from Baden-Württemberg. Zwiebelkuchen is a favored autumn dish commonly enjoyed at wine festivals. It is particularly popular in Germany's wine-producing regions, including Thuringia, Palatinate, Hessia, Franconia, Swabia, Alsace, and the Rhine and Moselle areas. People enjoy drinking "neuer Wein" with it. "Neuer Wein" is slightly fermented grape juice, before the squeezed grapes turn into proper wine to be bottled. See also * , similar Alsatian and south-western German dish * List of onion dishes This list consists of notable dishes and foods in which onion is used as a primary ingredient. Onions are widely used in cooking. They are very vers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |