|
Strathglass Fault
Strathglass is a strath or wide and shallow valley in the Northwest Highlands of Scotland down which runs the meandering River Glass from the point at which it starts at the confluence of the River Affric and Abhainn Deabhag to the point where, on joining with the River Farrar at Struy, the combined waters become the River Beauly. The A831 road runs southwest from the vicinity of Erchless Castle up the length of Strathglass and serves the village of Cannich which is the largest settlement within the valley. The road then runs east from here via Glen Urquhart to Drumnadrochit beside Loch Ness. A minor road continues southwest up the valley from Cannich towards Glen Affric. Strathglass was also followed by a line of electricity pylons but that has been replaced by a line of new pylons across Eskdale Moor to the east of the strath. Both flanks of the valley are heavily wooded; on the higher ground to the northwest, beyond the forests are the moors of Struy Forest and Balmore Fores ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Glass - Geograph
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of water. Small rivers can be referred to using names such as creek, brook, rivulet, and rill. There are no official definitions for the generic term river as applied to geographic features, although in some countries or communities a stream is defined by its size. Many names for small rivers are specific to geographic location; examples are "run" in some parts of the United States, "burn" in Scotland and northeast England, and "beck" in northern England. Sometimes a river is defined as being larger than a creek, but not always: the language is vague. Rivers are part of the water cycle. Water generally collects in a river from precipitation through a drainage basin from surface runoff and other sources such as groundwater recharge, springs, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Policy Of Scotland
Energy policy in Scotland is a matter that has been specifically reserved to the UK parliament under the terms of the Scotland Act 1998 that created the devolved Scottish Parliament. However, since planning is a matter that has been devolved, the Scottish government has the ability to shape the direction of energy generation in Scotland by approving or refusing new projects. In 2004, the Enterprise Committee of the Scottish Parliament called for the development of a 'fully fledged' Scottish energy policy. The SNP Government that took power in May 2007 specifically included the word 'energy' in a portfolio title when the junior ministerial position of Minister for Enterprise, Energy and Tourism was created to replace the position of ' Minister for Enterprise and Lifelong Learning'. Overview Fossil fuels The closure of the Longannet power station in March 2016 ended coal-fired power production in Scotland. Renewable energy The production of renewable energy in Scotland is an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Catholic Priest
The priesthood is the office of the ministers of religion, who have been commissioned ("ordained") with the Holy orders of the Catholic Church. Technically, bishops are a priestly order as well; however, in layman's terms ''priest'' refers only to presbyters and pastors (parish priests). The church's doctrine also sometimes refers to all baptised ( lay) members as the "common priesthood", which can be confused with the ministerial priesthood of the consecrated clergy. The church has different rules for priests in the Latin Church–the largest Catholic particular church–and in the 23 Eastern Catholic Churches. Notably, priests in the Latin Church must take a vow of celibacy, whereas most Eastern Catholic Churches permit married men to be ordained. Deacons are male and usually belong to the diocesan clergy, but, unlike almost all Latin Church (Western Catholic) priests and all bishops from Eastern or Western Catholicism, they may marry as laymen before their ordination as c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clan Cameron
Clan Cameron is a West Highland Scottish clan, with one main branch Lochiel, and numerous cadet branches. The Clan Cameron lands are in Lochaber and within their lands lies Ben Nevis which is the highest mountain in the British Isles. The Chief of the clan is customarily referred to as simply "Lochiel". History Origins The origins of Clan Cameron are uncertain and there are several theories. Traditionally, it is believed that the Camerons were originally descended from a Danish prince who assisted the restoration of Fergus II and that their progenitor was called ''Cameron'' from his crooked nose ( gd, cam-shròn, cf. Camshron) – such nicknames were and are common in Gaelic culture, and that his dependants then adopted the name.Clan Cameron History electricscotland.com. Retrieved 4 May 2013 It i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noblesse
The concept of the Scottish Noblesse, a class of nobles of either peerage or non-peerage rank, was prominently advocated for by Sir Thomas Innes of Learney during his tenure as an officer of arms. Innes of Learney believed that Scottish armigers, those individuals granted arms by the Court of the Lord Lyon, implicitly become 'Nobles in the Noblesse of Scotland': a form of hereditary nobility. The soundness of the basis for this belief is uncertain, and included drawing on historical English practice, and the belief that, because other officers of the Crown had been delegated the power to ennoble historically, the Lord Lyon should be able to as well. Despite relying heavily on historical documentation in England, he simultaneously also opposed the application of English heraldic practice and law as it related to heraldry in Scotland. In 2018, the Lord Lyon quietly dropped the so-called nobility clause from newly issued Letters Patent. See also * Peerage of Scotland * Barons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Cameron (priest)
Alexander Cameron S.J. (1701 – 19 October 1746) was a Scottish Noblesse, nobleman, servant to Prince Charles Edward Stuart, and Roman Catholic priest in the Society of Jesus. After travelling in Catholic Europe and the Caribbean, Cameron converted from the Non-juring schism, Non-Juring Anglican Communion to Roman Catholicism and was ordained as a priest. Fr. Cameron ran a highly successful vicariate for the still illegal and underground Catholic Church in Scotland in Lochaber and Strathglass before joining the as a military chaplain to the regiment of the Jacobite Army (1745), Jacobite Army commanded by his brother, Donald Cameron of Lochiel, during the Jacobite rising of 1745, Uprising of 1745. After the Battle of Culloden, Fr. Cameron was captured by the British Army and died of the hardships of his imprisonment while being held without trial aboard a prison hulk anchored in the Thames River. He is currently being promoted by the Knights of St Columba for Canonization by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Terrace
Fluvial terraces are elongated terraces that flank the sides of floodplains and fluvial valleys all over the world. They consist of a relatively level strip of land, called a "tread", separated from either an adjacent floodplain, other fluvial terraces, or uplands by distinctly steeper strips of land called "risers". These terraces lie parallel to and above the river channel and its floodplain. Because of the manner in which they form, fluvial terraces are underlain by fluvial sediments of highly variable thickness.Fairbridge, R. W., 1968, ''Encyclopedia of Geomorphology.'' Reinhold Book Company, New York.Blum, M., and T.E. Tonqvist, 2000, ''Fluvial responses to climate and sea-level change, a review and look forward.'' Sedimentology. v. 47 suppl. 1, pp. 2-48. River terraces are the remnants of earlier floodplains that existed at a time when either a stream or river was flowing at a higher elevation before its channel downcut to create a new floodplain at a lower elevation. Change ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alluvium
Alluvium (from Latin ''alluvius'', from ''alluere'' 'to wash against') is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. Alluvium is also sometimes called alluvial deposit. Alluvium is typically geologically young and is not consolidated into solid rock. Sediments deposited underwater, in seas, estuaries, lakes, or ponds, are not described as alluvium. Floodplain alluvium can be highly fertile, and supported some of the earliest human civilizations. Definitions The present consensus is that "alluvium" refers to loose sediments of all types deposited by running water in floodplains or in alluvial fans or related landforms. However, the meaning of the term has varied considerably since it was first defined in the French dictionary of Antoine Furetière, posthumously published in 1690. Drawing upon concepts from Roman law, Furetière defined ''alluvion'' (the F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caledonian Orogeny
The Caledonian orogeny was a mountain-building era recorded in the northern parts of the British Isles, the Scandinavian Mountains, Svalbard, eastern Greenland and parts of north-central Europe. The Caledonian orogeny encompasses events that occurred from the Ordovician to Early Devonian, roughly 490–390 million years ago ( Ma). It was caused by the closure of the Iapetus Ocean when the continents and terranes of Laurentia, Baltica and Avalonia collided. The orogeny is named for Caledonia, the Latin name for Scotland. The term was first used in 1885 by Austrian geologist Eduard Suess for an episode of mountain building in northern Europe that predated the Devonian period. Geologists like Émile Haug and Hans Stille saw the Caledonian event as one of several episodic phases of mountain building that had occurred during Earth's history. Current understanding has it that the Caledonian orogeny encompasses a number of tectonic phases that can laterally be diachronous. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fault (geology)
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic forces, with the largest forming the boundaries between the plates, such as the megathrust faults of subduction zones or transform faults. Energy release associated with rapid movement on active faults is the cause of most earthquakes. Faults may also displace slowly, by aseismic creep. A ''fault plane'' is the plane that represents the fracture surface of a fault. A '' fault trace'' or ''fault line'' is a place where the fault can be seen or mapped on the surface. A fault trace is also the line commonly plotted on geologic maps to represent a fault. A ''fault zone'' is a cluster of parallel faults. However, the term is also used for the zone of crushed rock along a single fault. Prolonged motion along closely spaced faults can bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
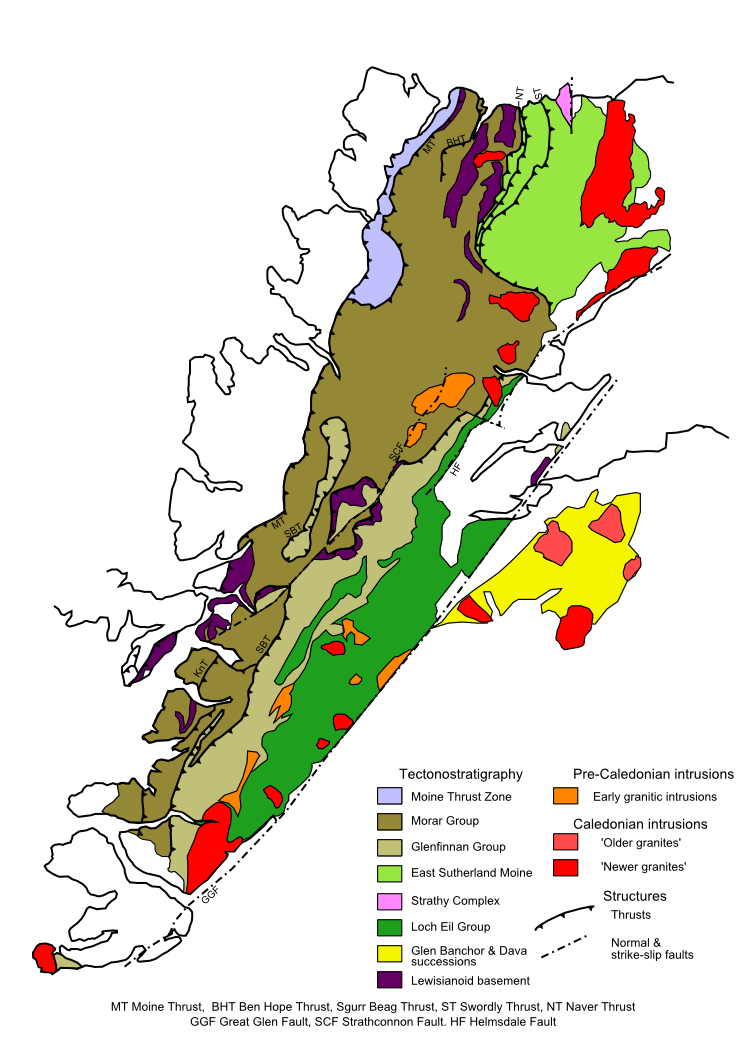
Moine Supergroup
The Moine Supergroup is a sequence of Neoproterozoic metamorphic rocks that form the dominant outcrop of the Scottish Highlands between the Moine Thrust Belt to the northwest and the Great Glen Fault to the southeast. The sequence is metasedimentary in nature and was metamorphosed and deformed in a series of tectonic events during the Late Proterozoic and Early Paleozoic. It takes its name from '' A' Mhòine'', a peat bog in northern Sutherland. Distribution The main outcrop of the Moine series lies northwest of the Great Glen Fault, structurally above the Moine Thrust to the west forming what is known as the Northern Highlands Terrane. A smaller area of similar rocks that are correlated with these, outcrop within the 'Grampian Terrane' to the southeast of the Great Glen. Moinian rocks are also recognised on Mull, Orkney and Shetland. Stratigraphy The Moine Supergroup has been subdivided into different groups or divisions. The relationship between individual groups in terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psammite
Psammite (Greek: ''psammitēs'' "(made) from sand", from ''psammos'' "sand") is a general term for sandstone. It is equivalent to the Latin-derived term areniteU.S. Bureau of Mines Staff (1996) ''Dictionary of Mining, Mineral, & Related Terms.'' Report SP-96-1, U.S. Department of Interior, U.S. Bureau of Mines, Washington, D.C.Neuendorf, K.K.E., J.P. Mehl, Jr., and J.A. Jackson, J.A., eds. (2005) ''Glossary of Geology'' (5th ed.). Alexandria, Virginia, American Geological Institute, Washington, DC 779 pp. and is commonly used in various publications to describe a metamorphosed sedimentary rock with a dominantly sandstone protolith A protolith () is the original, unmetamorphosed rock from which a given metamorphic rock is formed. For example, the protolith of a slate is a shale or mudstone. Metamorphic rocks can be derived from any other kind of non-metamorphic rock and t ....Tyrell, G. W. (1921) ''Some points in petrographic nomenclature.'' Geological Magazine. v. 58, no. 11, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)